21 Carbon Dioxide Transport Drag Each Label To The Appropriate Location On The Flowchart.
If the process of meiosis shown here proceeds normally, how many chromosomes will cells a, b, c, and d have? a 2 each b 6 each c 8 each d 4 each. ... Name the molecule that transports most of the carbon dioxide in the blood. Asked By adminstaff @ 17/12/2019 06:17 AM. Biology. 1 Answers. Carbon dioxide transport in the blood. Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood from the tissue to the lungs in three ways: 1 (i) dissolved in solution; (ii) buffered with water as carbonic acid; (iii) bound to proteins, particularly haemoglobin. Approximately 75% of carbon dioxide is transport in the red blood cell and 25% in the plasma.
Ventilation: Inspiration and expiration. 2. External respiration: Gas exchange between air (in lungs) and blood. Blood then transport Oxygen to the body tissue cells. 3. Internal respiration: Gas exchange between blood and tissue fluid. Blood then transports carbon dioxide to the lungs. 2.
 1 C Carbon dioxide Transport and Storage Carbon dioxide (CO2) capture and storage (CCS) involves the capture of CO2, its transport to a storage location and its long-term isolation from the atmosphere. Emissions associated with CO2 transport, injection and storage are covered under category 1C. Emissions (and reductions) associated with • To explore how carbon dioxide is transported in the blood. • To understand the effect of variables, such as PO2 and PCO2, on oxygen and carbon dioxide transport. Page 3. Oxygen Transport • Transport of oxygen during external respiration: • With its low solubility, only approximately 1.5% of the oxygen is transported dissolved in plasma. Transport of Carbon Dioxide in Venous Blood: Carbon dioxide diffuses from peripheral cells into venous blood and is transported to the lungs in three distinct chemical forms. Roughly 10% is transported as a simple dissolved gas. The remainder enters local erythrocytes and encounters one of two fates. A proportion binds directly to hemoglobin ...
1 C Carbon dioxide Transport and Storage Carbon dioxide (CO2) capture and storage (CCS) involves the capture of CO2, its transport to a storage location and its long-term isolation from the atmosphere. Emissions associated with CO2 transport, injection and storage are covered under category 1C. Emissions (and reductions) associated with • To explore how carbon dioxide is transported in the blood. • To understand the effect of variables, such as PO2 and PCO2, on oxygen and carbon dioxide transport. Page 3. Oxygen Transport • Transport of oxygen during external respiration: • With its low solubility, only approximately 1.5% of the oxygen is transported dissolved in plasma. Transport of Carbon Dioxide in Venous Blood: Carbon dioxide diffuses from peripheral cells into venous blood and is transported to the lungs in three distinct chemical forms. Roughly 10% is transported as a simple dissolved gas. The remainder enters local erythrocytes and encounters one of two fates. A proportion binds directly to hemoglobin ...
Carbon dioxide transport drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart.. Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. Drag each label to the appropriate location on this diagram of the human respiratory system. Most of the organs of the respiratory system help to distribute air but only the tiny grape like alveoli and the alveolar ducts are responsible for actual gas exchange. Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. 70 of this volume reaches the respiratory section of the lungs and 30 remains in the conducting section of the lungs the anatomic dead space. In this activity you will follow carbon dioxide on its path out of the body. Human respiratory system - Human respiratory system - Transport of carbon dioxide: Transport of carbon dioxide in the blood is considerably more complex. A small portion of carbon dioxide, about 5 percent, remains unchanged and is transported dissolved in blood. The remainder is found in reversible chemical combinations in red blood cells or plasma. Transport of Carbon Dioxide in Venous Blood: Carbon dioxide diffuses from peripheral cells into venous blood and is transported to the lungs in three distinct chemical forms. Roughly 10% is transported as a simple dissolved gas. The remainder enters local erythrocytes and encounters one of two fates. A proportion binds directly to hemoglobin ...
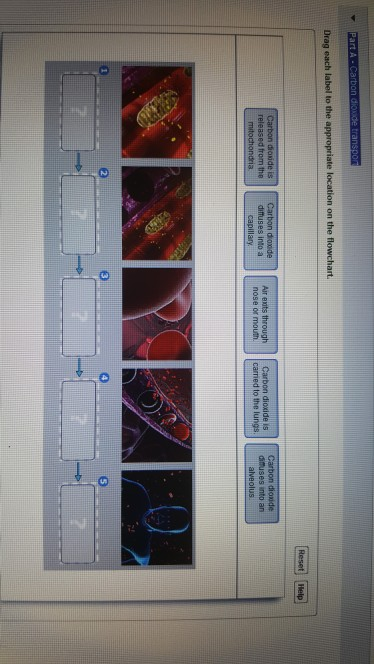
Part A - Carbon dioxide transport Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. ANSWER: Correct BioFlix Activity: Gas Exchange -- Oxygen Transport In this activity, you will follow oxygen on its path from the lungs to the body tissues.To review how oxygen is transported in the body, watch this BioFlix animation: Gas Exchange: Transporting Oxygen. Carbon 2. What elements are found in all living things? Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Sulfur, Phosphorous 3. What types of bonds are involved in the structure of all four macromolecules? Covalent bonds 4. Define dehydration synthesis. Does it build or break down molecules? Are bonds made or broken? Is water added or removed? Key events in gas exchange drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. 1 air enters through the nose or mouth. Help reset oxygen diffuses from the blood to the bodys tissues. Secrete gnrh in porta fsh and lh. Part a carbon dioxide transport drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. Out of the body. Part a path of air drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. Larynx the primary functions of the are to warm filter and humidify air. The respiratory system objectives after this lesson students will be able to d411. Part a carbon dioxide transport drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart.
Drag the labels from the left which represent numbers of carbon atoms onto the diagram to identify the number of carbon atoms in each intermediate in acetyl coa formation and the citric acid cycle. Next drag pink labels onto pink targets only to identify the process by which each stage occurs. Drag each label to the appropriate location on this diagram of the human respiratory system. To review how carbon dioxide is transported in the body watch this bioflix animation. 70 of this volume reaches the respiratory section of the lungs and 30 remains in the conducting section of the lungs the anatomic dead space. Where: CO 2 = carbon dioxide H 2 O = water light is required C 6 H 12 O 6 = glucose O 2 = oxygen Explanation In words, the equation may be stated as: Six carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules react to produce one glucose molecule and six oxygen molecules . Part A - Carbon dioxide transport Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. ANSWER: Help Reset INHALATION EXHALATION Air enters body. External intercostal muscles contract.
 Week 12 respiration flashcards quizlet
Week 12 respiration flashcards quizlet
Oxygen diffuses from alveoli in the lungs into capillaries. Part a carbon dioxide transport drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. Nasal cavity trachea diaphragm. Oxygen diffuses from the blood to the bodys tissues and carbon dioxide diffuses from the tissues to the blood.
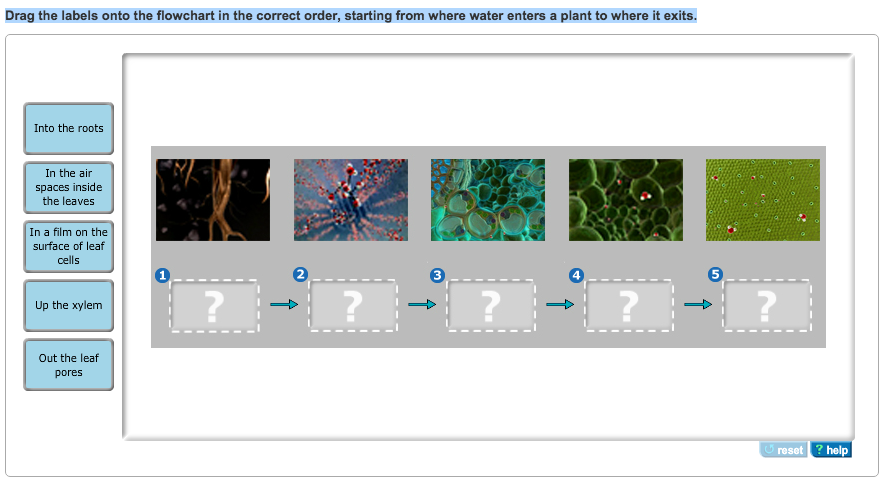 Solved drag the labels onto the flowchart in the correct
Solved drag the labels onto the flowchart in the correct
Carbon dioxide exits the cells, enters the bloodstream, travels back to the lungs, and is expired out of the body during exhalation. Breathing is both a voluntary and an involuntary event. How often a breath is taken and how much air is inhaled or exhaled is regulated by the respiratory center in the brain in response to signals it receives ...
Several properties of carbon dioxide in the blood affect its transport. First, carbon dioxide is more soluble in blood than oxygen. About 5 to 7 percent of all carbon dioxide is dissolved in the plasma. Second, carbon dioxide can bind to plasma proteins or can enter red blood cells and bind to hemoglobin.
Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. ResetHelp Carbon dioxide diffuses into a capillary.Carbon dioxide diffuses into a capillary. Air exits through nose or mouth.Air exits through nose or mouth. Carbon dioxide is carried to the lungs.
 Dujs 20f print journal by dartmouthjournalofscience issuu
Dujs 20f print journal by dartmouthjournalofscience issuu
Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, "biological machines" also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell.
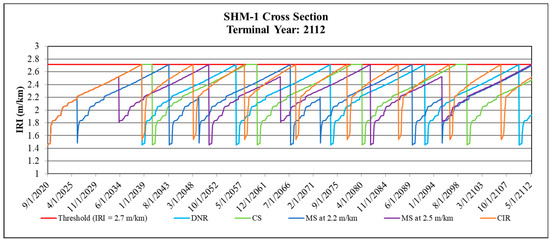 Sustainability free full text realistic traffic condition
Sustainability free full text realistic traffic condition
• To explore how carbon dioxide is transported in the blood. • To understand the effect of variables, such as PO2 and PCO2, on oxygen and carbon dioxide transport. Page 3. Oxygen Transport • Transport of oxygen during external respiration: • With its low solubility, only approximately 1.5% of the oxygen is transported dissolved in plasma.
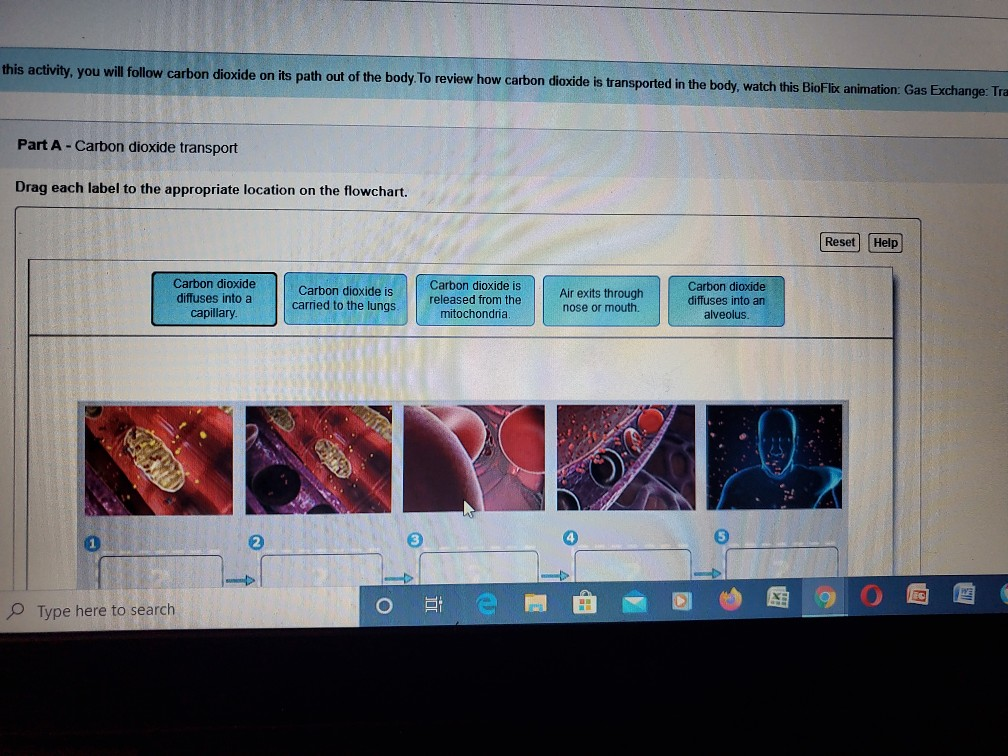 Solved this activity you will follow carbon dioxide on i
Solved this activity you will follow carbon dioxide on i
Then drag the pink labels to the pink targets to identify the processes in the carbon cycle. Drag the labels onto this diagram of the carbon cycle. Mastering environmental science 5th ed. In fuels in water co2 in. Drag the labels onto the flowchart to identify the sequence in which carbon moves through these organisms 1.
 Oxygen transport drag each label to the appropriate location
Oxygen transport drag each label to the appropriate location
The oxidative process occurring within living cells by which the chemical energy of organic molecules is released in a series of metabolic steps with the production of ATP, some occurring in the cytoplasm and some within the mitochondria, involving the consumption of oxygen and the liberation of carbon dioxide and water; it is generally divided into two stages: (1) anaerobic glycolysis in the ...
 A amp p2 ch22 respiratory system homework flashcards quizlet
A amp p2 ch22 respiratory system homework flashcards quizlet
Gas Transport Overview Here we discuss the processes and mechanisms responsible for transport of the two physiologically most important blood gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Circulatory Pathways. The blood vessels of the body are functionally divided into two distinctive circuits: pulmonary circuit and systemic circuit. The pump for the pulmonary circuit, which circulates blood through the lungs, is the right ventricle.The left ventricle is the pump for the systemic circuit, which provides the blood supply for the tissue cells of the body.
Part A - Carbon dioxide transport Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. 1. Carbon dioxide is released from the mitochondria. 2. Carbon dioxide diffuses into a capillary. 3. Carbon dioxide is carried to the lungs. 4. Carbon dioxide diffuses into an alveolus. 5. Air exits through nose or mouth.
 Papermaking vol 5 no 2 2019 by pita co uk issuu
Papermaking vol 5 no 2 2019 by pita co uk issuu
1 C Carbon dioxide Transport and Storage Carbon dioxide (CO2) capture and storage (CCS) involves the capture of CO2, its transport to a storage location and its long-term isolation from the atmosphere. Emissions associated with CO2 transport, injection and storage are covered under category 1C. Emissions (and reductions) associated with
The diagram below depicts the transport of carbon dioxide in blood, from body tissues to the lungs. Drag the labels to their appropriate locations on the diagram
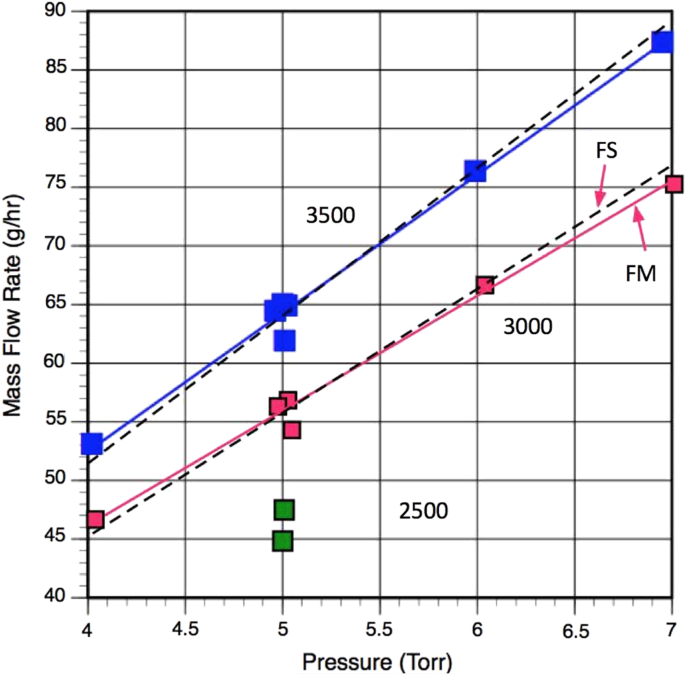 Mars oxygen isru experiment moxie springerlink
Mars oxygen isru experiment moxie springerlink
Drag each item into the appropriate bin depending on whether the process is associated with Photosystem II (PS II) only, Photosystem I (PS I) only, or both PS II and PS I. Note that "electron transport chain" here refers to the electron transport chain between the two photosystems, not the one that functions after PS I.
 Chapter 22 chapter 22 chapter22 due 9 59pmonwednesday
Chapter 22 chapter 22 chapter22 due 9 59pmonwednesday
Carbon dioxide molecules are transported in the blood from body tissues to the lungs by one of three methods: dissolution directly into the blood, binding to hemoglobin, or carried as a bicarbonate ion. Several properties of carbon dioxide in the blood affect its transport. First, carbon dioxide is more soluble in blood than oxygen.
 Mastering a amp p chapt 22 flashcards quizlet
Mastering a amp p chapt 22 flashcards quizlet
The 6 carbon fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is cleaved into two 3 carbon units; one glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP) and another molecule of dihydroxy acetone phosphate (DHAP). The enzyme which catalyses the reaction is aldolase. Since the backward reaction is an aldol condensation, the enzyme is called aldolase. The reaction is reversible.
 Solved part a carbon dionde transport drag each label to
Solved part a carbon dionde transport drag each label to
Carbon cycle explains the movement of carbon between the earth's biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere. Carbon is an important element of life. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is taken up by the green plants and other photosynthetic organisms and is converted into organic molecules that travel through the food chain.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify aspects of gas
Carbon Dioxide transport: Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. 1. CO2 is released from the mitochondria 2. CO2 diffuses into a capillary 3. CO2 is carried to the lungs ... Path of air: Drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. 1. air enters through the mouth or nose
 Week 12 respiration flashcards quizlet
Week 12 respiration flashcards quizlet
Part a carbon dioxide transport drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. Part a path of air drag each label to the appropriate location on the flowchart. In this interactive you can label parts of the human heart. Oxygen enters red blood cells where it binds to the protein hemoglobin. Oxygen diffuses from the blood to the bodys tissues and carbon dioxide diffuses from the tissues to the blood.
Title english semantic loans loan translations and loan
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) diffuses into the ocean carbon cycle via the air-sea surface exchange. Molecules of CO 2 enter the ocean by diffusing into the sea surface waters and dissolving — a physio-chemical process. The amount of CO 2 that diffuses and dissolves in the sea surface water depends on variables such as wind, sea surface mixing, concentrations of CO 2, and the temperature of the water.
The 2 pyruvic acids each contain 3 carbon atoms (the original glucose molecule had 6) , and there is a net gain of 2 ATP (2 are invested to split the glucose, and 4 are formed from ADP and P) that ...


0 Response to "21 Carbon Dioxide Transport Drag Each Label To The Appropriate Location On The Flowchart."
Post a Comment