21 Draw And Label A Wave
The P-wave, PR interval and PR segment. ECG interpretation traditionally starts with an assessment of the P-wave. The P-wave reflects atrial depolarization (activation). The PR interval is the distance between the onset of the P-wave to the onset of the QRS complex. The PR interval is assessed in order to determine whether impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricles is normal. If you were to trace your finger across the wave in the diagram above, you would notice that your finger repeats its path. A wave is a repeating pattern. It repeats itself in a periodic and regular fashion over both time and space. And the length of one such spatial repetition (known as a wave cycle) is the wavelength. The wavelength can be measured as the distance from crest to crest or from trough to trough.
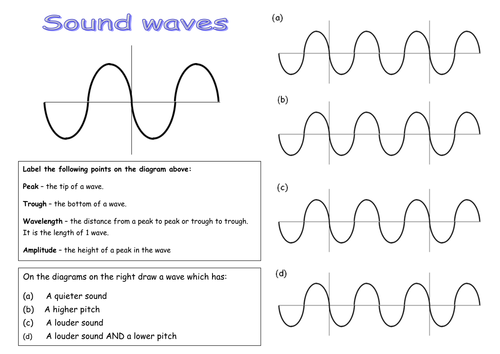
Wave Nature of Light 1. Draw a wave below and label the following parts: peak, trough, wavelength and amplitude . 2. Draw two waves with different frequencies and circle the wave that has a higher frequency.
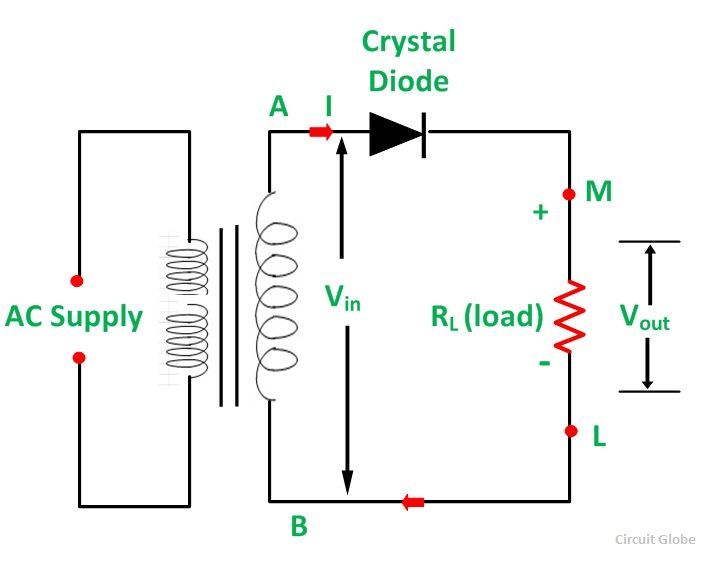 To make the output wave smooth and useful in a DC power supply, we have to use a filter across the load. Since only half-cycles of the input wave are used, it is called a half wave rectifier. Half Wave Rectifier Theory. Rectification is an application of the pn junction diode. Using a sharp eraser, keep a defined white line under the lip so it looks separate from the wave face. Add white highlights on the lip with your eraser to give it sparkle. The importance of perspective. Drawing a basic wave can be fun, but after a while it can get boring if you are merely following the same formula over and over again. On the graph below, draw 3-cycles of a transverse wave with an amplitude of 3 cm and a wavelength of 5 cm. Label the wave length , amplitude , crest and trough. If 1 cycle occurs every 2 seconds, calculate:
To make the output wave smooth and useful in a DC power supply, we have to use a filter across the load. Since only half-cycles of the input wave are used, it is called a half wave rectifier. Half Wave Rectifier Theory. Rectification is an application of the pn junction diode. Using a sharp eraser, keep a defined white line under the lip so it looks separate from the wave face. Add white highlights on the lip with your eraser to give it sparkle. The importance of perspective. Drawing a basic wave can be fun, but after a while it can get boring if you are merely following the same formula over and over again. On the graph below, draw 3-cycles of a transverse wave with an amplitude of 3 cm and a wavelength of 5 cm. Label the wave length , amplitude , crest and trough. If 1 cycle occurs every 2 seconds, calculate:
Draw and label a wave. a. a wave refracts due to changes in the properties of the medium. b. a wave reflects off a canyon wall and is heard shortly after it is formed. c. red, orange, and yellow wavelengths bend around suspended atmospheric particles. d. two identical waves moving different directions along the same medium interfere. Learn how to QUICKLY label a transverse wave with crest, trough, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, resting position and resting points. We will also learn h... Waves. As the ECG trace is recorded, there are a series of upwards, and downwards deflections created that represents atrial and ventricular depolarisation and repolarisation. These are known as the ECG waves. The P wave is the first positive deflection on the ECG. It is a small smooth-contoured wave and represents atrial depolarisation. Radio waves can vary between one meter (FM) and 1000 meters (AM). Assessment Pre-Lesson Assessment. Draw a Wave!: Ask students to take out a piece of paper and draw 3 or 4 ocean waves approaching a beach. Ask them to show the waves from the side, as if the students were out in a boat some distance from shore.
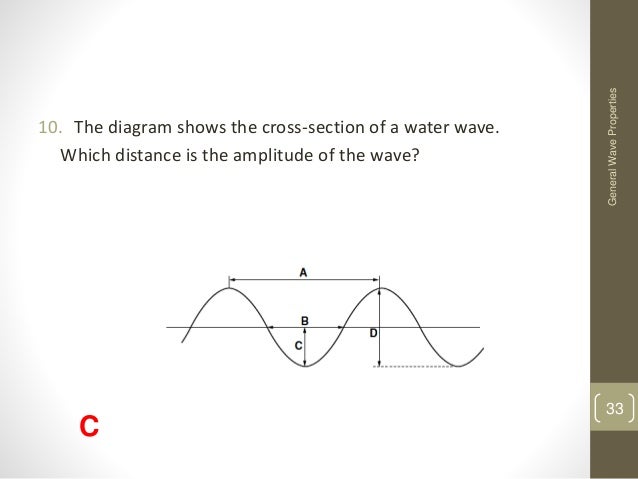
View Waves_worksheet.docx from MATH 123 at Braden River High School. Wave Practice 1) Draw a wave. Label the Amplitude, crest, trough, wavelength, and period Circle the correct answer 2) As frequency These make the sound waves propagate through the medium Questions Intext Question 1 Page 163 - Explain how sound is produced by your school bell. View Answer NCERT Question 2 - Describe with the help of a diagram, how compressions and rarefactions are produced in air near a source of sound. View Answer ... There are 2 complete waves shown in the diagram. The wavelength is the length of one wave, 40 cm. The amplitude is the height of the wave, 10 cm. Two waves, A and B, pass through the same medium at the same time. 44.Name a wave charactertistic that is different for wave A and wave B. 45.Name a wave characteristic that is the same for both wave A and wave B. 46.On the grid provided above, sketch the wave pattern produced when the two waves interfere.
1. What is a transverse wave? Draw one and label the following features on your drawing Crest Trough Equilibrium Wavelength Amplitude Direction of wave movement Answer: Click or tap here to enter text. 1. Draw a wave below and label the following parts: peak, trough, wavelength and amplitude. 2. Draw two waves with different frequencies and circle the wave that has a higher frequency. 3. A wave is simply energy moving from one place to another. It always needs something to move through. Example: Sound is the wave and the air is the medium. Wave Anatomy. Crest Trough Amplitude Wavelength= 𝑦 :𝜆 𝑖 : ( ) = 𝑦 :𝐴 𝑖 : ( ) In Phase. Period. Electromagnetic spectrum, the entire distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to frequency or wavelength.Although all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, they do so at a wide range of frequencies, wavelengths, and photon energies. The electromagnetic spectrum comprises the span of all electromagnetic radiation and consists of many subranges, commonly ...
 What is half wave and full wave rectifier operation
What is half wave and full wave rectifier operation
Draw and label a diagram of a transverse wave. Be sure to include the following parts: Crest . Trough. Amplitude. Wavelength . 5. Draw and label a diagram of a Compression wave. Be sure to include the following parts: Wavelength . Compression. Rarefaction. 6. Describe the characteristics of a longitudinal wave. Looks like a spring.
 Waves what are waves ms p ia ppt download
Waves what are waves ms p ia ppt download
Week #3 - Heart Function, EKG’s & Cardiac Cycle 1) Draw an EKG and label the P wave, QRS complex, T wave and the x and y axes. What does each of the wave forms in an EKG represent? 2) Answer the following questions about the cardiac cycle: A) How many isovolumetric periods are there per cycle and what is an isovolumetric period? There are 2 isovolumetric periods per cycle.
1. Introduce the parts of a wave. Draw a simple wave with two crests and one trough on the board so all students can see it. Explain that each part of a wave has a name, just like each part of the body has a name. Draw a line to the highest part of the wave and write the label crest. Tell students that the crest is the top of the wave.
 Pin by tiaret otarola on stickets how to draw hands labels
Pin by tiaret otarola on stickets how to draw hands labels
Label The Parts Of A Wave. Thursday, March 23rd 2017. | Free Labels. Wide collections of all kinds of labels pictures online. Make your work easier by using a label. Happy Labeling! Labels are a means of identifying a product or container through a piece of fabric, paper, metal or plastic film onto which information about them is printed. The information can be in the form of hand-written or printed text or symbols and gives details about manufacturer’s name, source of product, shelf-life ...

Using a sharp eraser, keep a defined white line under the lip so it looks separate from the wave face. Add white highlights on the lip with your eraser to give it sparkle. The importance of perspective. Drawing a basic wave can be fun, but after a while it can get boring if you are merely following the same formula over and over again.
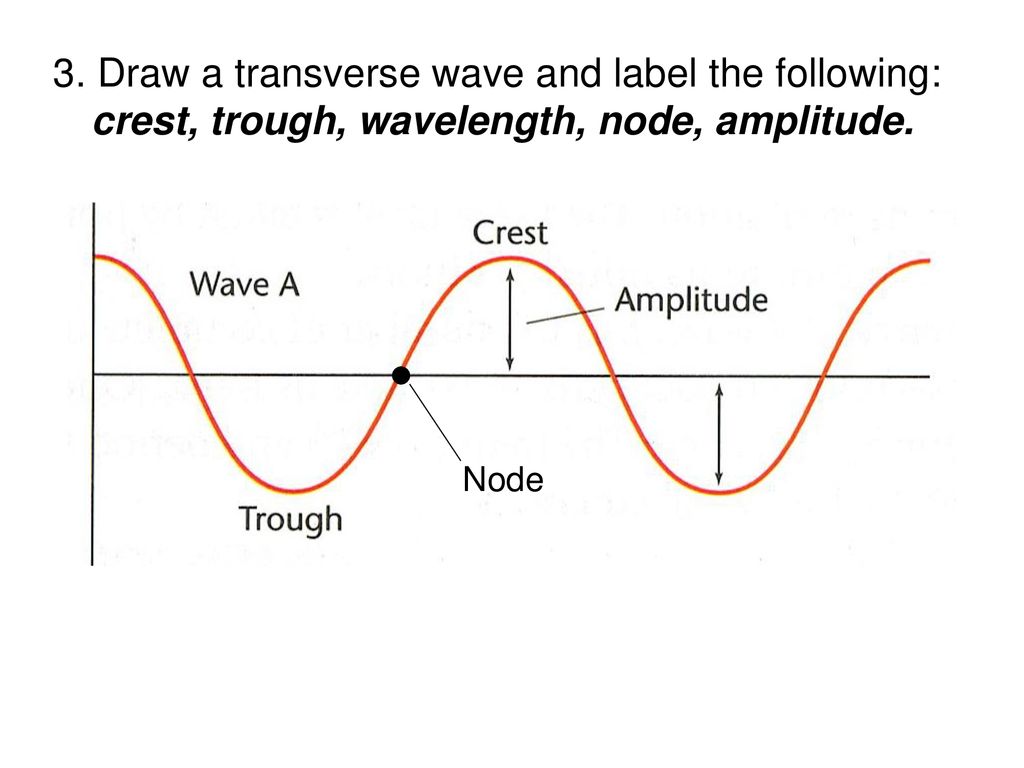 Wave test review worksheet ppt download
Wave test review worksheet ppt download
Draw a picture of this wave and describe it in words. A transverse wave moves across air or water at a right angle to the direction in which the waves are traveling. Some parts of the wave are high, while others are low. The highest parts of the wave are called crests, and the lowest parts are called troughs. This wave can be drawn as follows:
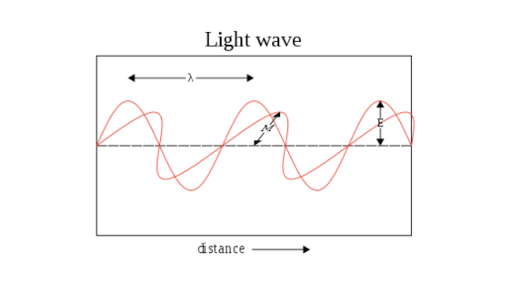
On the graph below, draw 3-cycles of a transverse wave with an amplitude of 3 cm and a wavelength of 5 cm. Label the wave length , amplitude , crest and trough. If 1 cycle occurs every 2 seconds, calculate:
686,419 wave drawing stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See wave drawing stock video clips. of 6,865. hello summers black&white patterns draw wave beach graphic vector wave sketch surfing line drawing sea waves doodle ocean wave horizon origami draw waves illustrations yacht in the sea.
 16 6 standing waves and resonance university physics volume 1
16 6 standing waves and resonance university physics volume 1
Back Waves Physics Contents Index Home. Standing waves are usually shown on a printed page as a static, or motionless, diagram. Of course, like all waves, they are dynamic; they have a motion. This interactive animation will help you understand how a static standing wave diagram is meant to convey the true motions of the standing wave.
 Label the parts of a transverse wave worksheet printable
Label the parts of a transverse wave worksheet printable
A square wave rises and falls regularly between two levels (Figure 2.20, left). A sawtooth wave rises and falls at an angle, like the teeth of a saw (Figure 2.20, center). A triangle wave rises and falls in a slope in the shape of a triangle (Figure 2.20, right). Square waves create a hollow sound that can be adapted to resemble wind instruments.
 Characteristics of a sound wave sound siyavula
Characteristics of a sound wave sound siyavula
Amplitude ( Top, Wave Home). The term amplitude can have slightly different meanings depending upon the context of the situation.. Its most general definition is that the amplitude is the maximum positive displacement from the undisturbed position of the medium to the top of a crest. This is shown in the following diagram:
 30 label the parts of a wave label design ideas 2020
30 label the parts of a wave label design ideas 2020
On Map 2, draw and label circles around the epicenter showing the distance the tsunami had traveled in 1 hour, 2 hours, 3 hours, and 4 hours. (You should have four labeled circles surrounding your epicenter representing the position of the leading edge of the tsunami as it traveled through the ocean after the earthquake occurred)
 Draw the diagram of electromagnetic wave
Draw the diagram of electromagnetic wave
An example of sound waves in a longitudinal direction is the tuning fork. In Sound waves, the amplitude of the wave is the difference between the maximum pressure caused by the wave and the pressure of the undisturbed air. The propagation speed of sound depends upon the type, composition of the medium, and temperature through which it propagates.
 1 of 10 c boardworks ltd 2006 waves 14 may 2015 objectives be
1 of 10 c boardworks ltd 2006 waves 14 may 2015 objectives be
Draw and label a transverse wave. The mathematics of wave motion easily maps into diagrams for transverse waves but it does not map so easily into diagrams for longitudinal waves. Of the longitudinal wave is parallel to the wave direction and the vibration is perpendicular to the direction in the transverse wave.
#____ = amplitude The distance from the line of origin to a crest or trough of a wave. Part 2 On separate sheets of graph paper, draw four different waves with the following measurements. Label the parts and include the measurements. wave # crest trough wavelength 1 1 cm 1 cm 2 cm 2 3.5 cm 3.5 cm 2.5 cm 3 .5 cm .5 cm 3 cm
 1 compare and contrast the two kinds of waves 2 draw a wave
1 compare and contrast the two kinds of waves 2 draw a wave
Draw a picture of a longitudinal wave. Label the following: COMPRESSION, RAREFACTION. Frequency. the number of wavelengths that pass by a given point during a period of time. Amplitude. the distance from the center or "equilibrium point" of a transverse wave to a crest or trough. Wavelength.
 Draw a transverse wave with an amplitude of 2 cm and a
Draw a transverse wave with an amplitude of 2 cm and a
Draw Elliott Waves (5 waves) manually. 1. Navigator Window (Ctrl + N), execute this script (double click) on chart. 2. It shows "0 1 2 3 4 5" (Blue) on the left of chart. Double click at number 0->5, then drag them to possible positions. 3. Unselect all (right click at any number 0-5), 4. Remove script to finish (right click on chart, choose Remove Script)
 Exit ticket exit slip parts of a wave
Exit ticket exit slip parts of a wave
10. Draw a diagram that shows what air molecules look like when a sound wave is traveling through the air. 11. Does sound travel faster in warm or cold air? Why? 12. Does a person’s voice sound higher or lower after inhaling helium gas? Why? 13. How is the wavelength of a sound wave related to its frequency? 14.
Draw a circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier explain its
3. Draw sketches to represent the following for 3s, 3p and 3d orbitals. (i) the radial wave function (ii) the radial distribution (iii) the angular wave function 4. Penetration and shielding are terms used when discussing atomic orbitals (i) Explain what the terms penetration and shielding mean.
 Draw a picture of two waves one with three times the
Draw a picture of two waves one with three times the
9.2 Compression and rarefaction (ESACT). However instead of crests and troughs, longitudinal waves have compressions and rarefactions.. Compression. A compression is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are closest together.. Rarefaction. A rarefaction is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are furthest apart.. As seen in Figure 9.2, there are regions where the ...
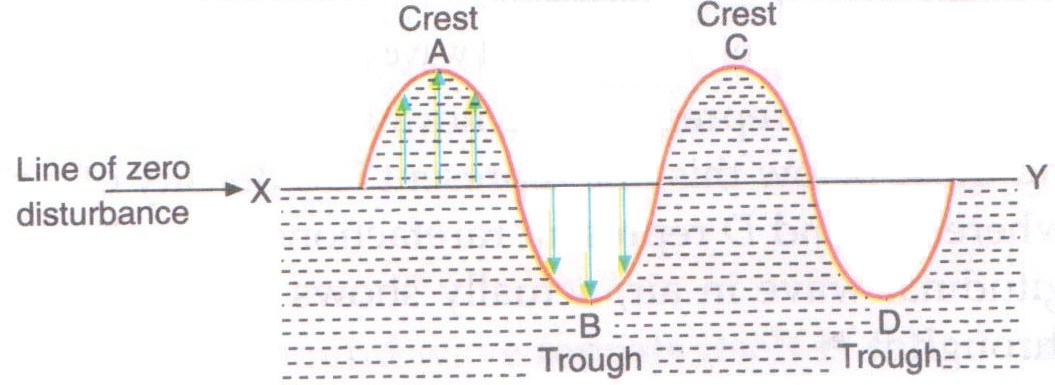 When a stone is thrown into a pond what type of waves are
When a stone is thrown into a pond what type of waves are
The wavelength of a wave is simply the length of one complete wave cycle. If you were to trace your finger across the wave in the diagram above, you would notice that your finger repeats its path. A wave has a repeating pattern. And the length of one such repetition (known as a wave cycle) is the wavelength. The wavelength can be measured as the distance from crest to crest or from trough to trough.

0 Response to "21 Draw And Label A Wave"
Post a Comment