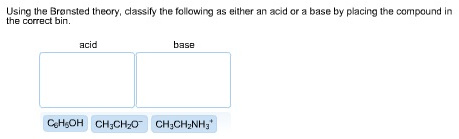
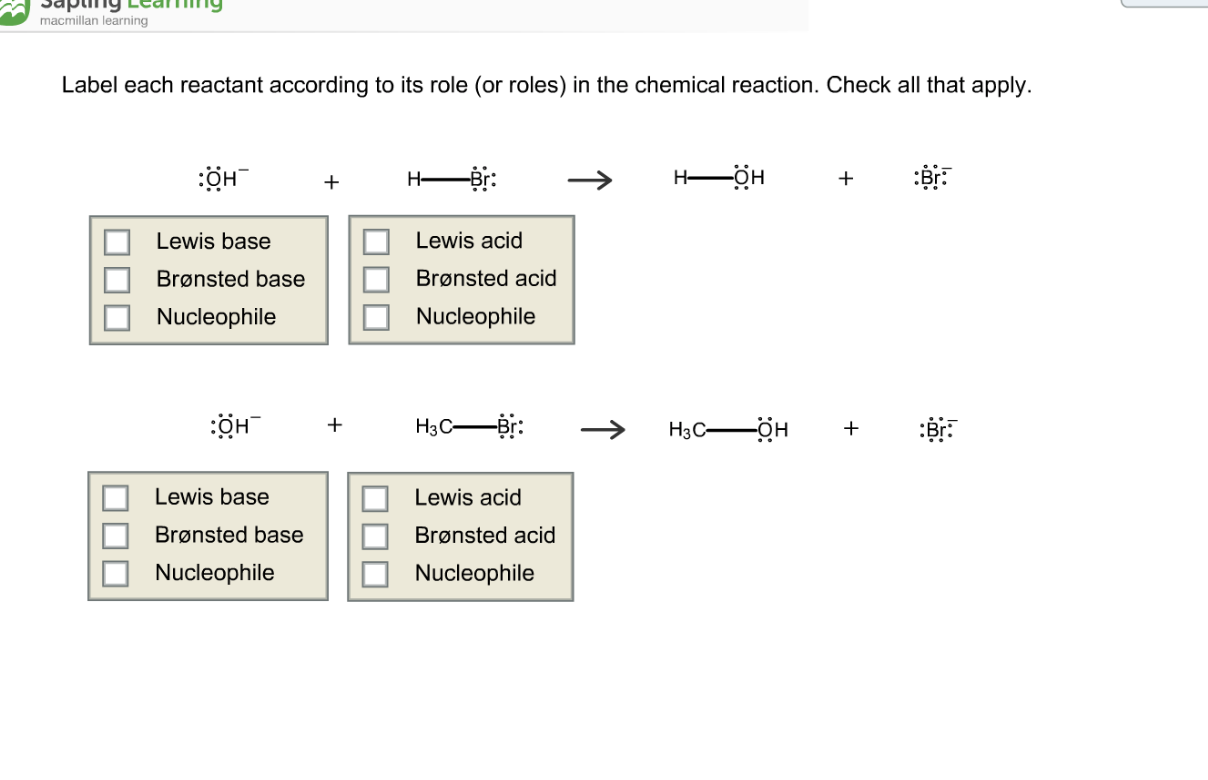
40 Label Each Reactant According To Its Role In The Chemical Reaction
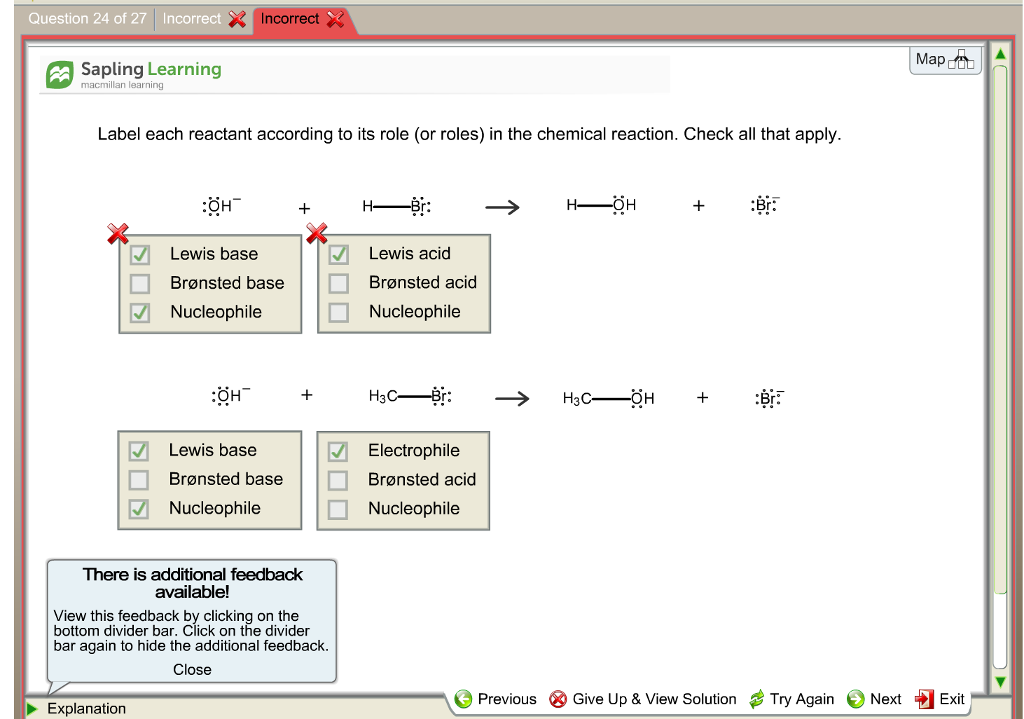
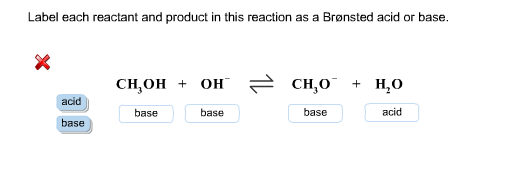
Approach 1 (The "Reactant Mole Ratio Method"): Find the limiting reactant by looking at the number of moles of each reactant. Determine the balanced chemical equation for the chemical reaction. Convert all given information into moles (most likely, through the use of molar mass as a conversion factor). View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply... Reaction 1: : 0H + H-Br: —Br: H-0-H + : Br: In Reaction 1, the reactant HO- is a: The reactant HBr is a: O Lewis base 0 Brønsted acid O Brønsted base Lewis acid Reaction 2: 10 -H + H3C- Br.
This is the comparison between the coefficients in front of the chemical formulas. If a formula lacks a coefficient, it is the same as saying there is 1 mole of that species. Mole ratios are used to predict how much product a reaction forms or to determine how much reactant is needed to make a set amount of product.

Label each reactant according to its role in the chemical reaction
Optimization of a chemical reaction is a complex, multidimensional challenge that requires experts to evaluate various reaction parameters, such as substrate, catalyst, reagent, additive, solvent. 8) role (or in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply. Label each reactant according to its role Br. HH QH Lewis acid Lewis base Bronsted base Bronsted acid H3C OH H3C Br OH Lewis base Lewis acid Bronsted base Bronsted acid For the following reaction, indicate which reactant is the Lewis acid and which is the Lewis base CH3cool is the Lewis acid CH3Cocl is the Lewis base FeCl3 is the. Here, the chemical system refers to the set of all N phases p i (i = 1, 2,., N) that can be produced from a designated set of chemical elements. Each reactant/product node on the graph is.
Label each reactant according to its role in the chemical reaction. Reactants to Products. A chemical equation is like a recipe for a reaction so it displays all the ingredients or terms of a chemical reaction. It includes the elements, molecules, or ions in the reactants and in the products as well as their states, and the proportion for how much of each particle is create relative to one another, through the stoichiometric coefficient. Question: Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply. This problem has been solved! See the. Problem. : Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction.Check all that apply. FREE Expert Solution. Based on the Bronsted-Lowry definition: Bronsted-Lowry acid → proton (H +) donor. Bronsted-Lowry base → proton (H +) acceptor. Based on the Lewis definition: Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor. Transcribed image text: Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply Br. Lewis base Brønsted base.
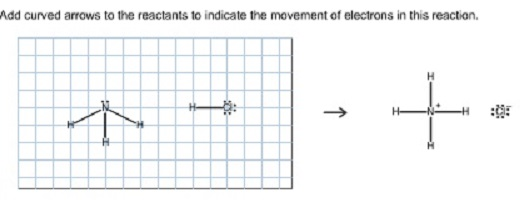
Question: Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply Add curved arrows to the reactants to indicate. A chemical imbalance in the brain is said to occur when the brain has either excessive or insufficient chemicals, called neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are natural chemicals that help ease. Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, "biological machines" also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell. The entropy change in a chemical reaction is given by the sum of the entropies of the products minus the sum of the entropies of the reactants. As with other calculations related to balanced equations, the coefficients of each component must be taken into account in the entropy calculation (the n , and m , terms below are there to indicate that.
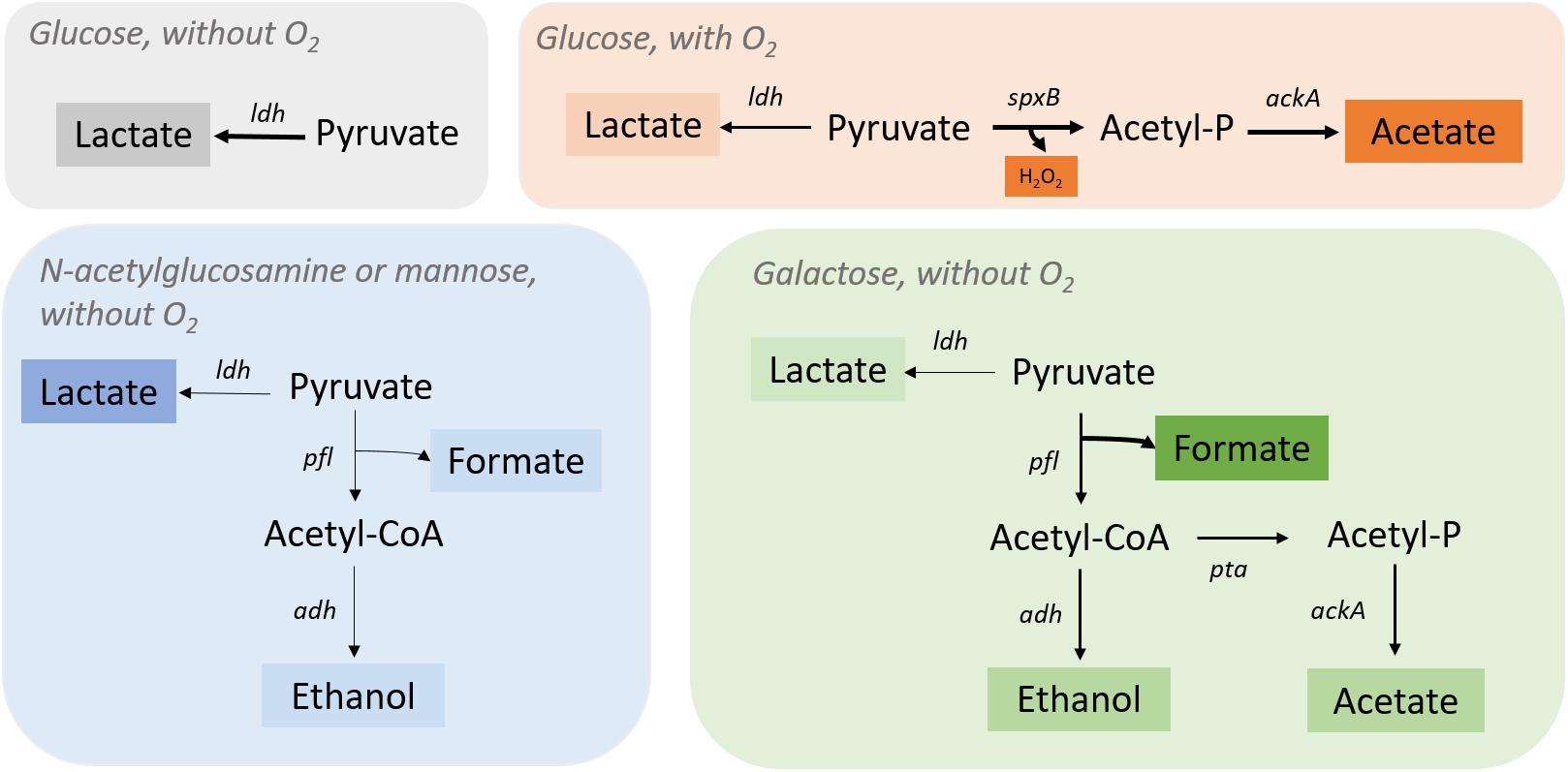
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C 6 H 12 O 6, into pyruvic acid, CH 3 COCOOH. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes.. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that does not require oxygen. Ozone (O3) is a highly reactive gas composed of three oxygen atoms. It is both a natural and a man-made product that occurs in the Earth's upper atmosphere. (the stratosphere) and lower atmosphere (the troposphere). Depending on where it is in the atmosphere, ozone affects life on Earth in either good or bad ways. elementary reaction. sum. N O 2 + C O → N O + C O 2. overall reaction. According to this mechanism, the overall reaction occurs in two steps, or elementary reactions. Summing steps 1 and 2 and canceling on both sides of the equation gives the overall balanced chemical equation for the reaction. Question: Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. Check all that. This problem has been solved! See the answer.
Transcribed image text: Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply. □ Lewis base 11 Lewis acid.
Optimization of a chemical reaction is a complex, multidimensional challenge that requires experts to evaluate various reaction parameters, such as substrate, catalyst, reagent, additive, solvent.
Transcribed image text: Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply. H Br: OH Br OH Lewis base Lewis.
Here, the chemical system refers to the set of all N phases p i (i = 1, 2,., N) that can be produced from a designated set of chemical elements. Each reactant/product node on the graph is.
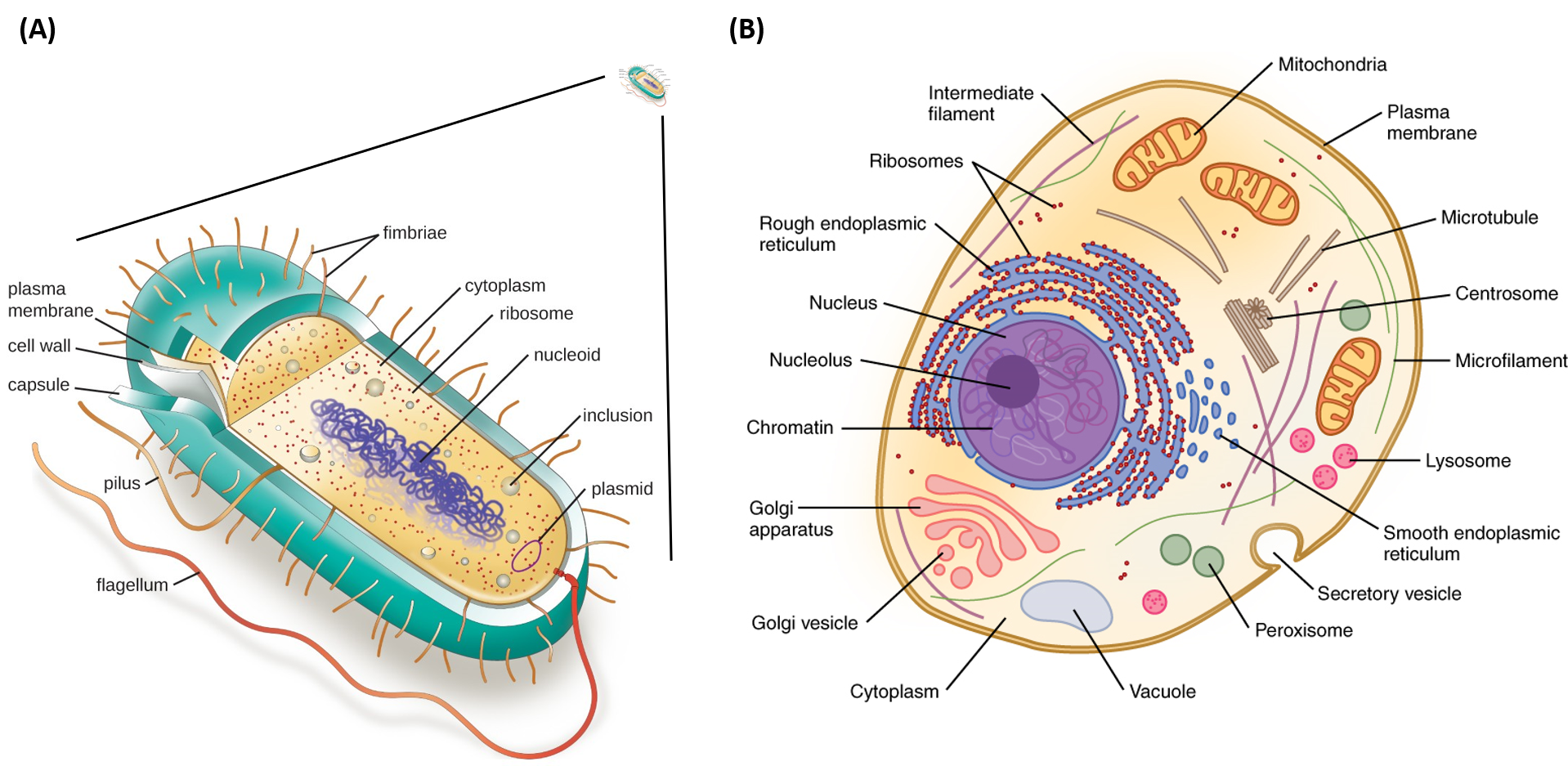
Enzymes bind with chemical reactants called substrates. There may be one or more substrates for each type of enzyme, depending on the particular chemical reaction. In some reactions, a single-reactant substrate is broken down into multiple products. In others, two substrates may come together to create one larger molecule.
Let's apply this method to the reaction of ammonia (NH 3) and molecular oxygen (O 2) to figure out the limiting reactant of the two. The reaction between NH 3 and O 2 yields NO (nitric oxide) and H 2 O (water). The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is: 4NH 3 + 5O 2 → 4NO + 6H 2 O.
Electrochemistry is the study of the relationship between electricity and chemical reactions. The oxidation-reduction reaction that occurs during an electrochemical process consists of two half-reactions, one representing the oxidation process and one the reduction process. The sum of the half-reactions gives the overall chemical reaction.
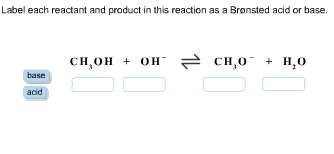
Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply. :OH H -Br: Lewis acid Lewis base Bronsted base Bronsted.
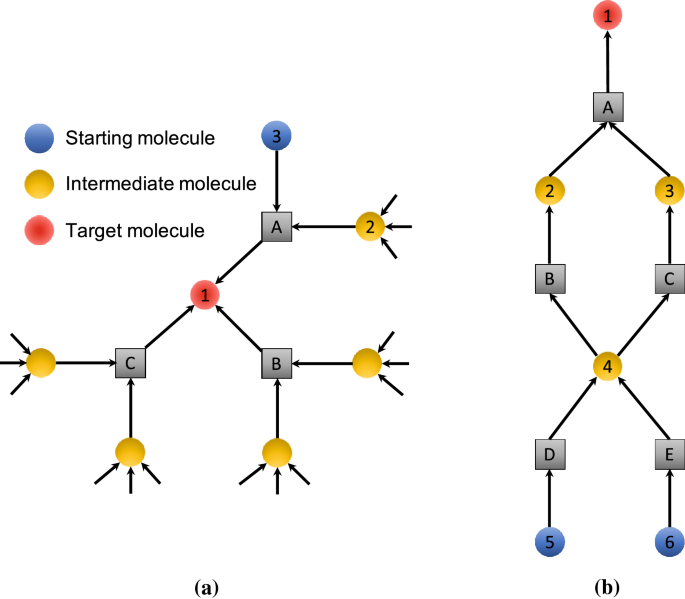
Reaction networks are essential tools for the description, illustration, and fundamental understanding of chemical processes in such diverse fields as catalysis 1,2,3,4, combustion 5,6,7.
Label each reactant according to it role or roles in the chemical reaction?. Chemical Reaction A is performed in a hot container, while Chemical Reaction B is performed in a cold container. Which of the answer. You can view more similar questions or ask a new question. Ask a New Question ...
12 Sep 2018 — Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. check all that apply. Get the answers you need, now!1 answer · 0 votes: Reaction no.1In a given reaction, the hydroxyl is acting as a Lewis base and the hydrogen bromide is acting as a Lewis acid giving the water and bromide.
According to this theory, no behavior is inherently deviant on its own but is made deviant based on the reaction of others. Being labeled as deviant can have long-term consequences for a person's.
Additional neutrons are also released that can initiate a chain reaction. When each atom splits, a tremendous amount of energy is released. Uranium and plutonium are most commonly used for fission reactions in nuclear power reactors because they are easy to initiate and control. The energy released by fission in these reactors heats water into.
The prospect of chemical reaction engineering using atmospheric pressure plasmas is an increasingly attractive one. The wide range of species known to be present, speed with which the plasma energy can be altered, ability to attain high energy conditions without the need for expensive high pressure and temperature equipment, and the sheer abundance and availability of the "raw materials.
Metabolic reactions, such as anabolic and catabolic processes, must proceed according to the demands of the cell. In order to maintain chemical equilibrium and meet the needs of the cell, some metabolic products inhibit the enzymes in the chemical pathway while some reactants activate them.
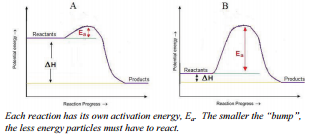
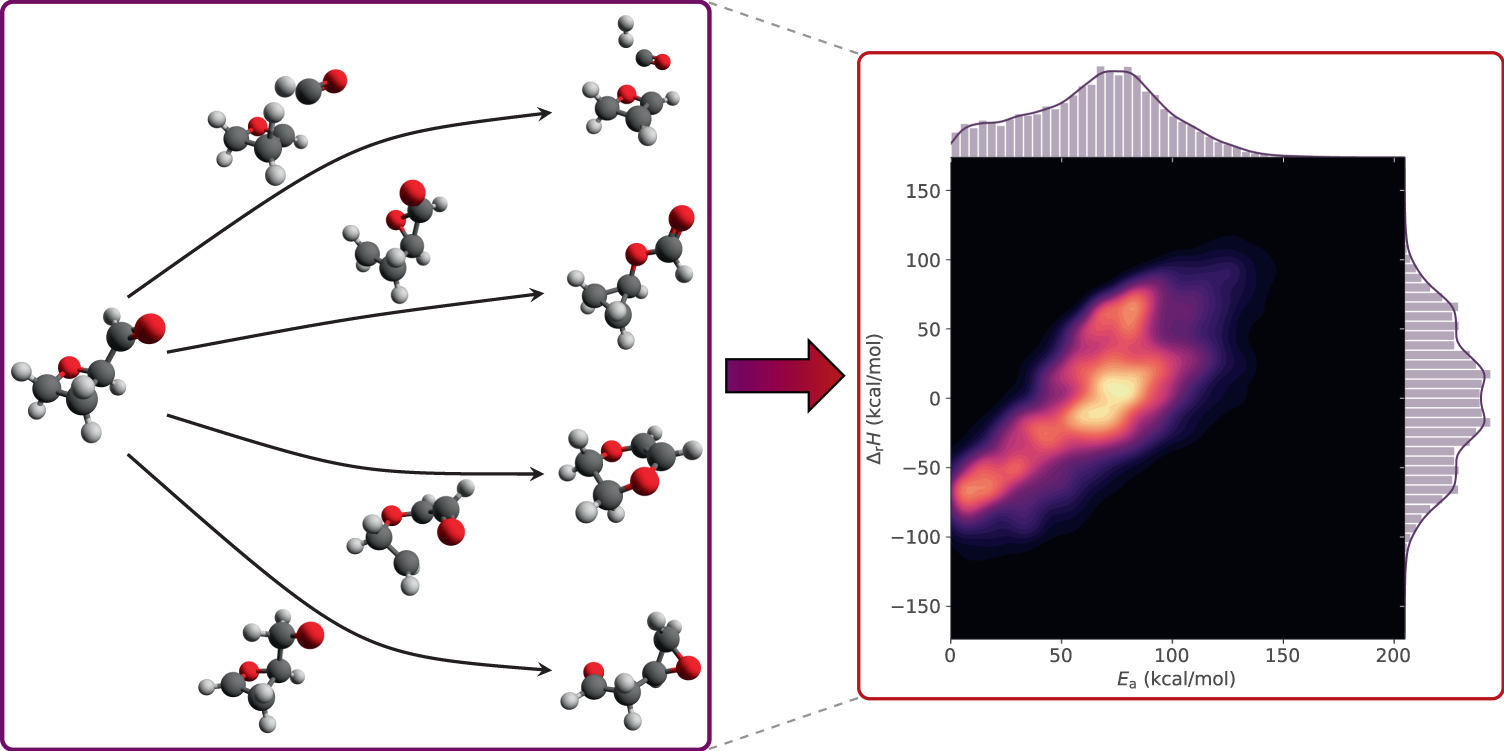
Activation Energy and the Arrhenius Equation. The minimum energy necessary to form a product during a collision between reactants is called the activation energ y (\(E_a\)). The kinetic energy of reactant molecules plays an important role in a reaction because the energy necessary to form a product is provided by a collision of a reactant molecule with another reactant molecule.
Store chemical groups below separately from one another, either in separate cabinets or in appropriate tubs or secondary containers. Clearly and legibly label each container and storage location to indicate its compatibility group. Flammable liquids. Compressed gases. Volatile poisons. Acids.
During the light reactions, ATP and NADPH are generated by two electron-transport chains, water is used and oxygen is produced. The chemical equation in the light reaction of photosynthesis can be reduced to: 2H 2 O + 2NADP+ + 3ADP + 3Pi → O 2 + 2NADPH + 3ATP. Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Light-independent Reaction
Transcribed image text: Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply. Reaction 1: :0 -H + H-Br: H-0 :0: -H : Br: In Reaction 1, the reactant HO- is a: The reactant HBr is a: Brønsted base Nucleophile Nucleophile Brønsted acid Lewis base Lewis acid Reaction 2: -H + H3C - Br: H3CO -H + :Br: In Reaction 2, the reactant HO- is a: The.
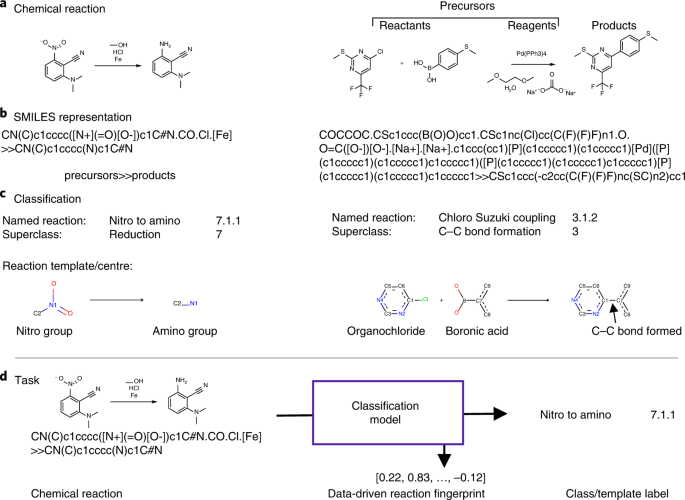
a-c, Two examples of chemical reactions (a,b) with associated classification labels and reaction templates describing the transformation (c). d , The task is to predict the reaction class or.
Neutralization Reaction. Neutralization is a type of chemical reaction in which a strong acid and strong base react with each other to form water and salt. Have you ever been unlucky enough to be.
Label each reactant according to its role. Asked by dena cali on february 6 2007. In a given reaction the hydroxyl is acting as a lewis base and the hydrogen bromide is acting as a lewis acid giving the water and bromide as a product after reacting with each other. Label each reactant according to its role or roles in the chemical reaction.
Complete each reaction Label each reactant or product as an acid or base List six weak acids in order of decreasing strength use your. Solution Classify each reaction first and then analyze the role of each species Reaction 318a is a Lewis acid-base dissociation Notice that a single …
8) role (or in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply. Label each reactant according to its role Br. HH QH Lewis acid Lewis base Bronsted base Bronsted acid H3C OH H3C Br OH Lewis base Lewis acid Bronsted base Bronsted acid For the following reaction, indicate which reactant is the Lewis acid and which is the Lewis base CH3cool is the Lewis acid CH3Cocl is the Lewis base FeCl3 is the.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply.
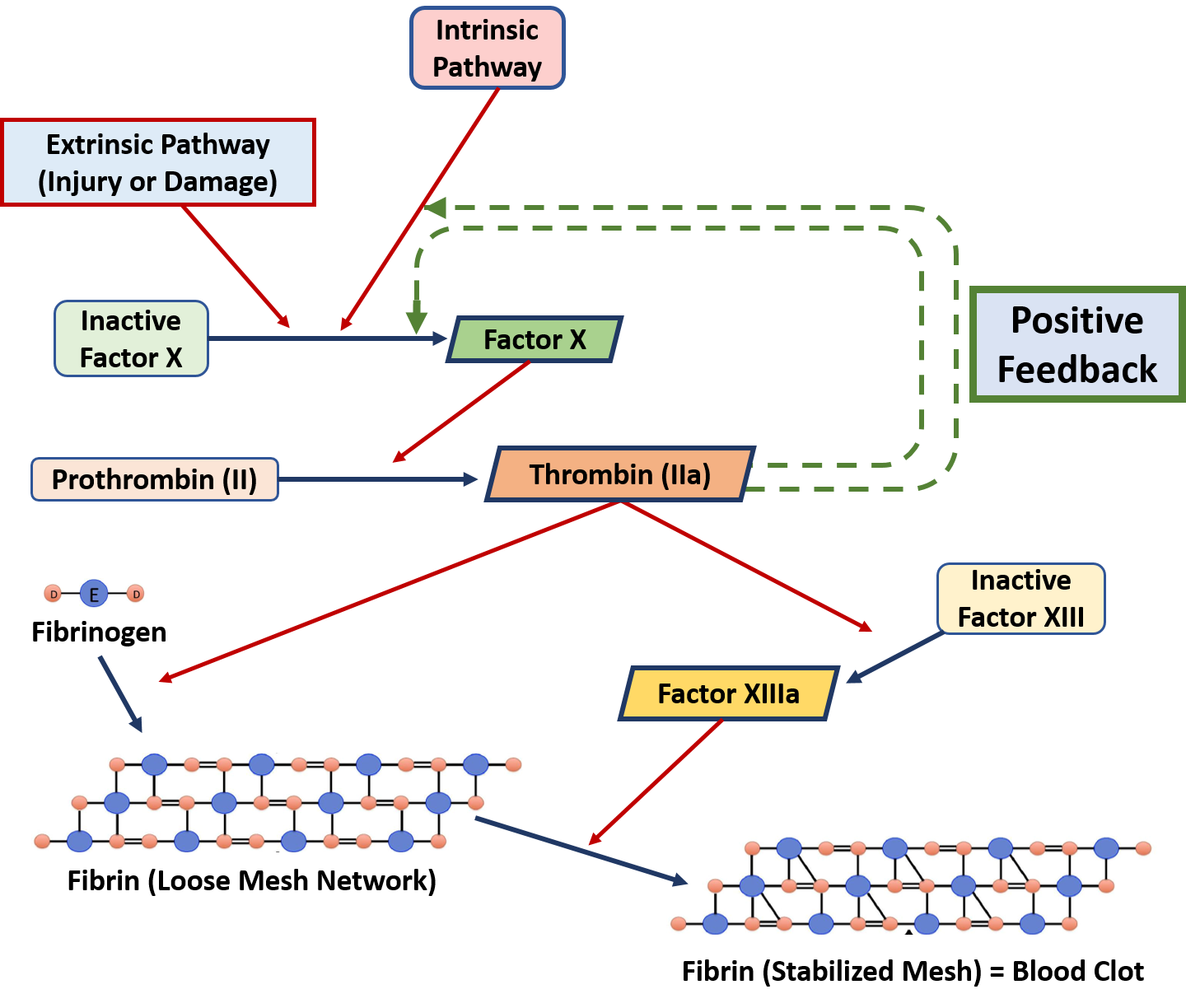
A redox reaction is a chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons and changes in oxidation number. Learn about redox reactions, and identify oxidizing and reducing agents, and explore.
Label each reactant according to its role (or roles) in the chemical reaction. Check all that apply. Complete the equations for the following equilibria and calculate Keq where the Keq expression includes [H2O].
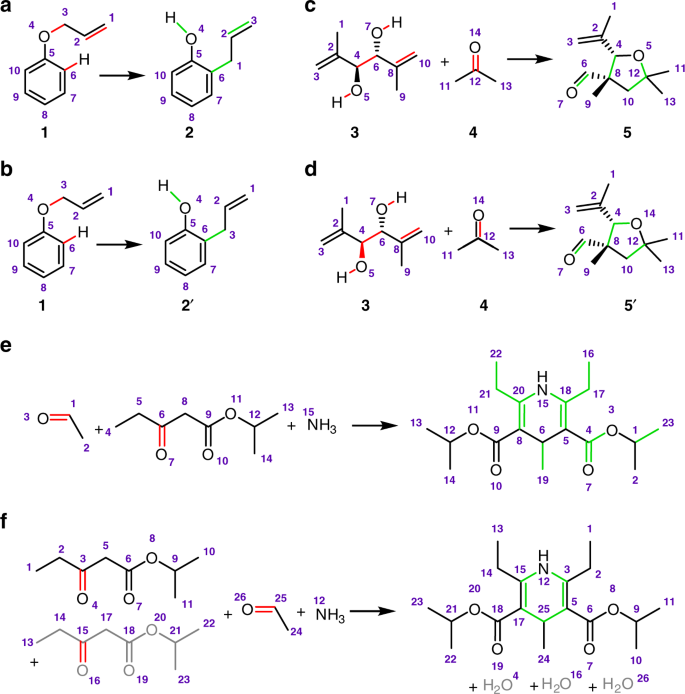
Chemical reactions describe how precursor molecules react and form product molecules. Figure 1 shows an example of a chemical reaction and a graphical overview of different chemical terms. The.
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles (neutrons or protons).The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or the absorption of energy.This difference in mass arises due to the difference in atomic binding energy between the nuclei before and.
Oxidative phosphorylation works by using energy-releasing chemical reactions to drive energy-requiring reactions.The two sets of reactions are said to be coupled.This means one cannot occur without the other. The chain of redox reactions driving the flow of electrons through the electron transport chain, from electron donors such as NADH to electron acceptors such as oxygen and hydrogen.
Enzymes (/ ˈ ɛ n z aɪ m z /) are proteins that act as biological catalysts (biocatalysts). Catalysts accelerate chemical reactions.The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products.Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life.














0 Response to "40 Label Each Reactant According To Its Role In The Chemical Reaction"
Post a Comment