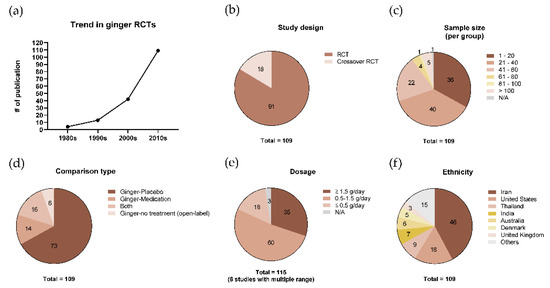
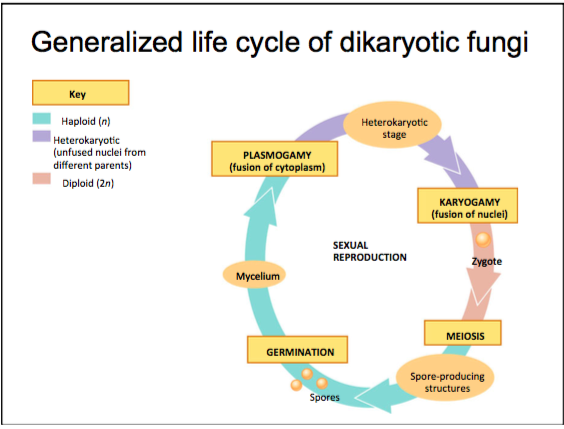
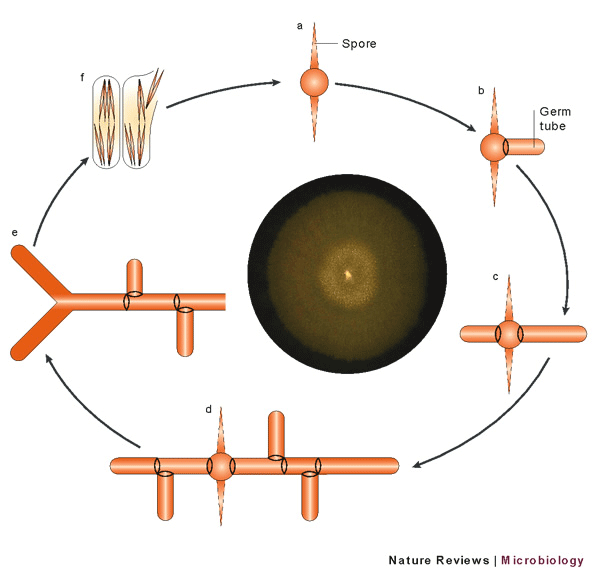
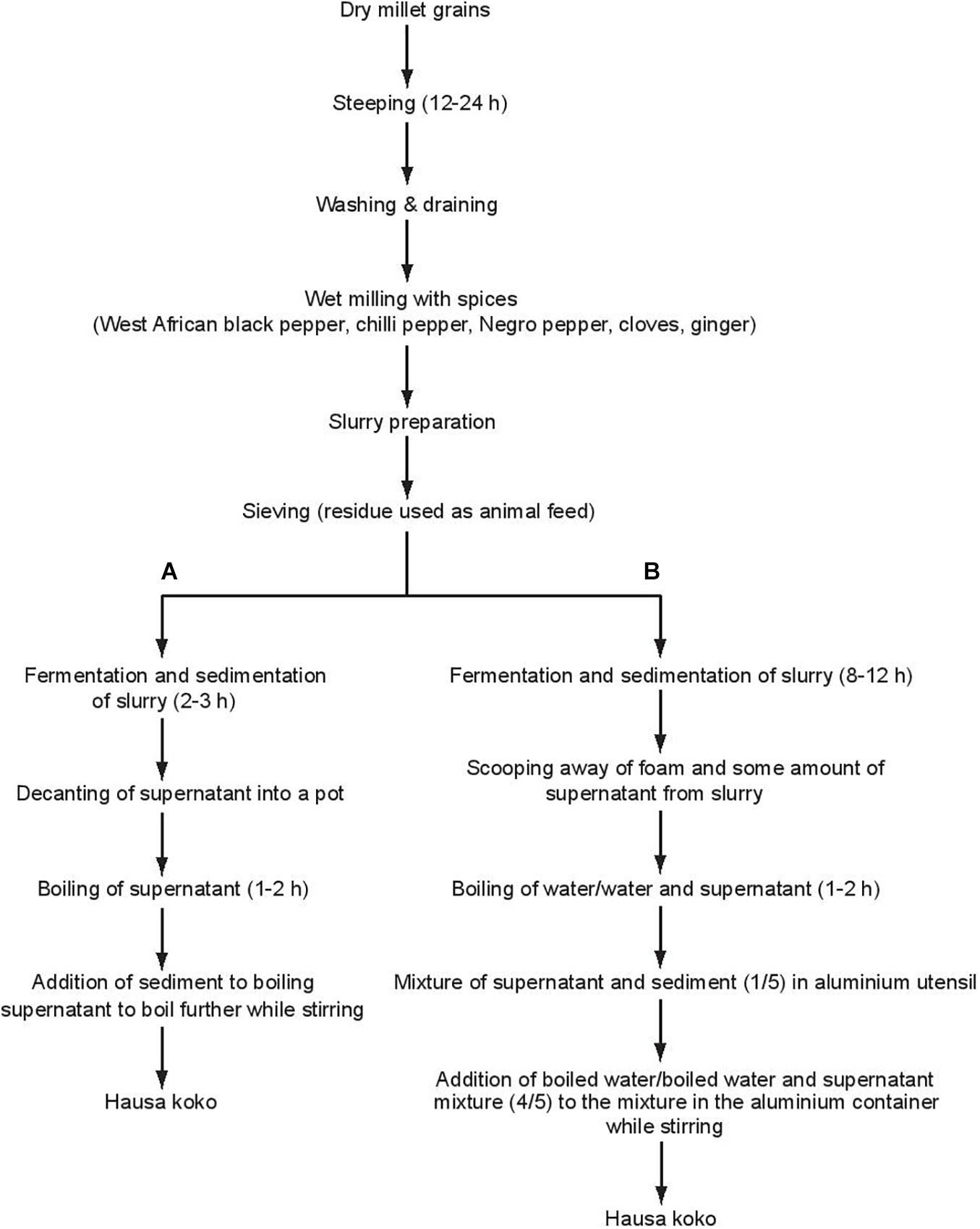
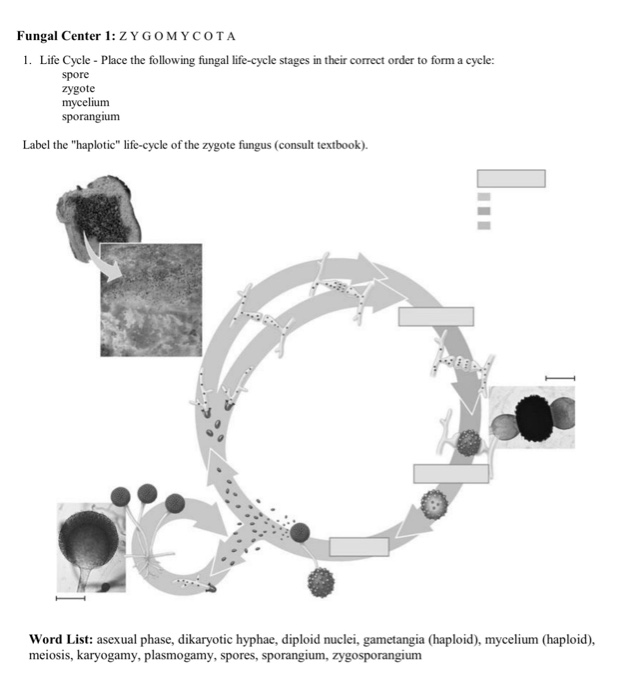
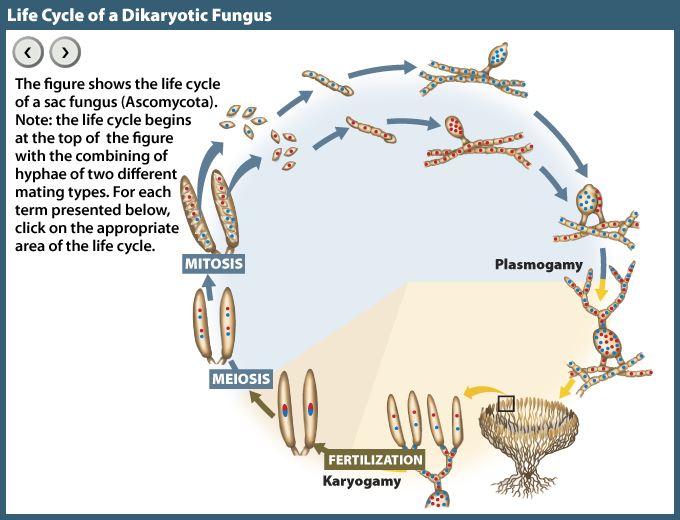
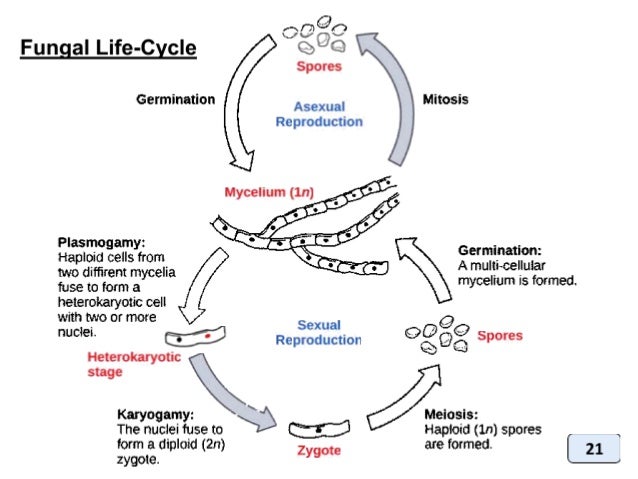
40 Label The Features Of A General Fungal Life Cycle With The Correct Descriptions.
The life cycle of Bryophytes is like all the other land plants (embryophytes) with alternation of generations. A haploid gametophyte cell contains a fixed number of unpaired chromosomes. It gives rise to diploid sporophyte, which, however, contains twice the number of paired chromosomes. Diploid zygotes formed by the fusion of haploid sperm and. Mycology Myco- = fungus -ology= study of General Characteristics of Fungi: Eukaryotic Decomposers - the best recyclers around No chlorophyll - non-photosynthetic Most multicellular (hyphae) - some unicellular (yeast) Non-motile Cell walls made of chitin (kite-in) instead of cellulose like that of a plant Are more related to animals than the plant kingdom Lack true…
The life cycle of higher plants is dominated by the sporophyte stage, with the gametophyte borne on the sporophyte. In ferns, the gametophyte is free-living and very distinct in structure from the diploid sporophyte. In bryophytes, such as mosses, the haploid gametophyte is more developed than the sporophyte.
Label the features of a general fungal life cycle with the correct descriptions.
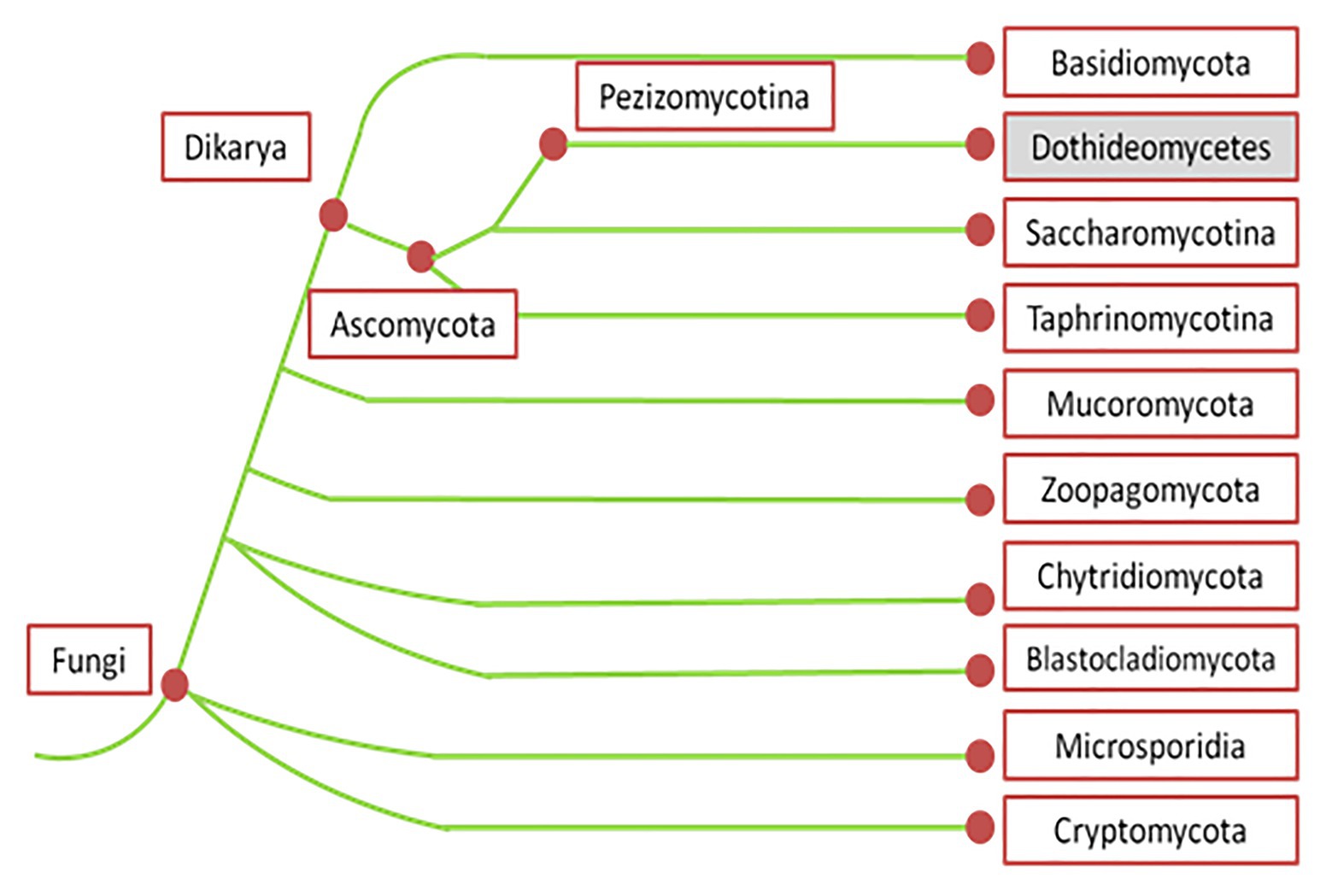
Label (B) in the generalized fungal life cycle. Spore producing structure. Label (A) in the generalized fungal life cycle.. Label (M) in the generalized fungal life cycle. Moulds, yeasts. Two types of fungi that reproduce asexually. Karyogamy.... General term for a fungal infection. Hyphae. Fungus - Fungus - Lichens: A lichen is an association between one or two fungus species and an alga or cyanobacterium (blue-green alga) that results in a form distinct from the symbionts. Although lichens appear to be single plantlike organisms, under a microscope the associations are seen to consist of millions of cells of algae (called the phycobiont) woven into a matrix formed of the. Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. Label the following diagram to describe the evolutionary history of the phyla within the kingdom fungi. Animals Myxomycota Glomeromycota Zygomycota MiciopordtaChytibomyozta Ascomycota Basidiomycota common ancesior.
Label the features of a general fungal life cycle with the correct descriptions.. All fungi begin their life cycle in this stage. This is the first stage in the life cycle of a fungus. In the beginning, all spores are haploid which means that they have only a single copy of their entire genetic material. These spores migrate far distances through air by grabbing on to other organisms on the way. An estimated 25 percent of all marine life, including over 4,000 species of fish, are dependent on coral reefs at some point in their life cycle. Approximately half a billion people globally depend on coral reef ecosystems for food, coastal protection, and income from tourism and fisheries. General Mycology 427R/527R. Multiple Choice: Circle all the correct answers. There may be more than one correct answer. (0.5 points for each correct answer) 1. Fungi are different from plants because a. they lack organelles b. they are unable to fix CO 2 c. they rely on absorptive nutrition This form of sexual reproduction in fungi is called conjugation (although it differs markedly from conjugation in bacteria and protists), giving rise to the name "conjugated fungi." Figure 2. Zygomycetes have asexual and asexual life cycles. In the sexual life cycle, plus and minus mating types conjugate to form a zygosporangium. Figure 3.
Bacteriophage Structure. The bacteriophage consists of a polyhedral head, a short collar and a helical tail. Head- The head consists of 2000 capsomeres with double-stranded DNA enclosed within. Tail- The tail consists of an inner hollow tube which is surrounded by a contractile sheath with 24 annular rings. The distal end consists of a basal. Fungus - Fungus - Lichens: A lichen is an association between one or two fungus species and an alga or cyanobacterium (blue-green alga) that results in a form distinct from the symbionts. Although lichens appear to be single plantlike organisms, under a microscope the associations are seen to consist of millions of cells of algae (called the phycobiont) woven into a matrix formed of the. Put the following steps of Koch's postulates in order: a. The suspected infectious agent must be isolated and grown outside the host. b. The suspected infectious agent causes the disease when it is introduced to a healthy, experimental host. c. The suspected infectious agent must be found in every case of the disease. Fungi: Reproduction & Life-cycle The morphology of the mycelium, mode of spore formation and fruiting bodies form the basis for the division of the kingdom into various classes. Reproduction in fungi can take place by vegetative means - fragmentation, fission and budding. Asexual
Place the stages of the sexual life cycle of a basidiomycete in the order in which they occur, beginning at the top with the fusion of haploid hyphae.. Select all of the following that are characteristics of fungi.-store carbohydrates as glycogen... Match each label to its correct fungal phylum.-Chytridiomycota: swimming spores 1. Eukaryotic. 2. Heterotrophic via absorption (will secrete enzymes for digestion; nutrients absorbed through cell wall & cell membrane) 3. Have tubular cells called hyphae. 4. Cell walls composed of chitin. Click again to see term 👆. Label the features of a general fungal life cycle with the correct descriptions. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. The outside of the autoclave has indicators so the user can ensure the equipment is working properly. Label the features of a general fungal life cycle with the correct descriptions. Autoclave An Overview Sciencedirect Topics Interesterification An Overview Sciencedirect Topics Journaltocs Quantifying Methane And Methanol Metabolism Of
Label (B) in the generalized fungal life cycle. Spore producing structure. Label (A) in the generalized fungal life cycle.. Label (M) in the generalized fungal life cycle. Moulds, yeasts. Two types of fungi that reproduce asexually. Karyogamy.... General term for a fungal infection. Hyphae.
Indicate the general characteristics of ascomycetes. Fill in the boxes on the Ascomycete life cycle below with the correct terms: Lab Study C: Club Fungi - Phylum Basidiomycota Caprinus Label the parts of the basidiocarp shown to the right.
Drag the symptoms and mode of transmission to the correct zygomycoses. A. Rhinocerebral Zygomycota. Label the photograph with the type of fungal spore. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Diagram question. Label the features of a general fungal life cycle with the correct descriptions.
The housefly (Musca domestica) is the most common of all domestic flies. The body of housefly is distinguished into head, thorax and abdomen. The head is hemispherical in shape and bears two lateral compound eyes. Three simple eyes (ocelli) are also present on dorsal side of the head. Two small and mobile antennae are present in the head region.
The rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in Earth’s crust. Grades. 5 - 8. Subjects. Chemistry, Earth Science, Geology. Image. Reunion Island Volcano. Active volcanoes like this one on Reunion Island—east of Madagascar, in the Indian Ocean—forms a type of igneous rock. Extrusive, or volcanic.
Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. Label the following diagram to describe the evolutionary history of the phyla within the kingdom fungi. Animals Myxomycota Glomeromycota Zygomycota MiciopordtaChytibomyozta Ascomycota Basidiomycota common ancesior.
The fungi comprise a diverse group of organisms that are heterotrophic and typically saprozoic. In addition to the well-known macroscopic fungi (such as mushrooms and molds), many unicellular yeasts and spores of macroscopic fungi are microscopic. For this reason, fungi are included within the field of microbiology.
In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of ascomycetes, explained with the help of a suitable diagram. Despite their diversity in many features, the Ascomycetes possess certain common unifying characteristics, namely, the somatic body composed of a loose, indefinite mass of septate mycelium; the mode of asexrual reproduction; and sexual reproduction. In general, they have two.
The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their club-shaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha.The basidia, which are the reproductive organs of these fungi, are often contained within the familiar mushroom, commonly seen in fields after rain, on the supermarket shelves, and growing.
Polyphyletic, unrelated fungi that reproduce without a sexual cycle are placed for convenience in a sixth group called a "form phylum." Not all mycologists agree with this scheme. Rapid advances in molecular biology and the sequencing of 18S rRNA (a part of RNA) continue to show new and different relationships between the various categories.
Fungi are eukaryotic, non-vascular, non-motile and heterotrophic organisms. They may be unicellular or filamentous. They reproduce by means of spores. Fungi exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation. Fungi lack chlorophyll and hence cannot perform photosynthesis. Fungi store their food in the form of starch.
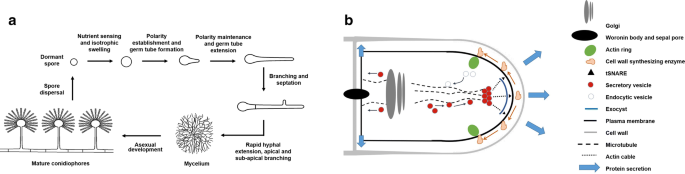
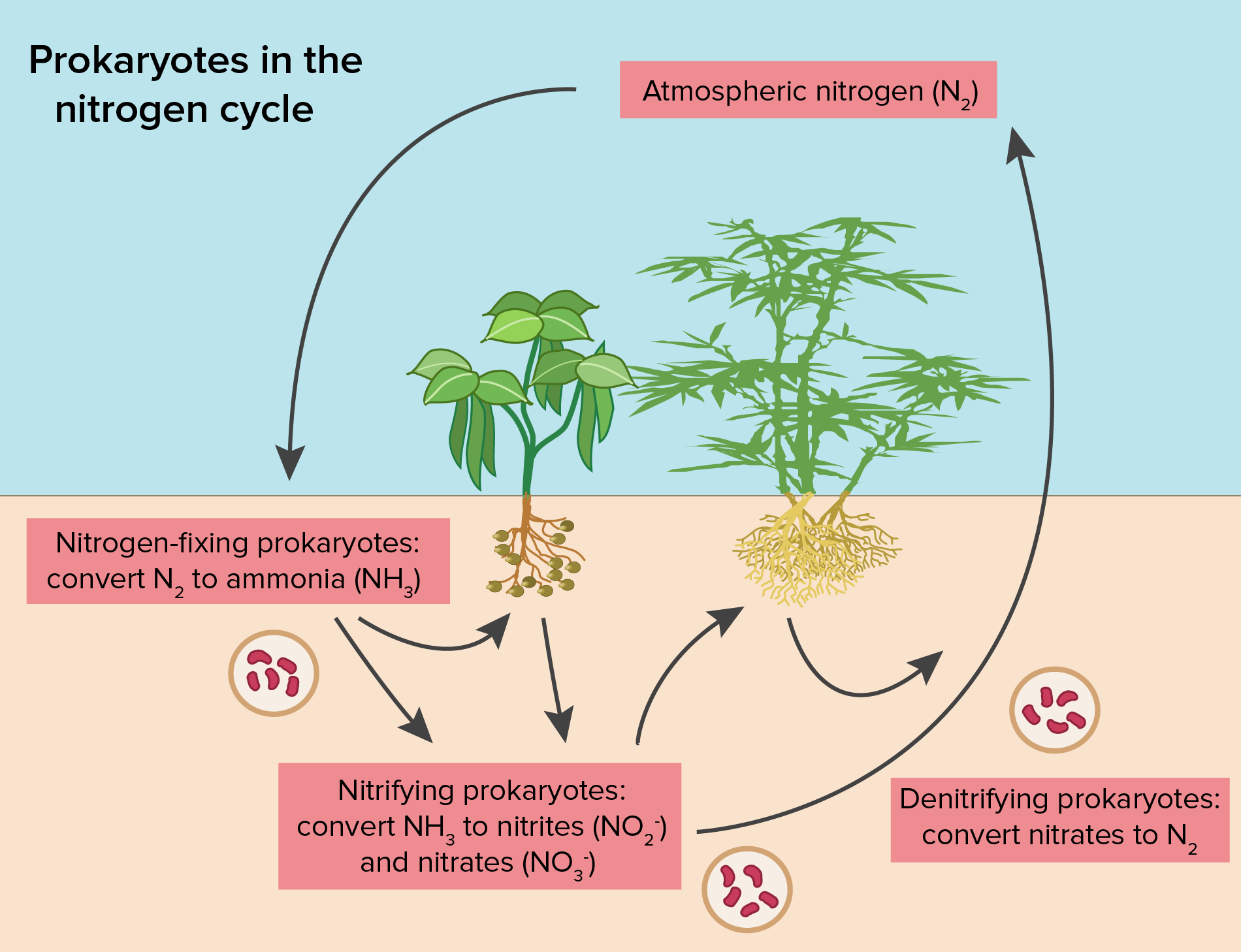
Fungus - Fungus - Life cycle of fungi: In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus, a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion, and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote (the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells). Meiosis (reduction division) restores the haploid number of chromosomes and.
Correct Visualize It! Figure 1 You will identify the steps of the bacteriophage life cycle. Part A Viruses are composed of both protein and lipid. Viruses are composed of protein only. Viruses have no protein structure. Viruses lack genetic material. Viruses lack cytoplasm and organelles. complex True False
Label the features of a general fungal life cycle with the correct descriptions. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Left side starting at the top:
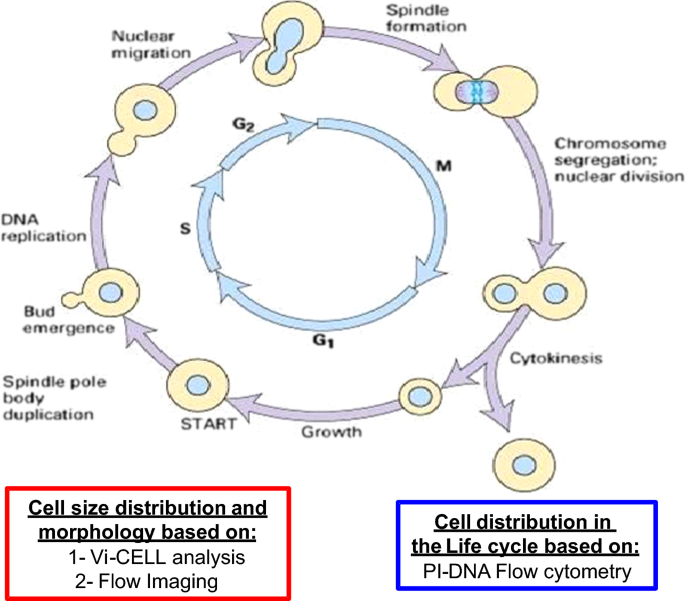
The duration of the cycle, however, varies from organism to organism and cell to cell. A typical eukaryotic cell cycle is divided into two main phases:-Interphase. Also known as the resting phase of the cell cycle; interphase is the time during which the cell prepares for division by undergoing both cell growth and DNA replication.
Mycelia in the Life Cycle of Fungi. The life cycle of most fungi starts with the production of spores that germinate to form hyphal threads. Given that most of these fungi are sessile, apical extension/growth of the hyphae ultimately results in the formation and growth of the mycelia (mycelial network).
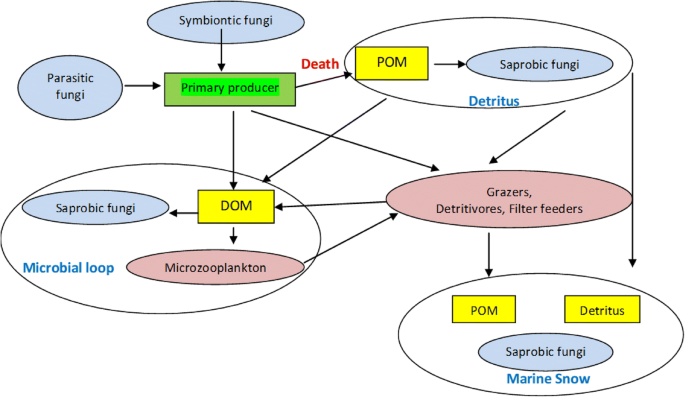
Fungus - Fungus - Ecology of fungi: Relatively little is known of the effects of the environment on the distribution of fungi that utilize dead organic material as food (i.e., saprobic fungi; see above Nutrition). The availability of organic food is certainly one of the factors controlling such distribution. A great number of fungi appear able to utilize most types of organic materials, such.

















nice...Cycling Deals
ReplyDelete