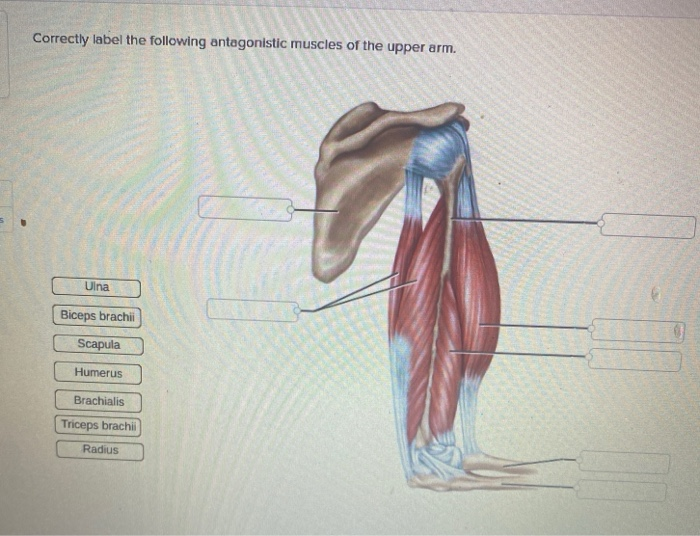
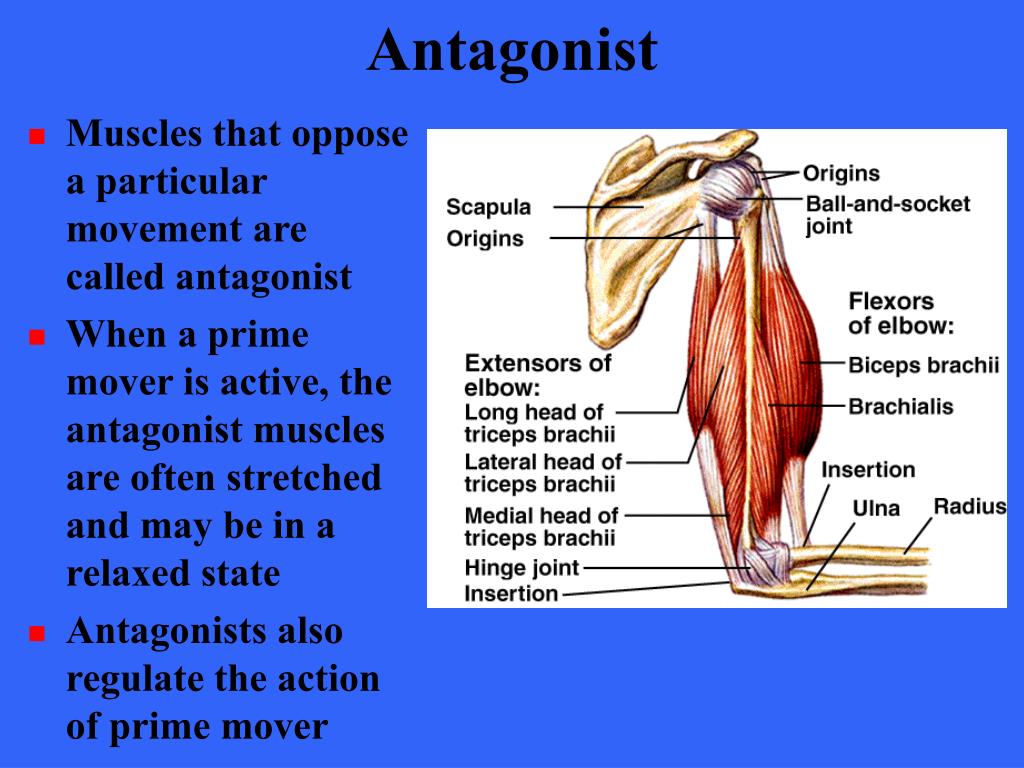
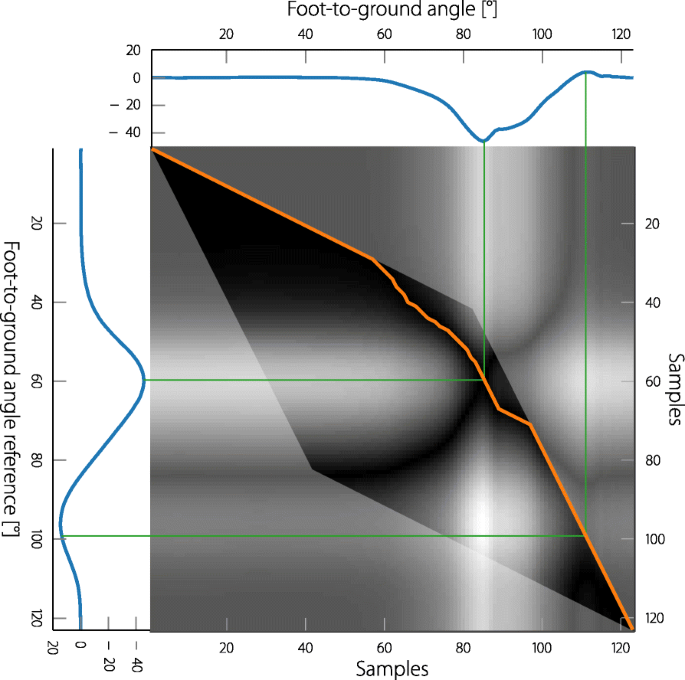
39 Correctly Label The Following Antagonistic Muscles Of The Upper Arm.
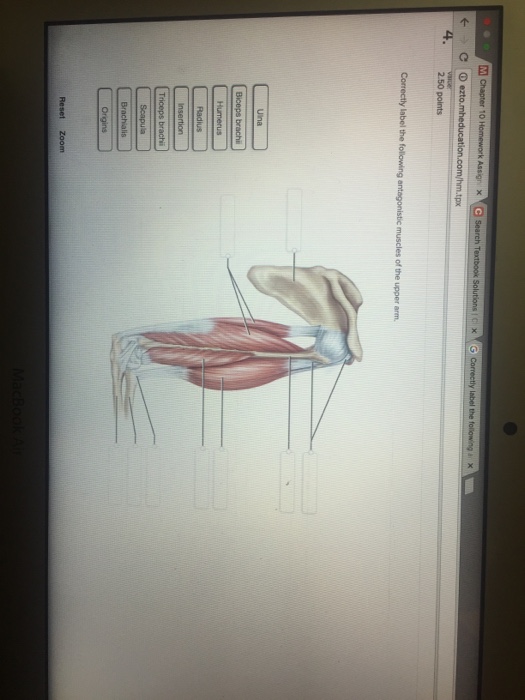
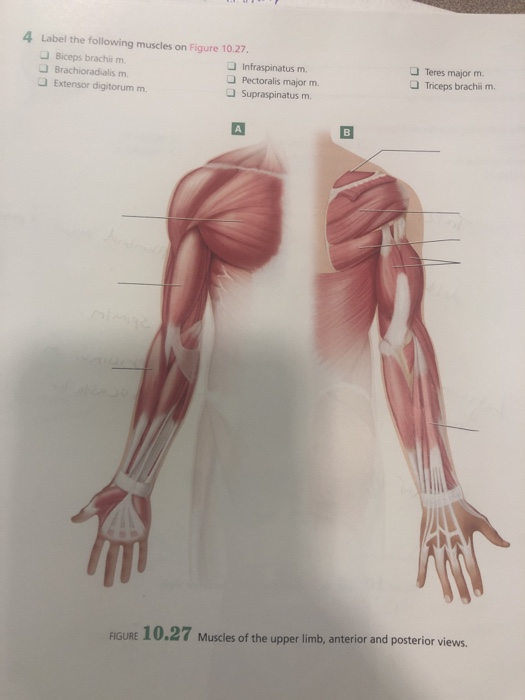
Unformatted text preview: 4. Award: 1.00 point Problems? Adjust credit for all students. Correctly label the following antagonistic muscles of the upper arm. brachii Triceps brachii Biceps Scapula Origins Humerus Triceps brachii Triceps brachii Scapula Biceps brachii Brachialis Insertion Radius Ulna Origins Humerus Biceps brachii Brachialis Insertion Radius Ulna Zoom Explanation: The biceps. Skeletal muscles work across a joint and are attached to the bones by strong cords known as tendons. Movement of the arm at the elbow Antagonistic Muscles They work in pairs, each contracting or relaxing in turn to create movement. E.g Biceps brachii and triceps brachii = known as ANTAGONISTIC MUSCLE ACTION.
Antagonistic muscles are necessary for balance, as well as extending and contracting limbs. There are many groups of antagonistic muscles in the body. The most famous of these pairings is the biceps and the triceps on the arm. Additional sets include muscles in the chest and back of the torso, as well as the quadriceps and hamstrings of the leg.

Correctly label the following antagonistic muscles of the upper arm.
the deltoid muscle is the principle abductor of the arm but due to poor mechanical advantage it cannot initiate this action; it is assisted by the supraspinatus m. dorsal interosseous (hand) four muscles, each arising from two adjacent metacarpal shafts A muscle with the opposite action of the prime mover is called an antagonist. Antagonists play two important roles in muscle function: They maintain body or limb position, such as holding the arm out or standing erect; They control rapid movement, as in shadow boxing without landing a punch or the ability to check the motion of a limb There's another muscle on the underside of your upper arm, called the triceps, or lower arm muscle. The triceps in this case is the antagonist muscle, relaxing and providing movement control while.
Correctly label the following antagonistic muscles of the upper arm.. The gracilis muscle is used in muscle transplants as it is a small synergistic muscle in humans. This long, slender muscle originates from the body and inferior ramus of the pubic bone, and inserts on the proximal medial shaft of the tibia. In addition to adduction of the thigh, it functions in flexion of the leg. Experiment HM-2: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Antagonistic Muscles Exercise 1: Antagonistic Muscles in Forearm Aim: To study the EMG activity in muscles that work in opposition to each other to flex or extend the hand. Procedure 1. Instruct the subject that he or she will be doing the following during this exercise: • Before the recording. Information. Anatomists refer to the upper arm as just the arm or the brachium. (The lower arm is the forearm or antebrachium.) There are three muscles on the upper arm that are parallel to the long axis of the humerus, the biceps brachii, the brachialis, and the triceps brachii. A muscle of the medial thigh that originates on the pubis. It inserts onto the linea aspera of the femur. It adducts, flexes, and rotates the thigh medially. It is controlled by the obturator nerve. It pulls the leg toward the body's midline (i.e. adduction) Biceps brachii. An upper arm muscle composed of 2 parts, a long head and a short head.
Question: Correctly Label The Following Antagonistic Muscles Of The Upper Arm. Ulna Biceps Brachii Scapula Humerus Brachialis Triceps Brachii Radius This problem has been solved! See the answer Muscles of the Upper Extremity. The muscles of the upper extremity include those that attach the scapula to the thorax and generally move the scapula, those that attach the humerus to the scapula and generally move the arm, and those that are located in the arm or forearm that move the forearm, wrist, and hand. The illustration below shows some of the muscles of the upper extremity. Answer to Correctly label the following muscles of the. Transcribed image text: Correctly label the following muscles of the posterior view. Latissumus dorsi Occipitalis Teres major Splenius capitis Gluteus maximus Infraspinatus lliotibial tract Occipitalis Gluteus medius Gracilis Extensor carpi radialis Extensor digitorum Match each label to its corresponding muscle of the quadriceps femoris. Correctly label the following antagonistic muscles of the upper arm. Correctly label the following anatomical features of the vertebra. Name the bony structures of the thoracic cage.
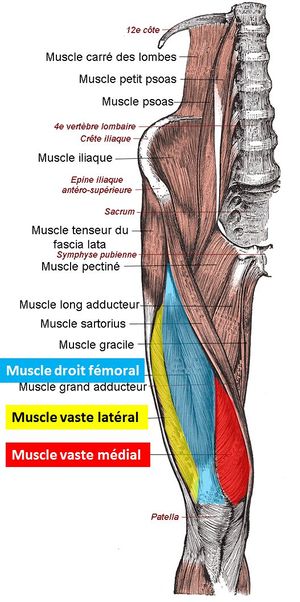
Other antagonist muscle pairs involve two types of deltoids, abdominals versus spinal erectors, two types of oblique muscles and two forearm muscle pairs. Agonists create the normal range of motion of a joint, while subsequent antagonists return the joint to its normal position, notes MIT. Antagonist and agonist muscles often occur in pairs, called antagonistic pairs.As one muscle contracts, the other relaxes.An example of an antagonistic pair is the biceps and triceps; to contract, the triceps relaxes while the biceps contracts to lift the arm."Reverse motions" need antagonistic pairs located in opposite sides of a joint or bone, including abductor-adductor pairs and flexor. The biceps muscle is located on the front of your upper arm and is composed of two heads. The triceps makes up the back of your arm and is made up of three heads. Together, through a series of equal and opposite contractions, these muscles are responsible for flexion and extension of your elbow joint and contribute to functional movement. Science. Anatomy and Physiology. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. Correctly label the anterior muscles of the thigh. Quadriceps femoris: Vastus lateralis Quadriceps femoris tendon Quadriceps femoris: Patellar ligament Quadriceps femoris: Rectus femoris liotibial tract Sartorius Reset Zoom <Prev 7 of soll! Next>.
Antagonistic muscle pairs. Muscles transfer force to bones through tendons. They move our bones and associated body parts by pulling on them – this process is called muscle contraction.
Which of the following muscles does not have an action that is antagonistic to the action of the brachialis muscle?. head *brachioradialis. A muscle that assists the muscle that is primarily responsible for a given action is a(n) agonist. antagonist. *synergist. originator.... The major abductor muscle of the upper arm is the. supraspinatus ...
A muscle with the opposite action of the prime mover is called an antagonist. Antagonists play two important roles in muscle function: They maintain body or limb position, such as holding the arm out or standing erect; They control rapid movement, as in shadow boxing without landing a punch or the ability to check the motion of a limb
There's another muscle on the underside of your upper arm, called the triceps, or lower arm muscle. The triceps in this case is the antagonist muscle, relaxing and providing movement control while.
Gwinnett Technical College BIO 2113 LAB Anatomy and Physiology 1 Martini Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.
Flexion and Extension: Record Your Antagonistic Muscles. Now that you've completed the "Getting Started with the Muscle Spikerbox" experiment, you've learned about muscle physiology through viewing electromyograms (EMGs) of your own muscles. More specifically, you've observed the electrical impulses that muscles fibers create to cause a contraction of a muscle.
View Homework Help - 3E670117-4075-4FAC-B483-486887D4FFA2.jpeg from BIO 203 at Bunker Hill Community College. Correctly label the following muscles of the posterior view." Fibularis longus _Deep |
Antagonistic pairs of muscles are. muscle where one move the bone in one direction and the other moves it back the other way in transmission of nerve impulses to the muscles. That means that it is impossible to fully stimulate the contraction of two antagonistic muscles at the same time.
Arm muscles. The (upper) arm muscles are a group of five muscles located in the region between the shoulder and elbow joints. They are divided into two distinct compartments of the arm. The anterior (flexor) compartment contains the biceps brachii, coracobrachialis and brachialis muscles. The posterior (extensor) compartment contains mainly the.
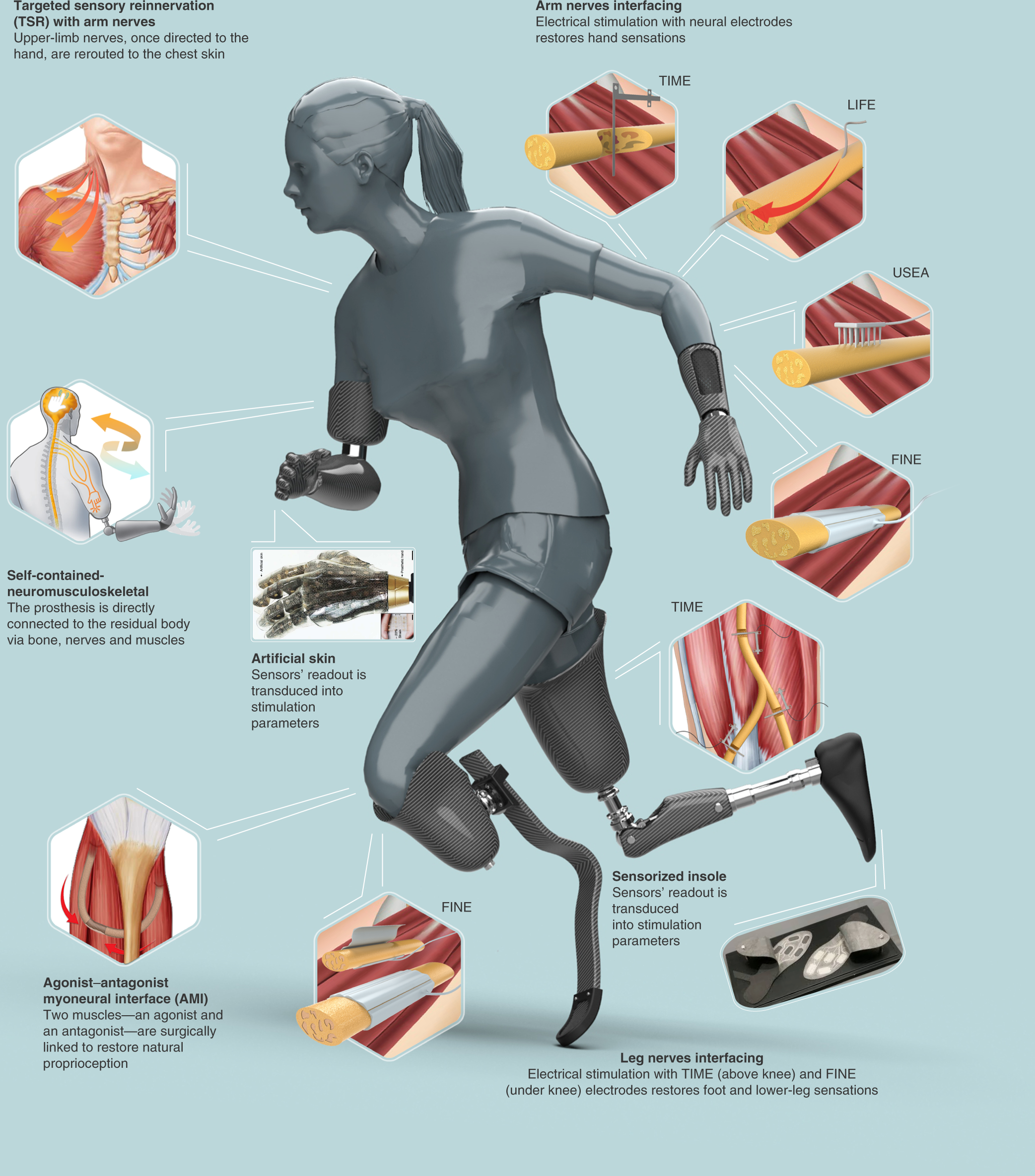
Agonist and antagonist muscle pairs An explanation of how the muscular-skeletal system functions during physical exercise Muscles are attached to bones by tendons.
Name Of Muscles In Upper Arm / Correctly Label The Following Antagonistic Muscles Of Chegg Com - Jul 20, 2017 · the "pecs" are popular:. Its name means "belly of the leg,"and its common name is the calf muscle. In that manner of speaking, this article will explain all the anatomical aspects of the muscles of the scapula, arm, forearm and hand.
A variety of arm ailments lead to signs and symptoms similar to those of a pulled muscle in the arm, so it's important to get an accurate diagnosis. Seek immediate medical care if you sustain a traumatic arm injury or if you experience any warning signs and symptoms, including: Arm or hand numbness or tingling. Severe or rapidly worsening pain.
Arm Muscles. There are various muscles in the arm which control various functions of this limb. Both, arm bones and muscles work in coordination with each other to makes various functions of the hand possible. Basically, the muscles of the arm assist the bones in executing the following functions. Bend or flex the elbow; Extend or straighten.
Such muscles causing opposing movements are called as antagonistic muscles. Example: The flexor muscles or the biceps of the upper arm bends the lower arm over the upper arm (flexes). Extension of the lower arm is caused by the extensor muscles or the triceps. Hence these two muscles are antagonistic or work in the opposite direction. 5.
Muscles contract to produce movement at joints, and the subsequent movements can be precisely described using this terminology. The terms used assume that the body begins in the anatomical position. Most movements have an opposite movement - also known as an antagonistic movement.
the deltoid muscle is the principle abductor of the arm but due to poor mechanical advantage it cannot initiate this action; it is assisted by the supraspinatus m. dorsal interosseous (hand) four muscles, each arising from two adjacent metacarpal shafts
A muscle with the opposite action of the prime mover is called an antagonist. Antagonists play two important roles in muscle function: (1) they maintain body or limb position, such as holding the arm out or standing erect; and (2) they control rapid movement, as in shadow boxing without landing a punch or the ability to check the motion of a limb.







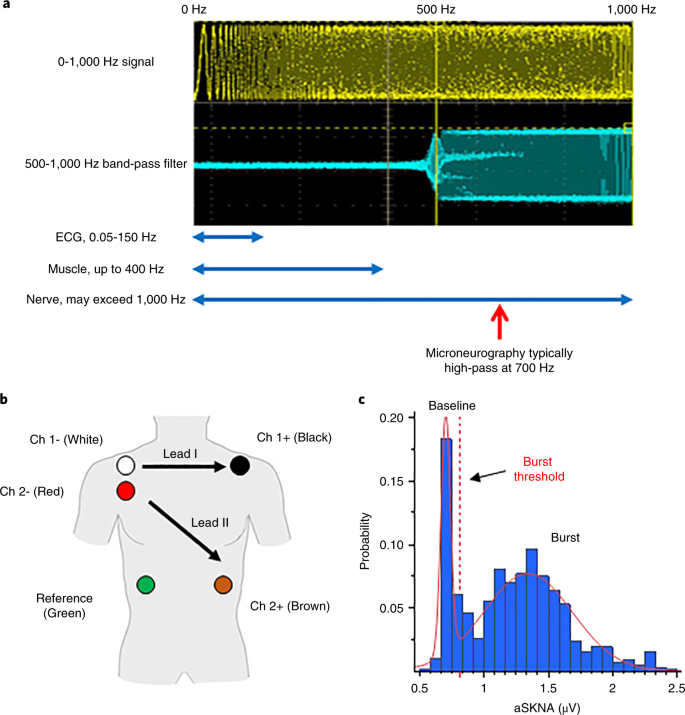






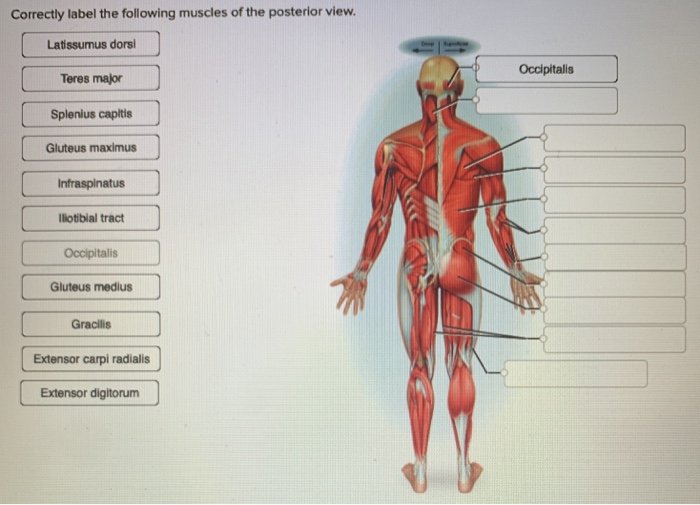





0 Response to "39 Correctly Label The Following Antagonistic Muscles Of The Upper Arm."
Post a Comment