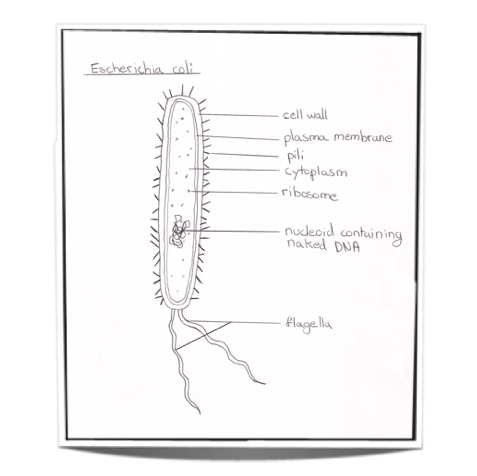
34 Label The Structures Of This Prokaryotic Cell.
Can you label the structures of a prokaryotic cell? Can you label the structures of a prokaryotic cell? Answers: 1 Get Other questions on the subject: Biology. Biology, 21.06.2019 15:30, tylerj1133. 15 points come and ! which characteristic describes all bacteria?. ADVERTISEMENTS: Some of the major cell organs involved in ultra-structure of prokaryotic cell are as follows: 1. Cell envelope 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleoid 4. Appendages. Prokaryotic cells are the simplest of most primitive cells. The records of microfossils suggest that they have evolved 2.5 billion years ago and existed as the only organisms on earth […]
A long, hairlike structure that grows out of a cell and enables the cell to move. nucleoid A non-membrane-bounded region in a prokaryotic cell where the DNA is concentrated.
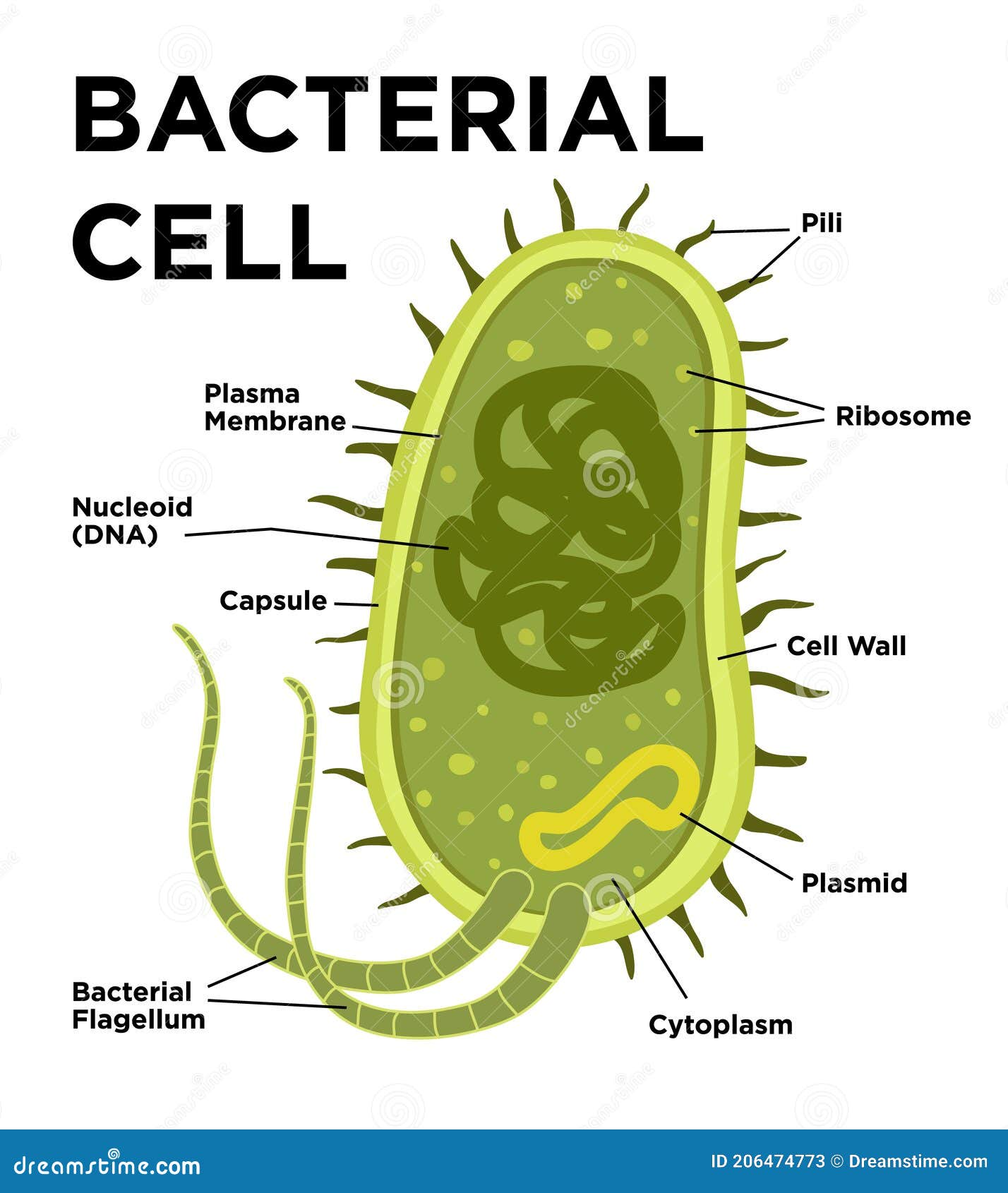
Label the structures of this prokaryotic cell.
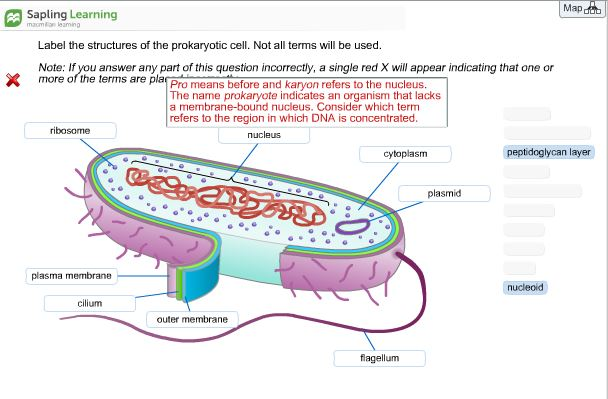
Science. Biology. Biology questions and answers. s and Due Dates > Chi Intro to Biochemistry Label the structures of the prokaryotic cell. Not all terms will be used. Answer Bank peptidoglycanlayer cytoplasm ribosome plasmid flagellum plasma membrane outer membrane wbout us. Question: s and Due Dates > Chi Intro to Biochemistry Label the. and eukaryotic cells 1. Create a Venn diagram or concept map that clearly distinguishes bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic cells in terms of their genome organization, organelles, cell envelopes, ribosome size and component molecules, and cytoskeleton. 2. Determine the type of microbe when given a description of a newly discovered microbe. 56 Related For Prokaryotic Cell Diagram With Labels Well Labelled Diagram Of Human Digestive System | Diagram Labels {Label Gallery} Get some ideas to make labels for bottles, jars, packages, products, boxes or classroom activities for free.
Label the structures of this prokaryotic cell.. The cell (from Latin cellula 'small room') is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known organisms.A cell is the smallest unit of life, and therefore, cells are often described as the "building blocks of life". Cell biology (also called cellular biology or cytology) is the study of cells.. Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many. Nov 13, 2015 · It is a gel-like matrix composed of water, enzymes, nutrients, wastes, and gases and contains cell structures such as ribosomes, a chromosome, and plasmids. The cell envelope encases the cytoplasm and all its components. Unlike the eukaryotic (true) cells, bacteria do not have a membrane enclosed nucleus. Definition of Prokaryotic Cell. Unicellular organisms of the domains Archaea and Bacteria are classified as prokaryotes. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bounded cellular organelles like lysosomes, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi complex, and endoplasmic reticulum.. Prokaryotic microorganisms are found to be more primitive than eukaryotes which are originated from Prokaryotes. Science. Biology. Biology questions and answers. s and Due Dates > Chi Intro to Biochemistry Label the structures of the prokaryotic cell. Not all terms will be used. Answer Bank peptidoglycanlayer cytoplasm ribosome plasmid flagellum plasma membrane outer membrane wbout us. Question: s and Due Dates > Chi Intro to Biochemistry Label the.
Above provided image is a rough figure of the prokaryotic cell, from the figure, A - Ribosome : a complex of RNA and protein, and it is found free in the… View the full answer Transcribed image text : Question 10 of 22 > Attempt 6 Label the structures of the prokaryotic cell. Science Biology library Structure of a cell Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Cell size. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells. This is the currently selected item. Intro to eukaryotic cells. Practice: Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Plasma membrane and cytoplasm. Nucleus and ribosomes. Practice. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea. All prokaryotes have plasma membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, a cell wall, DNA, and lack membrane-bound organelles. Many also have polysaccharide capsules. Prokaryotic cells range in diameter from 0.1-5.0 µm. Like a prokaryotic cell, a eukaryotic cell has a plasma. The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1 – How Is a Cell Like a Factory? Part of factory Cell organelle Function Control.
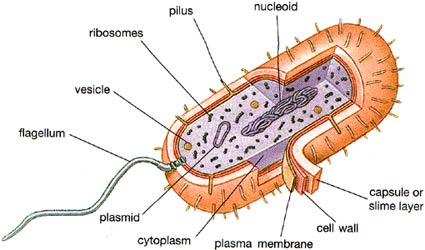
This is an online quiz called Label the Prokaryotic cell There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Your Skills & Rank Key points: Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms belonging to the domains Bacteria and Archaea. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, have no nucleus, and lack organelles. All prokaryotic cells are encased by a cell wall. Many also have a capsule or slime layer made of polysaccharide. Label all the organelles and structures present in a typical prokaryotic cell. Carmen Newkirk 2. Complete the following table by listing various organelles and structures commonly found in a Prokaryotic cell and describe their functions in 1-2 sentences. •Their internal structures –No complex, membrane-bound organelles. 4.1 Prokaryotic Form and Function. Structures in bacterial cells Structures common to all bacterial cells. prokaryotic cell biology in the last decade has been discovery of the prokaryotic cytoskeleton. Up until recently, thought to be a feature only of eukaryotic cells.
Label the structures of the prokaryotic cell. The prokaryotic cell prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack organelles or other internal membrane bound structures. If you answer any part of this question incorrectly a single red x will appear indicating that one or more of the terms are pro means before and karyon refers to the nucleus.
The cell is the basic functional and structural unit of life. Many organisms are single-celled like amoeba and bacteria. Rest, are multi-celled with billions and trillions of cells that make up an animal body. Cells are covered in a protective membrane. At the center of the cell is the cell nucleus which contains the genetic code (DNA).
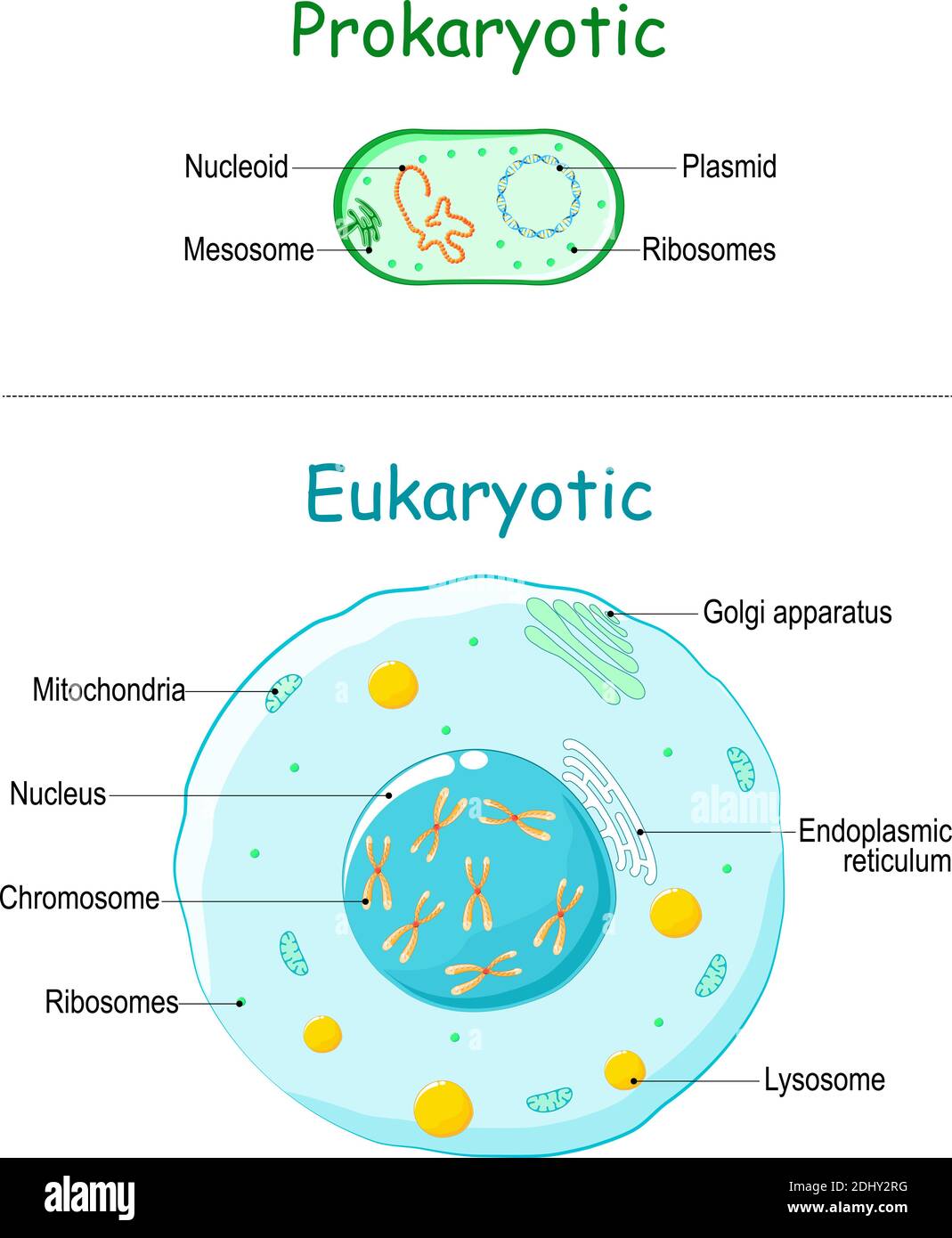
However, prokaryotes differ from eukaryotic cells in several ways. A prokaryote is a simple, mostly single-celled (unicellular) organism that lacks a nucleus, or any other membrane-bound organelle. We will shortly come to see that this is significantly different in eukaryotes. Prokaryotic DNA is in the cell's central part: the nucleoid ().
Jun 07, 2019 · An organelle is a tiny cellular structure that performs specific functions within a cell.Organelles are embedded within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.In the more complex eukaryotic cells, organelles are often enclosed by their own membrane.Analogous to the body's internal organs, organelles are specialized and perform valuable functions.
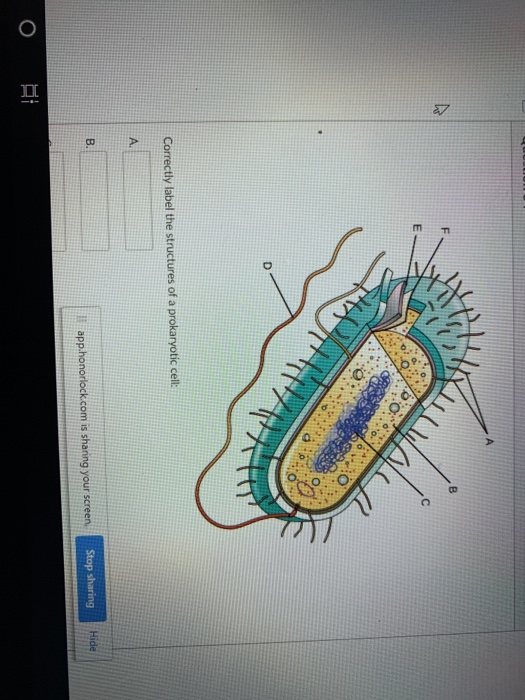
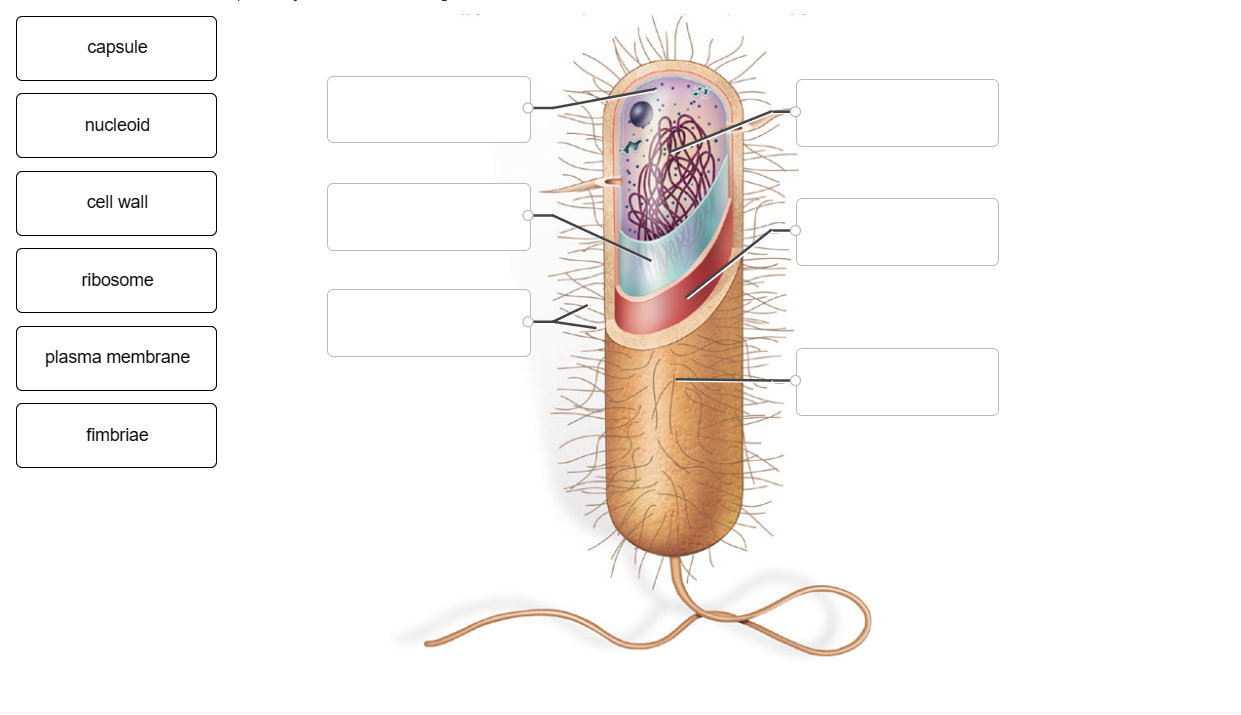
The structures of the prokaryotic cell can be labeled as follows:. The structure labeled a is the pilus (plural, pili); The structure labeled b is the cytoplasm; The structure labeled c is the plasma membrane; The structure labeled d is the cell wall; The structure labeled e is the capsule; The structure labeled f is the flagella (singular, flagellum); The structure labeled g is the nucleoid
Prokaryotic Cell - Summary. Prokaryotic cells are the unicellular cells that lack a well-defined nucleus, i.e. genetic material is not enclosed by a nuclear membrane. These cells are very minute in size 0.1 to 5.0 μ m. Common prokaryotic cell is a bacterial cell. Our body has over 100 trillion bacterial cells.
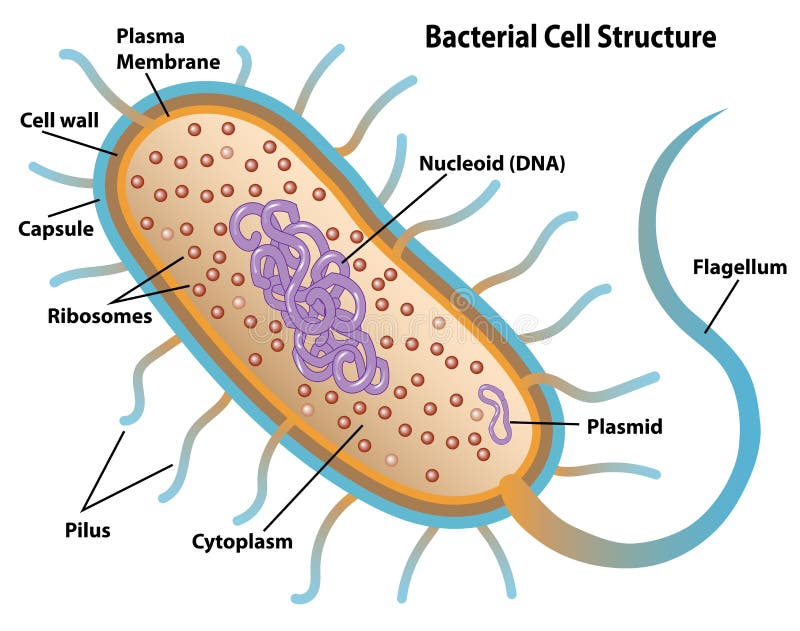
Bacterial Cell Anatomy and Internal Structure. Jack0m/Getty Images. Prokaryotic cells are not as complex as eukaryotic cells.They have no true nucleus as the DNA is not contained within a membrane or separated from the rest of the cell, but is coiled up in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid.. Prokaryotic organisms have varying cell shapes.
Related For Prokaryotic Cell Diagram With Labels Well Labelled Diagram Of Human Digestive System | Diagram Labels {Label Gallery} Get some ideas to make labels for bottles, jars, packages, products, boxes or classroom activities for free.
Answers. The structures of the prokaryotic cell can be labeled as follows:The structure labeled a is the pilus (plural, pili)The structure labeled b is the cytoplasmThe structure labeled c is the plasma membraneThe structure labeled d is the cell wallThe structure labeled e is the capsuleThe structure labeled f is the flagella (singular, flagellum)The structure labeled g is the nucleoidThe structure labeled h is the ribosomeMore about the structure of the prokaryotic cell can be found here:.
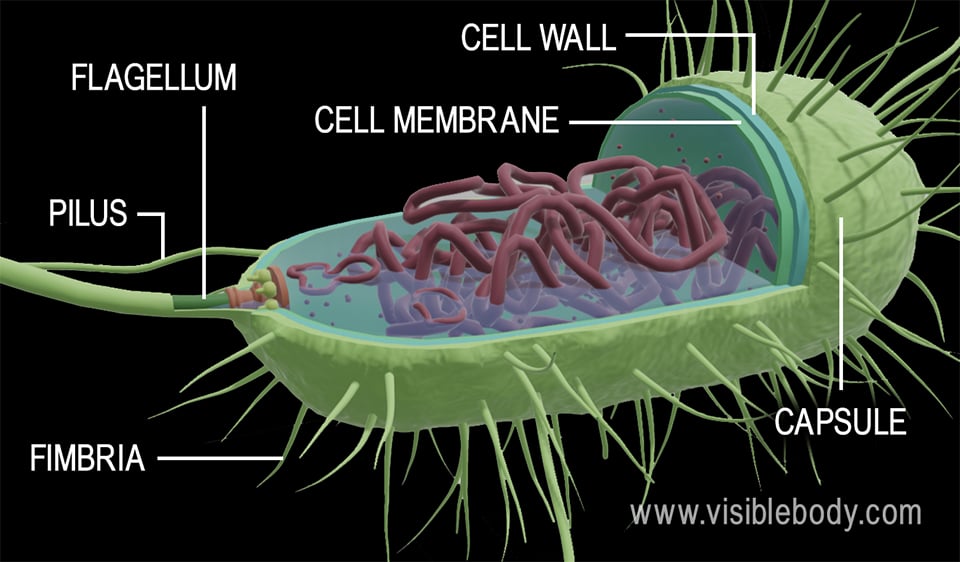
Labeling the Prokaryotic Cell. STUDY. Flashcards. Learn. Write. Spell. Test. PLAY. Match. Gravity. Created by. jeana_strickland. Terms in this set (10) Prokaryotic Cell. Capsule. A sticky layer that surrounds the cell walls of some bacteria, protecting the cell surface and sometimes helping to glue the cell to surfaces.
A prokaryotic cell structure is as follows: Capsule – It is an outer protective covering found in the bacterial cells, in addition to the cell wall. It helps in moisture retention, protects the cell when engulfed, and helps in the attachment of cells to nutrients and surfaces. Cell Wall – It is the outermost layer of the cell which gives.
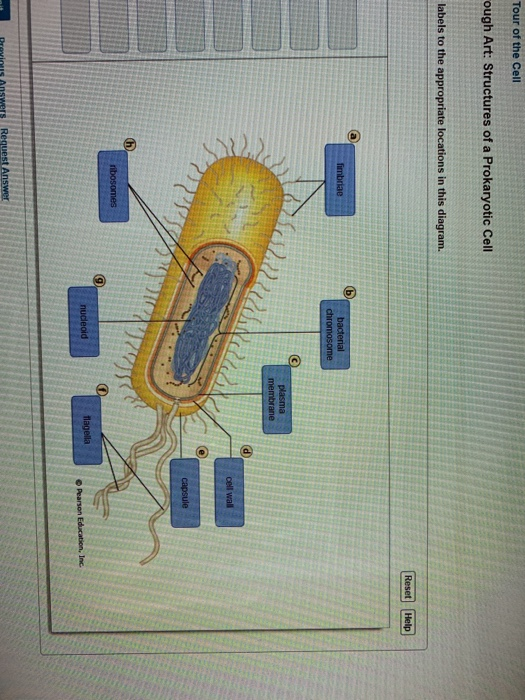
100% (4 ratings) If you like.. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Can you label the structures of a prokaryotic cell? Part A Drag the labels to the appropriate locations in this diagram. Reset Helio capsule timbrie Homes plama membrane Rucold bacten apote Parduction, Submit Previous Answers Flequest Answer.
The cytoskeleton helps a prokaryotic cell to divide and to maintain its plump, round shape. As is the case in eukaryotic cells, the cytoskeleton is the framework along which particles in the cell—including proteins, ribosomes, and small rings of DNA called plasmids—move around. It's the cell's "highway system" suspended in Jell-O.
The following interactive animations provide graphic roadmaps to the organization of both of these cell types. Eukaryotic Cell Organelles. Prokaryotic Cell Model. Unique Animal, Plant and Bacteria Characteristics. For life all cells have basic needs. Cells have diverged in their structure and function to accommodate these survival requirements.
Cell wall Cell membrane Free-floating DNA Cell wall Flagellum Ribosomes Cytoplasm 1. The three bacterial shapes in Model 1 are referred to as coccus (sphere), spirillum, and bacillus (rod). Label the diagrams in Model 1 with the correct descriptions. 2. What is represented by the small dots found in each of the bacteria cells? 3.
Flagellum (plural = flagella) are long, tail-like structure that rotate, enabling the prokaryote to move (a bit like a propeller) Some prokaryotes have more than one. Additional structures unique to prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are often described as being 'simpler' than eukaryotic cells, and they are believed to have emerged as the.
About this Quiz. This is an online quiz called The Prokaryotic Cell (Bacteria) There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper.
To help protect the cell from outside dangers and helps keep the cells structure. Capsule. encases the prokaryotic cell and it gives it its shape and protects the cell. Plasma Membrane. selectively allows things to go in and out of the prokaryotic cell. Cytoplasm.
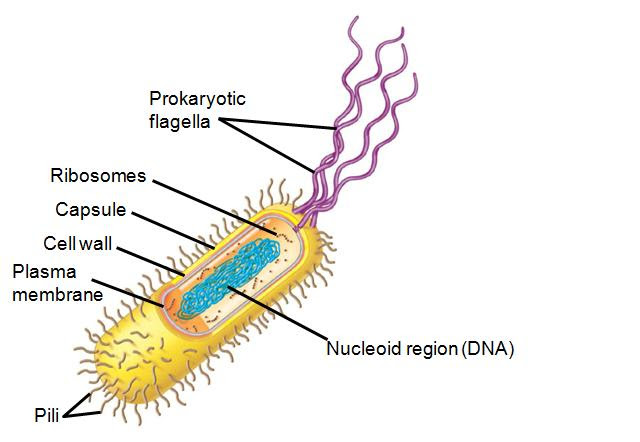
A generalized prokaryotic cell is shown. It is colored so that the features are easily distinguished from each other for identification purposes. Label six structures of the generalized prokaryotic cell. Not all terms will be used.-nucleus-cell wall-outer membrane-plasma membrane-flagellum-nucleic acid material-ribosome
Find the cell membrane, nucleus, nuclear envelope, and cytoplasm. Draw three representative cells, each about 2 cm in diameter. Label one cell with structures listed above. What purpose do epithelial cells serve? Part 2: Plant Cells. There are two fundamental cell types:
Label the structures of the prokaryotic cell in the figure below. capsule nucleoid cell wall ribosome plasma membrane fimbriae The post Label the structures of the prokaryotic cell in the figure below appeared first on nursing assignment tutor.
Prokaryotic cells lack a defined nucleus, but have a region in the cell, termed the nucleoid, in which a single chromosomal, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule is located. Archaeal membranes have replaced the fatty acids of bacterial membranes with isoprene; some archaeal membranes are monolayer rather than bilayer.
Can you label the structures of a prokaryotic cell? Drag the labels to the appropriate locations in this diagram Answers: 1 Get Other questions on the subject: Biology. Biology, 22.06.2019 02:20, emileep13. What type of synovial joint is formed between all of the tarsal bones.
Structures that enclose the cytoplasm and internal structures of the cell are known collectively as the cell envelope. In prokaryotic cells, the structures of the cell envelope vary depending on the type of cell and organism. Most (but not all) prokaryotic cells have a cell wall, but the makeup of this cell
Whereas eukaryotic cells have many different functional compartments, divided by membranes, prokaryotes only have one membrane (the plasma membrane) enclosing all of the cell's internal contents. If a eukaryotic cell is analogous to a big house with many different rooms, a prokaryotic cell is like a one-room, studio apartment.
FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOCHEMISTRY, CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOPHYSICS - Vol. II - Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function - T. G. Downing ©Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS) Prokaryotic cells typically range in size from 0.2 µm to 2.0 µm in diameter and from 1 to over 6 µm in length. Certain Spirochaeta may be as long as 250 µm (although they
and eukaryotic cells 1. Create a Venn diagram or concept map that clearly distinguishes bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic cells in terms of their genome organization, organelles, cell envelopes, ribosome size and component molecules, and cytoskeleton. 2. Determine the type of microbe when given a description of a newly discovered microbe. 56
Periplasmic Space: This cellular compartment is found only in those bacteria that have both an outer membrane and plasma membrane (e.g. Gram negative bacteria).In the space are enzymes and other proteins that help digest and move nutrients into the cell. Cell Wall: Composed of peptidoglycan (polysaccharides + protein), the cell wall maintains the overall shape of a.






/shigella-bacteria--illustration-758308491-5a02252f9e9427003c1759be.jpg)










0 Response to "34 Label The Structures Of This Prokaryotic Cell."
Post a Comment