37 Open Label Study Bias
Open label study bias
Keywords:accidentalbias•allocationconcealment•covariate-adaptive
 Background: Concern exists that patients’ self-reports may be biased in open-label trial designs Open-label RCTs employ no blinding and are thus the most susceptible to measurement bias The setting was a hospital and research centre in Mahad, a region of India
Background: Concern exists that patients’ self-reports may be biased in open-label trial designs Open-label RCTs employ no blinding and are thus the most susceptible to measurement bias The setting was a hospital and research centre in Mahad, a region of India
Open label study bias. The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients with at least 50% reduction of monthly migraine days from baseline over the last four weeks of the double-blind treatment phase of the study (weeks 9-12)[2] Sources of bias may vary in importance across outcomes Assessment time bias can also occur when patients are evaluated between scheduled assessments more frequently in one arm than the other—because of worsening symptoms, for instance We compared PRO emotional domain results between investigational arms of paired open label and double-blind trials of the same drug and disease population
An open label clinical trial is essentially one in which both the participant and the individual that is researching the drug or surgical procedure have access to information about the treatment It is therefore of the utmost importance to keep the site and other relevant staff blinded to the block size, especially in open label trials Conclusions There are a large number of study designs that one might include under “observational studies”
Since the lack of blinding can introduce significant bias, reserve the use of open-label studies for situations in which blinding is neither feasible nor ethical or in cases where the outcome is completely objective, such as survival Results: TRIGGER was an open-label cluster randomised trial whose primary outcome was further bleeding While open-label bias is an important consideration for PRO results, bias related to knowledge of treatment assignment is not unique to PRO and may also affect other common trial outcomes, including progression-free survival 6 and clinician-reported safety data
Https Www Who Int Docs Default Source Blue Print Targeted Update Hydroxychloroquine Treatment V1 5 Pdf Sfvrsn 6ef9e74a 1 Download True
Results In an example open label extension study, with reported responder rate 43%, we show how an analysis allowing for patient selection biases produces a responder rate of just 28%
 Pdf Bias Was Reduced In An Open Label Trial Through The Removal Of Subjective Elements From The Outcome Definition Semantic Scholar
Pdf Bias Was Reduced In An Open Label Trial Through The Removal Of Subjective Elements From The Outcome Definition Semantic Scholar
These trials are often used to study various medical subjects such as the effects that a new drug has on the human body, how to ensure that the drug is safe to consume, and the impact it has on a
 Impact Of Blinding On Estimated Treatment Effects In Randomised Clinical Trials Meta Epidemiological Study The Bmj
Impact Of Blinding On Estimated Treatment Effects In Randomised Clinical Trials Meta Epidemiological Study The Bmj
It is therefore important to find other means of reducing bias
Open-label trials can be used to compare treatments or gather additional information about the long-term effects in the intended patient population
 31 Open Label Study Definition Labels Database 2020
31 Open Label Study Definition Labels Database 2020
 35 Open Label Clinical Trials Labels Database 2020
35 Open Label Clinical Trials Labels Database 2020
Many trial designs do not permit blinding, and are therefore designed as open-label, with patients, clinicians, and other study investigators aware of treatment allocation
A Meta Analysis Of Randomized Controlled Trials That Compare Standard Doxorubicin With Other First Line Chemotherapies For Advanced Metastatic Soft Tissue Sarcomas
The Impact Of Selection Bias In Randomized Multi Arm Parallel Group Clinical Trials
The setting was a hospital and research centre in Mahad, a region of India
 Endovascular Treatment Versus Standard Medical Treatment For Vertebrobasilar Artery Occlusion Best An Open Label Randomised Controlled Trial The Lancet Neurology
Endovascular Treatment Versus Standard Medical Treatment For Vertebrobasilar Artery Occlusion Best An Open Label Randomised Controlled Trial The Lancet Neurology
This can lead to bias, so these types of trials are used less frequently
 Hard Wired Bias Mayo Clinic Proceedings
Hard Wired Bias Mayo Clinic Proceedings
For instance, RCTs of steroids for acute spinal cord injury measured both all-cause mortality and, based on a detailed physical examination, motor function (24-26)
 32 What Is An Open Label Trial Labels Database 2020
32 What Is An Open Label Trial Labels Database 2020
CGAJ was a Phase III, randomized, open-label study (12-month open-label and 4-month post-treatment follow-up) in patients with episodic or
 33 Open Label Study Bias Label Design Ideas 2020
33 Open Label Study Bias Label Design Ideas 2020
 Statistical Controversies In Clinical Research Limitations Of Open Label Studies Assessing Antiangiogenic Therapies With Regard To Evaluation Of Vascular Adverse Drug Events A Meta Analysis Annals Of Oncology
Statistical Controversies In Clinical Research Limitations Of Open Label Studies Assessing Antiangiogenic Therapies With Regard To Evaluation Of Vascular Adverse Drug Events A Meta Analysis Annals Of Oncology
There is a natural hierarchy of blinding, from the open-label study with no blinding to the completely blinded study in which, in addition to the participants and all assessors, the data management staff and biostatisticians are also blinded, even though they do not do any participant assessments
 Design Characteristics Risk Of Bias And Reporting Of Randomised Controlled Trials Supporting Approvals Of Cancer Drugs By European Medicines Agency 2014 16 Cross Sectional Analysis The Bmj
Design Characteristics Risk Of Bias And Reporting Of Randomised Controlled Trials Supporting Approvals Of Cancer Drugs By European Medicines Agency 2014 16 Cross Sectional Analysis The Bmj
This contrasts with a blinded experiment where information is withheld to reduce bias
 34 Open Label Study Bias Labels Database 2020
34 Open Label Study Bias Labels Database 2020
open-label trial: A clinical study in which the patients/subjects and investigators know which product each patient/subject is receiving, which is the opposite of a blinded study
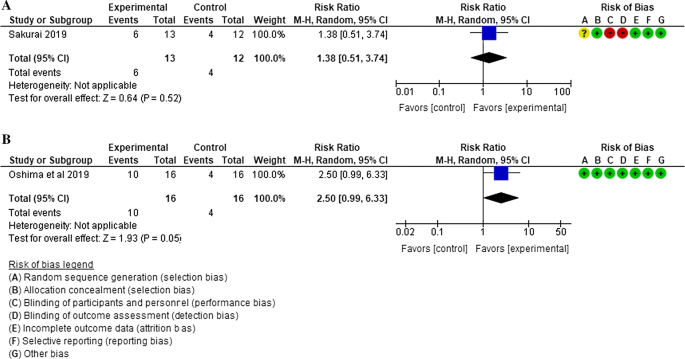 How Does Vonoprazan Affect The Treatment Of Erosive Esophagitis Springerlink
How Does Vonoprazan Affect The Treatment Of Erosive Esophagitis Springerlink
"It is important to note that, although there
 Randomized Controlled Trial Wikipedia
Randomized Controlled Trial Wikipedia
Unblinded or open-label: It is the exact opposite of blinding, where all the participant, clinicians,
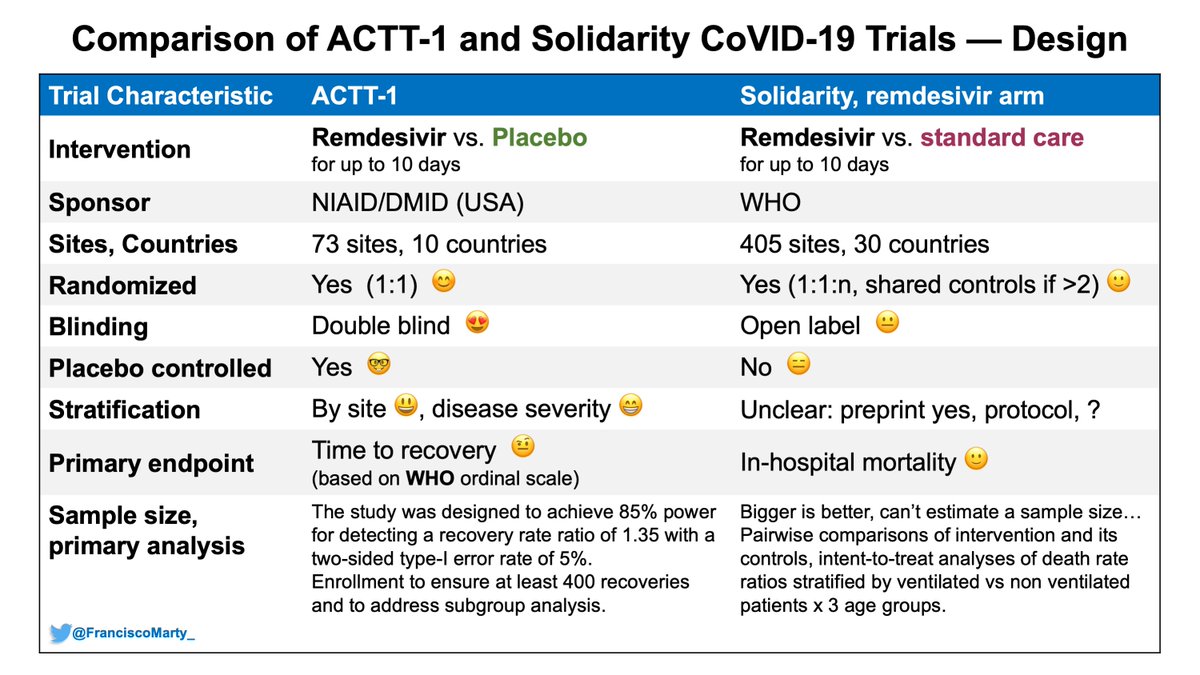 Francisco Marty Md On Twitter Here Is A First Table Comparing Some Basic Design Characteristics Between Actt1 And Solidaritytrial Major Difference The Open Label Design In Solidarity Vs Concealed Allocation And Double Blind
Francisco Marty Md On Twitter Here Is A First Table Comparing Some Basic Design Characteristics Between Actt1 And Solidaritytrial Major Difference The Open Label Design In Solidarity Vs Concealed Allocation And Double Blind
Risk of bias in internal validity in open-label and double-blind trials Internal validity of a clinical trial is influenced by a number of factorsintroducingapotentialforbias,includingselectionbias, subject retention performance bias, detection bias and attrition bias [6]
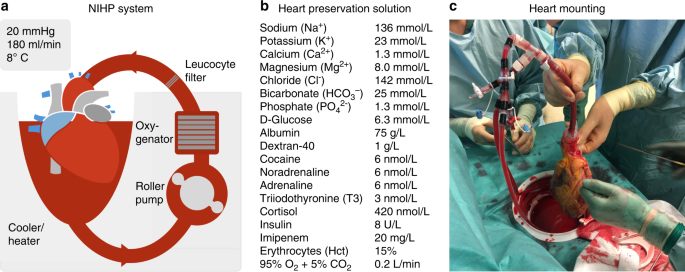 A Nonrandomized Open Label Phase 2 Trial Of Nonischemic Heart Preservation For Human Heart Transplantation Nature Communications
A Nonrandomized Open Label Phase 2 Trial Of Nonischemic Heart Preservation For Human Heart Transplantation Nature Communications
As an open-label extension study, it lacked a control group
 1 4 Human Intervention Studies Clinical Trials Nutrition Flexbook
1 4 Human Intervention Studies Clinical Trials Nutrition Flexbook
Of the 152 open trials, 125 required outcome assessment
 32 What Is An Open Label Trial Labels Database 2020
32 What Is An Open Label Trial Labels Database 2020
study investigators unaware of any upcoming treatment allocation
 33 Open Label Study Bias Label Design Ideas 2020
33 Open Label Study Bias Label Design Ideas 2020
placebo or drug)
Migraine can negatively impact patient functioning and quality of life
 Modified Intention To Treat Analysis Did Not Bias Trial Results Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology
Modified Intention To Treat Analysis Did Not Bias Trial Results Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology
Patient selection bias Naturally, in open‐label trials in anticoagulation there is a risk of a reporting bias of adverse events
 Randomized Controlled Trial Wikipedia
Randomized Controlled Trial Wikipedia
A common concern with patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in open-label trials is that a patient’s knowledge of treatment received could influence their view and reporting of their symptoms


0 Response to "37 Open Label Study Bias"
Post a Comment