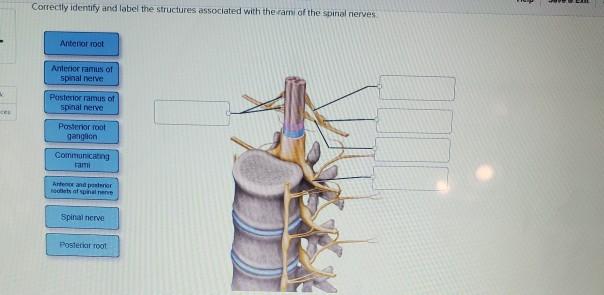
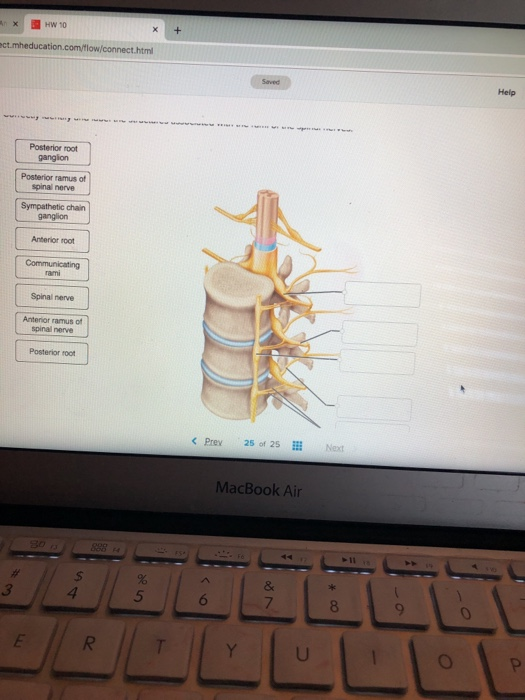
37 Correctly Identify And Label The Structures Associated With The Rami Of The Spinal Nerves.
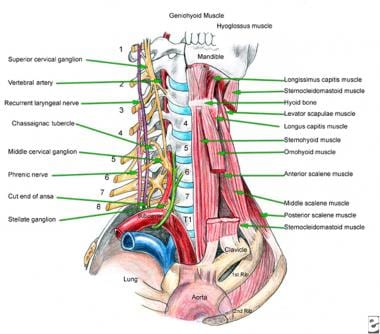
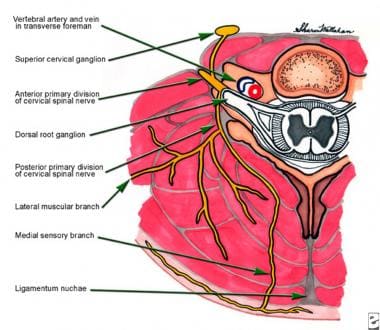
About the size of a pearl, the hypothalamus directs a multitude of important functions in the body. Located in the diencephalon region of the forebrain, the hypothalamus is the control center for many autonomic functions of the peripheral nervous system.Connections with structures of the endocrine and nervous systems enable the hypothalamus to play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis. The interjoining of nerves in the neck (cervical plexus) is formed by the anterior rami of the spinal nerves of segments C1-C4 and is located on the side of the transverse processes of the cervical spine between the prevertebral muscles (scalenus and levator scapulae) and below the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
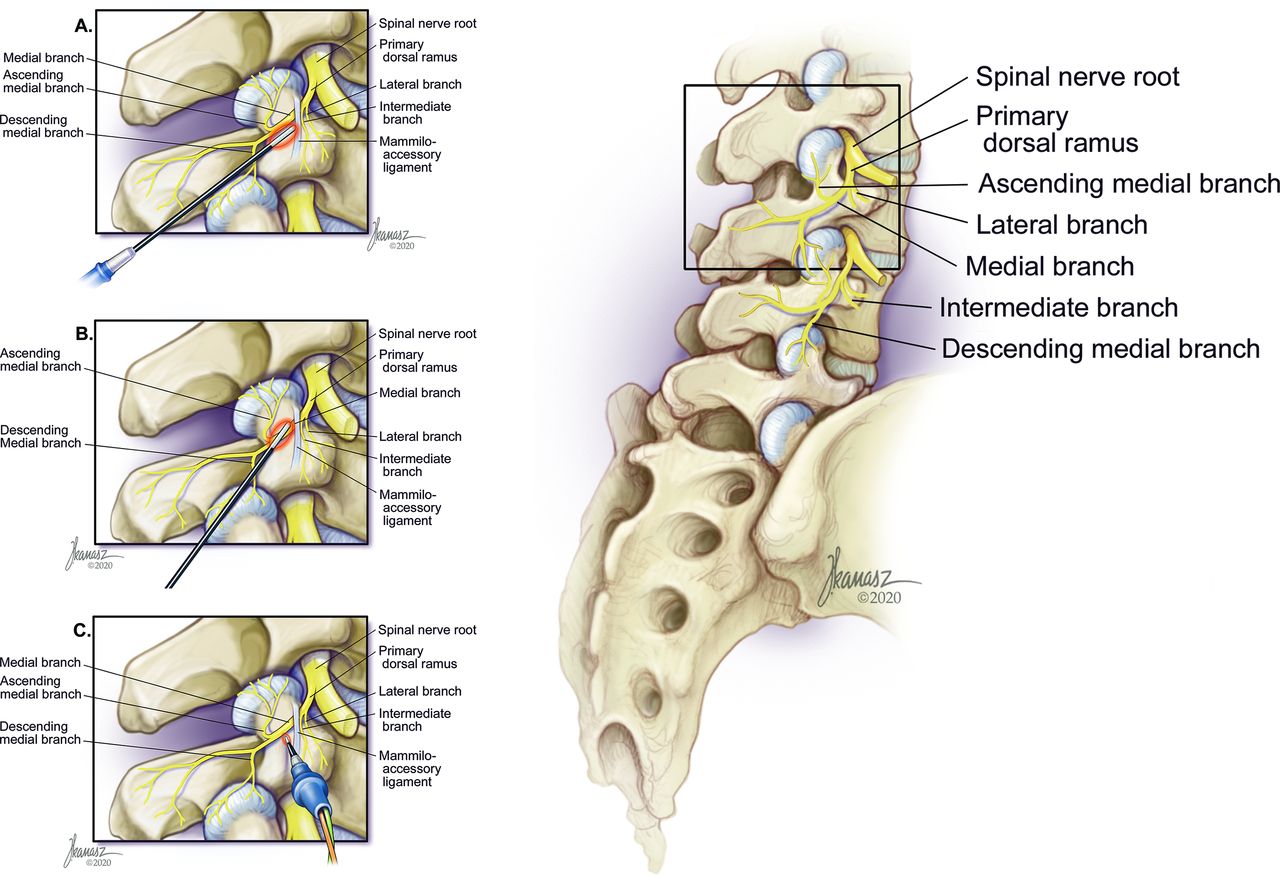
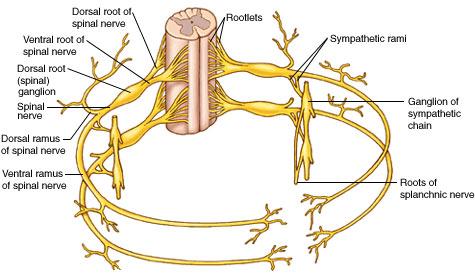
The 31 pairs of human spinal nerves are formed by the combination of the ventral and dorsal roots of the spinal cord. Rami. Almost immediately after being formed, each spinal nerve divides into dorsal and ventral rami, making each spinal nerve only about 1/2 inch long; the rami contains both sensory and motor fibers. Dorsal rami.

Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the rami of the spinal nerves.
Correctly identify and label the structures associated with rami of the spinal nerves 711 lumbar spine anatomy diagram stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See lumbar spine anatomy diagram stock video clips. of 8. spinal vertebrae bone spine vertebra toracica spinal cord spine structure back diagram spine sections spinal cord vertebrae spinal structure health diagram. Try these curated collections. Dermatomes are areas of skin that receive sensations from sensory nerves exiting the spinal cord. Sensory nerves provide the feeling of hot, cold, pain, etc. There are 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, and 1 coccygeal nerve dermatomes. Doctors use dermatomes to help diagnose diseases and conditions. Myotomes is a group of single spinal nerves that originate from groups of muscles.
Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the rami of the spinal nerves.. Spinal Nerves. Extending from the left and right sides of the spinal cord are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. The spinal nerves are mixed nerves that carry both sensory and motor signals between the spinal cord and specific regions of the body. The 31 spinal nerves are split into 5 groups named for the 5 regions of the vertebral column. The end of the spinal cord is called the cauda equine because it looks like a horse's tail with its cascade of nerves. The Structure. Exiting through a big hole at the bottom of the skull, the spinal cord is covered by the vertebral column that protects it. The spinal nerves come out from the spaces between the bony arches in pairs. Correctly identify and label the structures associated with rami of the spinal nerves All basic life functions originate in the brain stem, including heartbeat, blood pressure and breathing. In humans, this area contains the medulla, midbrain and pons. This is commonly referred to as the simplest part of the brain, as most creatures on the evolutionary scale have some form of brain creation that resembles the brain stem.
Question: Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the. root Spinal cord Posterior ramus Posterior root ganglion Anterior ramus... The peripheral nervous system is an essential part of the body and its functions. This lesson examines of the peripheral nervous system, as well as its official definition, parts, functions, and. Correctly label the structures and areas associated with a neuron at rest.. Correctly identify and label the dermatome(s) represented by the statement(s) associated with them.... The anterior rami of the brachial plexus are the continuations of the anterior rami of spinal nerves _____ . These rami emerge from the intervertebral foramina and ... The cerebellum is the second largest part of the brain and it is involved in coordinated movement, posture, and balance. The cerebral cortex has a series of folds that allow for a larger surface area to house more gray matter and its powerful information processing. 1. Each groove or low point is known as a sulcus.
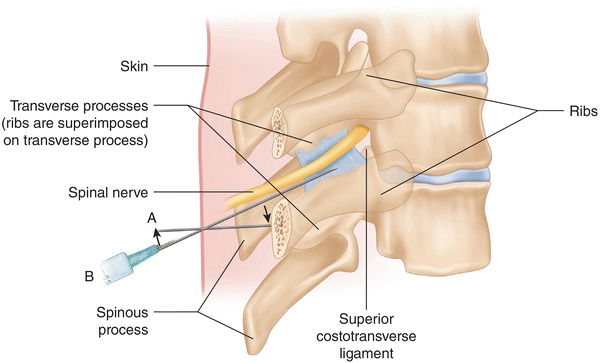
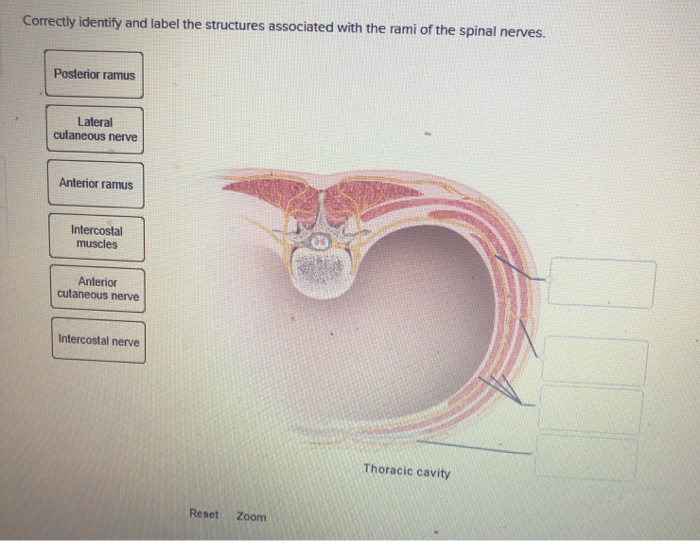
Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the rami of the spinal nerves. Correctly identify and label the dermatome(s) represented by the statement(s) associated with them. Correctly identify the function of each structure that comprises a tendon reflex by dragging the appropriate label into place. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the rami of the spinal nerves. 20 Intercostal nerve 0.5 points Posterior ramus eBook Anterior cutaneous nerve References Lateral cutaneous nerve Anterior ramus Intercostal muscles < Prey 20 of 30 !! Next >. Dermatomes are areas of skin that receive sensations from sensory nerves exiting the spinal cord. Sensory nerves provide the feeling of hot, cold, pain, etc. There are 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, and 1 coccygeal nerve dermatomes. Doctors use dermatomes to help diagnose diseases and conditions. Myotomes is a group of single spinal nerves that originate from groups of muscles. Spinal roots carry sensory (dorsal root) or motor (ventral root) neurons, whereas the spinal nerves and rami contain a mixture of sensory and motor neurons. The dorsal rami seg-mentally innervate deep back muscles (motor) and the skin of the back (sensory). This section of the chapter helps to differentiate among vertebral levels, spinal cord.
Match the structure with the correct label using the picture of a superior view of a cross section of the spinal cord.. Correctly match the structures associated with spinal cord with the label in the picture. Dura mater - A Subdural space - B... The _____ rami of spinal nerves innervate the ribs, the intercostal muscles and the skin of the ...
Answer The label is indicated from RIGHT SIDE of.. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the rami of the spinal nerves. Anterior and posterior rootlets of spinal nerve Anterior ramus of spinal nerve Posterior root ganglion Spinal nerve Posterior ramus of spinal nerve.
Thalamus is a large egg-shaped mass of grey matter, having a small amount of white matter located at the base of the forebrain, just above the midbrain. It is a part of the diencephalon and is located lateral to the third ventricle. It consists of three lamina of white matter: Stratum Zonale, covering the. superior surface of thalamus.
Gross anatomy. The pelvis marks an important transition point between the thoracoabdominal region and the lower limbs.Not only is it important for walking, but it also houses organs of the urogenital and distal digestive systems and acts as a conduit for arteries, veins, lymphatic vessels, and nerves necessary for daily functioning. The pelvis is a musculoskeletal structure that is made up of.
T1 - T8 Spinal Cord Injuries. The first eight segments of the thoracic spine connect to the rib cage and control the trunk of the body. The thoracic region of the spinal column is made up of 12 segments referred to as T1 - T12. It is located in the middle of the spine between the cervical and lumbar levels. The 12 thoracic vertebrae which make.
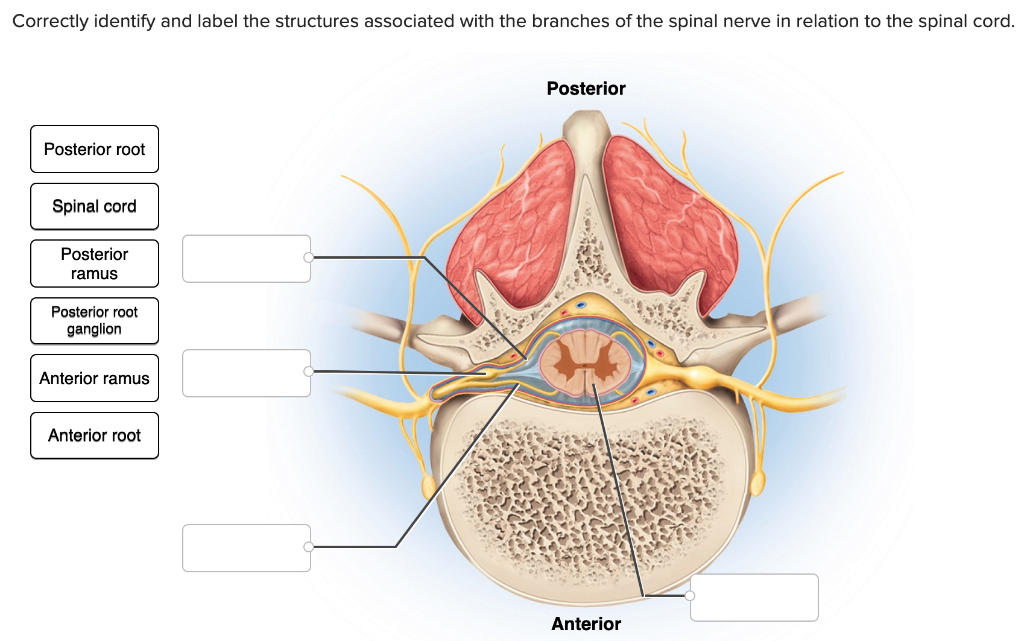
Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the branches of the spinal nerve in relation to the spinal cord. Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the rami of the spinal nerves.
Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the rami of the spinal nerves. Posterior ramus Lateral cutaneous nerve Anterior ramus Intercostal muscles Anterior cutaneous nerve Intercostal nerve Thoracic cavity Reset Zoom.
Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the rami of the spinal nerves. Correctly identify and label the spinal nerves and their plexuses. Correctly match the nerve plexus with the spinal nerves that comprise it.
The interscalene block is indicated for procedures on the shoulder and proximal humerus as well as the lateral two thirds of the clavicle. The interscalene block can also be utilized for surgery of the arm or forearm; however, the higher incidence of incomplete blockade of the inferior trunk with this technique may provide inadequate analgesia in the ulnar distribution.
Types. In the central nervous system, a synapse is a small gap at the end of a neuron that allows a signal to pass from one neuron to the next. Synapses are found where nerve cells connect with other nerve cells. Synapses are key to the brain's function, especially when it comes to memory. 1 . The term synapse was first introduced in 1897 by.
711 lumbar spine anatomy diagram stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See lumbar spine anatomy diagram stock video clips. of 8. spinal vertebrae bone spine vertebra toracica spinal cord spine structure back diagram spine sections spinal cord vertebrae spinal structure health diagram. Try these curated collections.
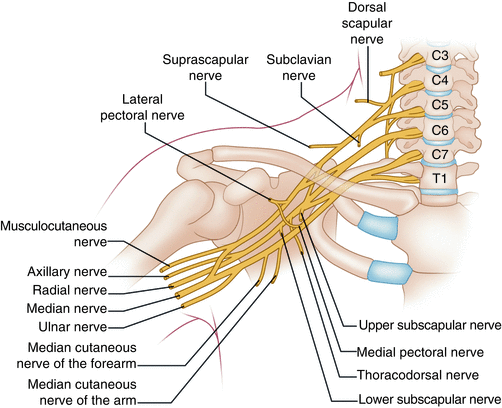
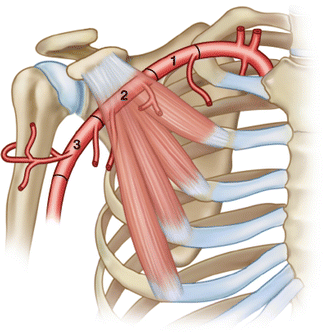
Overview of the brachial plexus. The brachial plexus is a complex intercommunicating network of nerves formed by spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8 and T1. It supplies all sensory innervation to the upper limb and most of the axilla, with the exception of an area of the medial upper arm and axilla, which is supplied by the intercostobrachial nerve T2.
Brain stem injuries cause serious problems and require intensive treatment. Below are some of the most common effects of brain stem damage. 1. Coma. The brain stem houses a network of neurons called the reticular activating system (RAS), which helps a person wake up. When the brain stem is damaged, the RAS is compressed and can cause a coma.
The lumbar plexus is a network of nerve fibres that supplies the skin and musculature of the lower limb. It is located in the lumbar region, within the substance of the psoas major muscle and anterior to the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae.. The plexus is formed by the anterior rami (divisions) of the lumbar spinal nerves L1, L2, L3 and L4.
Origin and insertion. The diaphragm is a musculotendinous structure with a peripheral attachment to a number of bony structures. It is attached anteriorly to the xiphoid process and costal margin, laterally to the 11th and 12th ribs, and posteriorly to the lumbar vertebrae.The posterior attachment to the vertebrae is by tendinous bands called crura.The crura are attached to the anterior aspect.
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord and acts as the main control system for the body. The peripheral nervous system is made up of all the nerves and ganglia (nerve cell clusters) found outside of the central nervous system; its role is receiving information from various stimuli and sending it to the brain.
Transcribed image text: Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the rami of the spinal nerves. Posterior root ganglion Copyright The.
There are around 100-500 trillion such connections in the human brain, between two nerves or nerves and glands. In this article we will discuss only the junction. Structure of Neuromuscular Junction. As we have read, the junction consists of a neuron and a skeletal muscle cell. The neuron in the combination is referred to as spinal motor neuron.
Pain is a somatic and emotional sensation which is unpleasant in nature and associated with actual or potential tissue damage. Physiologically, the function of pain is critical for survival and has a major evolutionary advantage. This is because behaviours which cause pain are often dangerous and harmful, therefore they are generally not reinforced and are unlikely to be repeated.
Transcribed image text: Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the rami of the spinal nerves. Anterior ramus of spinal nerve Anterior.
Spinal Cord & Nerves. The length of the spinal cord is approximately 45 cm in men and 43 cm in women. The diameter ranges from 13 mm in the cervical and lumbar regions to 6.4 mm in the thoracic area. The cord is protected within the spinal canal and runs from the brainstem to the lumbar area where the cord fibres separate.
This human anatomy module is about the cranial nerves. It consists of 15 vector anatomical drawings with 280 anatomical structures labeled. It is intended for the use of medical students working on human anatomy, student nurses, physiotherapists, electro-radiological technicians and residents - especially those working in neurology, neurosurgery, otolaryngology - and for any physician.
The ventricular system is a set of communicating cavities within the brain. These structures are responsible for the production, transport and removal of cerebrospinal fluid, which bathes the central nervous system. In this article, we shall look at the functions and production of cerebrospinal fluid, and the anatomy of the ventricles that contains it.
Correctly identify and label the structures associated with the rami of the spinal nerves. Classify the following structures with the region of the spinal cord in which they are located. Each of the labels below describes a sensory or motor innervation.
The medulla is located directly above the spinal cord in the lower part of the brain stem and controls many vital autonomic functions such as heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure. Pons The pons connects the cerebral cortex to the medulla and to the cerebellum and serves a number of important functions.
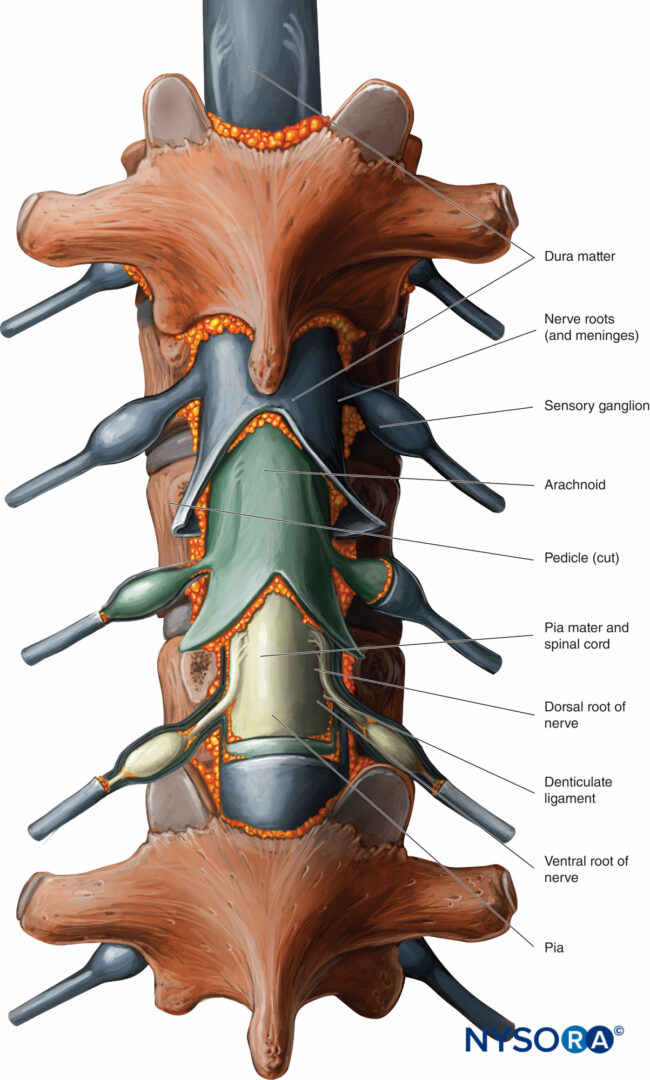
The dorsal root ganglion is a collection of neuronal cell bodies associated with the sensory root of the spinal nerves. These ganglia are considered to be a part of the grey matter of the spinal cord. The dorsal root ganglia are present very close to the spinal cord. The posterior root expands to form the ganglia as soon as it leaves the spinal.
SPINAL ROOTS At each spinal cord segment, paired dorsal and ventral roots exit the lateral sides of the cord to form left and right spinal nerves. As a result of unequal growth between the vertebral canal and the spinal cord (the vertebral canal is longer than the spinal cord in adults), the nerve roots follow an oblique course from superior to.











0 Response to "37 Correctly Identify And Label The Structures Associated With The Rami Of The Spinal Nerves."
Post a Comment