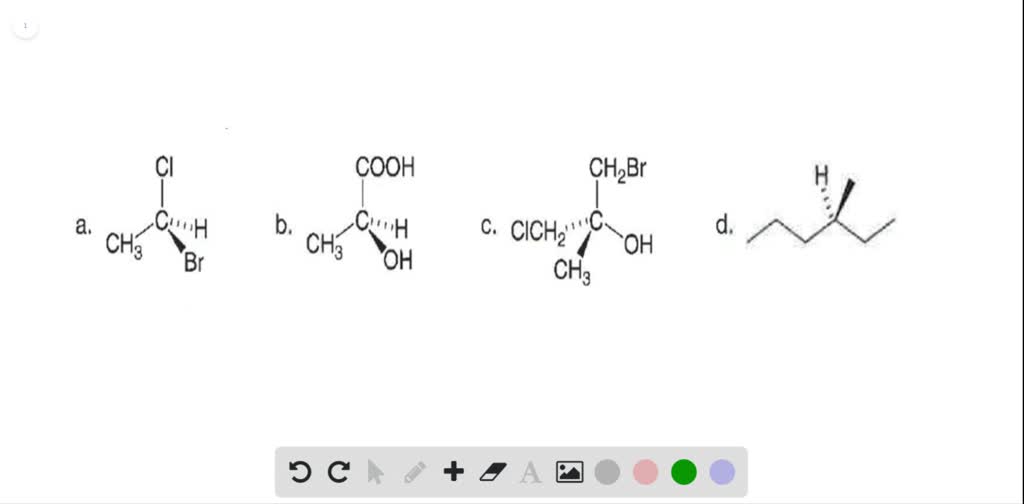
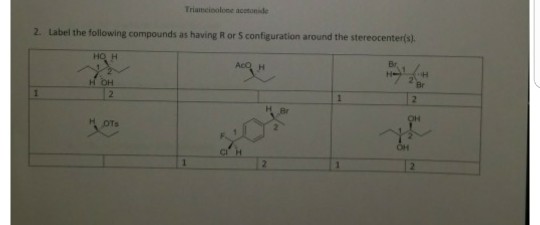
35 Label The Following Compound As R Or S
Identify the following pairs of compounds as enantiomers, diastereomers, constitutional isomers, or the same. a. diastereomers b. enantiomers 15. Identify the stereocenters in the following molecules and indicate whether they are R or S. 16. Using the tests for chirality we have learned, determine whether the following molecules are chiral. diastereomers, or the same compound? CH3 H3C OH HO 8) Label each asymmetric carbon in the compound below as R or S. OH CH3 9) Label each asymmetric carbon in the compound below as R or S. OH H CH3 OH H CH3 10) Label each assymetric carbon in the compound below as R or S. Cl 11) Draw the structure of (2R,3S)-2,3-dichloropentane. Take particular care to indicate three-
Label each asymmetric carbon in the compound below as R or S. R and S Configuration: Any carbon which is attached to four different groups is known as an asymmetric carbon atom.
Label the following compound as r or s
Let’s do the R and S for this molecule: Bromine is the priority and the hydrogen is number four. Carbon “a” is connected to one oxygen and two hydrogens. Carbon “b” is connected to one oxygen and one hydrogen. However, because of the double bond, carbon “b” is treated as if it is connected to two oxygens. 36) Label each asymmetric carbon in the compound below as R or S. 37) When I-bromo-2, 2-dimethylcyclopentane is heated in ethanol, one of the products which results is shown below. Provide a detailed, stepwise mechanism for the production of this compound, and give the name of the mechanism by which it is produced. The relationship between the following two structures is: (A) enantiomers(B) diastereomers(C) structural isomers (D) identical(E) none of the above The key here is to know the definition of all terms and then determine R or S configuration for each chiral carbon. The answer is (B) (by definition) 4. The specific rotation of pure (R)-2-butanol.
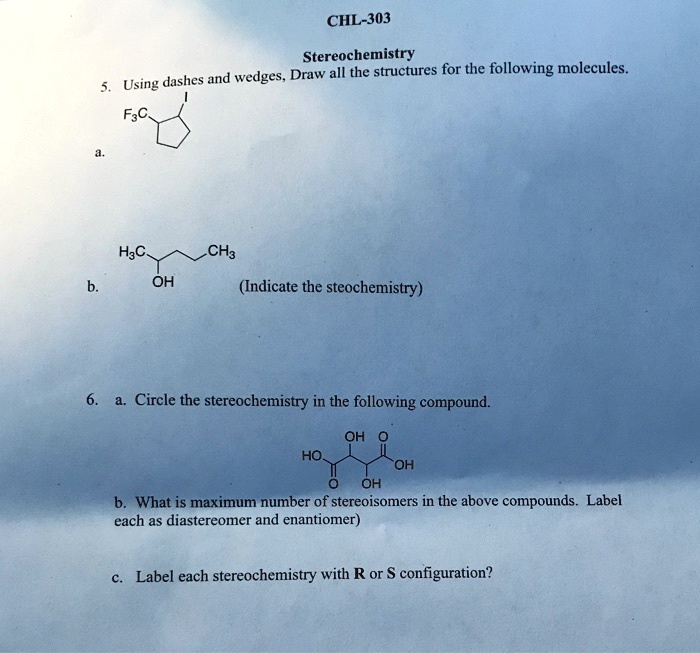
Label the following compound as r or s. 52) Label each asymmetric carbon in the compound below as R or S. 54) Draw the structure of the enantiomer of (2S, 3R)-2,3-dichloropentane. Take particular care to indicate three-dimensional stereochemical detail properly. R and S S and R Identical compounds have the same R,S designations at every tetrahedral stereogenic center. Enantiomers have exactly opposite R,S designations. Diastereomers have the same R,S configuration for at least one stereogenic center and the opposite for at least one of the other stereogenic centers. Oct 19, 2019 · R isomer s isomer. Label the following compounds as having r or s configuration around the stereocenters. R and s configuration any carbon which is attached to four different groups is known as an asymmetric carbon atom. Label the following compound as r or s. R isomer s isomer by signing up youll get thousands of step by step. 2 orient the molecule with the lowest priority group 4 back on a dash. Label each asymmetric carbon in the compound below as r or s. R and S configuration can be assign to the compound by using the following CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) sequence rules: Rule 1: Select the chiral center in the compound and assign priorities to the atoms based on its atomic number.
Compound A, CH916, was found to be optically active. On catalytic reduction over a palladium catalyst, 2 equivalents of hydrogen were absorbed to yield compound B. Ozonolysis of A gave two compounds. One was identified as acetaldehyde, CH CHO3. The other compound, C, was an optically active dialdehyde, CHO58 2. Formulate the reactions and draw. For the following molecules a. Identify chiral center(s) in each molecule and label with "*". b. Assign R/S configuration of each chiral center on the molecule. 2. Nomenclature a. Name the following molecules b. Draw structure of the following molecule: (1 R,3 R)-1-sec-butyl-3-methylcyclohexane 3. Plane of symmetry, chirality and optical. Stereocenters are labeled R or S. The "right hand" and "left hand" nomenclature is used to name the enantiomers of a chiral compound. The stereocenters are labeled as R or S. Consider the first picture: a curved arrow is drawn from the highest priority ( 1) substituent to the lowest priority (4) substituent. c, If you wanted to label only the DNA, what compound(s) could you label? You could label either deoxyribose or thymine., Based on your answers to questions 1-7, what simple rule(s) can you use to identify the following macromolecules? Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids DNA vs RiNA Look for a 1:2:1 C:H:O ratio. Many carbohydrates will.
Rank the compounds below from strongest acid to weakest acid. thrr GfitMl thbtlrcd h7 Qes*n*w1 ! it t> rri>ft gl.-W'; s circle the Lewis acids and put a box around "rPr?*ir*6-r.sk,ffffi of molecutes below: r'1 (Y (el'lifr) @ @,, \-, -F ',"N,YK' For the following reaction, label reactants and products as acids/bases and conjugate acid/bases. Label the following compound as r or s.. Manner we label the stereocenter as r latin. Consider the first picture. Identical same compound. 9 label each asymmetric carbon in the compound below as r or s. The groups which are connected to. Stereochemistry practice part 10. Draw all possible stereoisomers for each of the following. The R/S Naming System. Two or more Stereogenic Centers. Optical Activity. R/S Naming. Diastereoisomerism. Meso Compounds. Today, we'll look at naming compounds with stereocenters, and then we'll examine the complications which arise when a molecule has more than one stereocenter in it. First, though, let';s look at a property in which one. 36) Label each asymmetric carbon in the compound below as R or S. 37) When I-bromo-2, 2-dimethylcyclopentane is heated in ethanol, one of the products which results is shown below. Provide a detailed, stepwise mechanism for the production of this compound, and give the name of the mechanism by which it is produced.
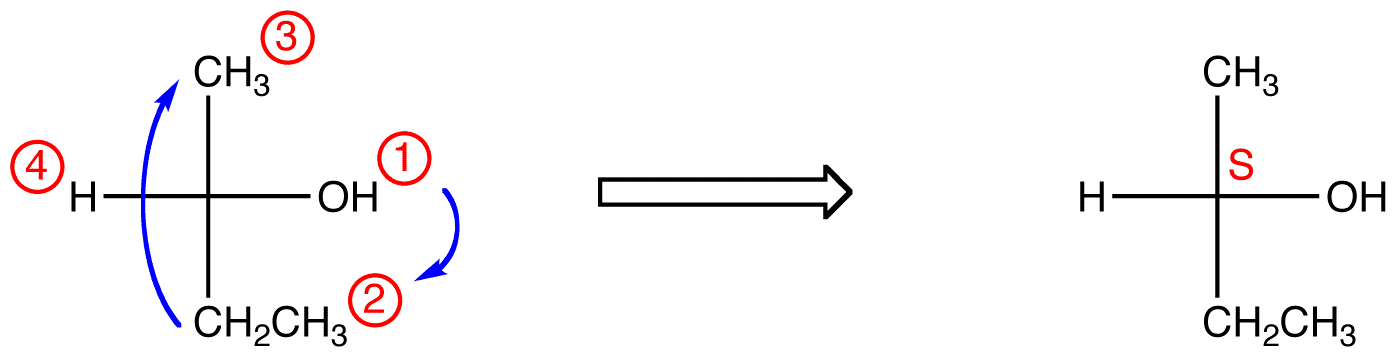
R and S are labels assigned to the stereocenters of a molecule. To easily find the R and S centers, label the four bonded molecules 1 to 4 in order of atomic number. Place the 4 molecule in the back of the chiral center and then in a clockwise (R) or counterclockwise (S) direction label the bonds with atoms 1, 2, 3.
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing acidity:HC=CCH2CH3,CH3CH2CH2CH3, CH3CH=CHCH3 CH3CH2CH2CH3 (sp3)< CH3CH=CHCH3(sp2) <HC=CCH2CH3 (sp1) Classify this compound as a Lewis base, a Bronsted-Lowry base, both or neither: a.
Classify the following pair of compounds as the same compound, enantiomers, diastereomers, constitutional isomers, or not isomeric. Also, select the correct IUPAC name, including the correct (R) or (S) designation, for each.
Label the following compound as R or S. R isomer S isomer; Question: Label the following compound as R or S. R isomer S isomer. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Explain, please... S or R? Show transcribed image text Expert Answer.
Now, our final goal is to be able to fill in truth tables with more compound statements which have more than just one logical connective in them. Statements like q→~s or (r∧~p)→r or (q&rarr~p)∧(p↔r) have multiple logical connectives, so we will need to do them one step at a time using the order of operations we defined at the beginning of this lecture.
(15 points) Identify each stereocenter in each of the following compounds as either R or S. Identify double bonds as E or Z where appropriate. Identify the relationship, using appropriate terminology, between the two compounds in each part. a) b) c) 3. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the.
a. Radioactive P b. Radioactive N c. Radioactive S d. Radioactive C To distinguish between protein and RNA in a virus, you could use radioactively labeled P compounds. If you grew viruses on cells with radioactively labeled P compounds, the phosphate groups in the virus';s RNA would become labeled but the protein would not become labeled. 7.
The resulting nomenclature system is sometimes called the CIP system or the R-S system. In the CIP system of nomenclature, each chiral center in a molecule is assigned a prefix (R or S), according to whether its configuration is right- or left-handed. No chemical reactions or interrelationship are required for this assignment.
1. Consider the following molecule. Label all chiral atoms as either R or S. Draw the compound in Newman projection (looking down the C2-C3 bond) and Fischer projection. Draw a diastereomer in Newman projection. Need to change one of the chiral centers for a diastereomer. If both chiral centers are changed would obtain the enantiomer.
Label the following compound as R or S. R or S Configuration The (R) or (S) configuration is assigned by the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention in fisher projections.
Let’s do the R and S for this molecule: Bromine is the priority and the hydrogen is number four. Carbon “a” is connected to one oxygen and two hydrogens. Carbon “b” is connected to one oxygen and one hydrogen. However, because of the double bond, carbon “b” is treated as if it is connected to two oxygens.
The relationship between the following two structures is: (A) enantiomers(B) diastereomers(C) structural isomers (D) identical(E) none of the above The key here is to know the definition of all terms and then determine R or S configuration for each chiral carbon. The answer is (B) (by definition) 4. The specific rotation of pure (R)-2-butanol.
View Test Prep - Chiral Centers Questions-Answers from CH 328M at University of Texas. Q- Label the following compounds R or S if they are chiral. If there are not chiral write A in the box for
If a molecule has a chiral center that is designated R, the chiral center will be S in the molecule';s enantiomer. You need to be able to assign whether a chiral center is R or S. To do so, you need to follow three steps: Number each of the substituents on the chiral center carbon using the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog system.



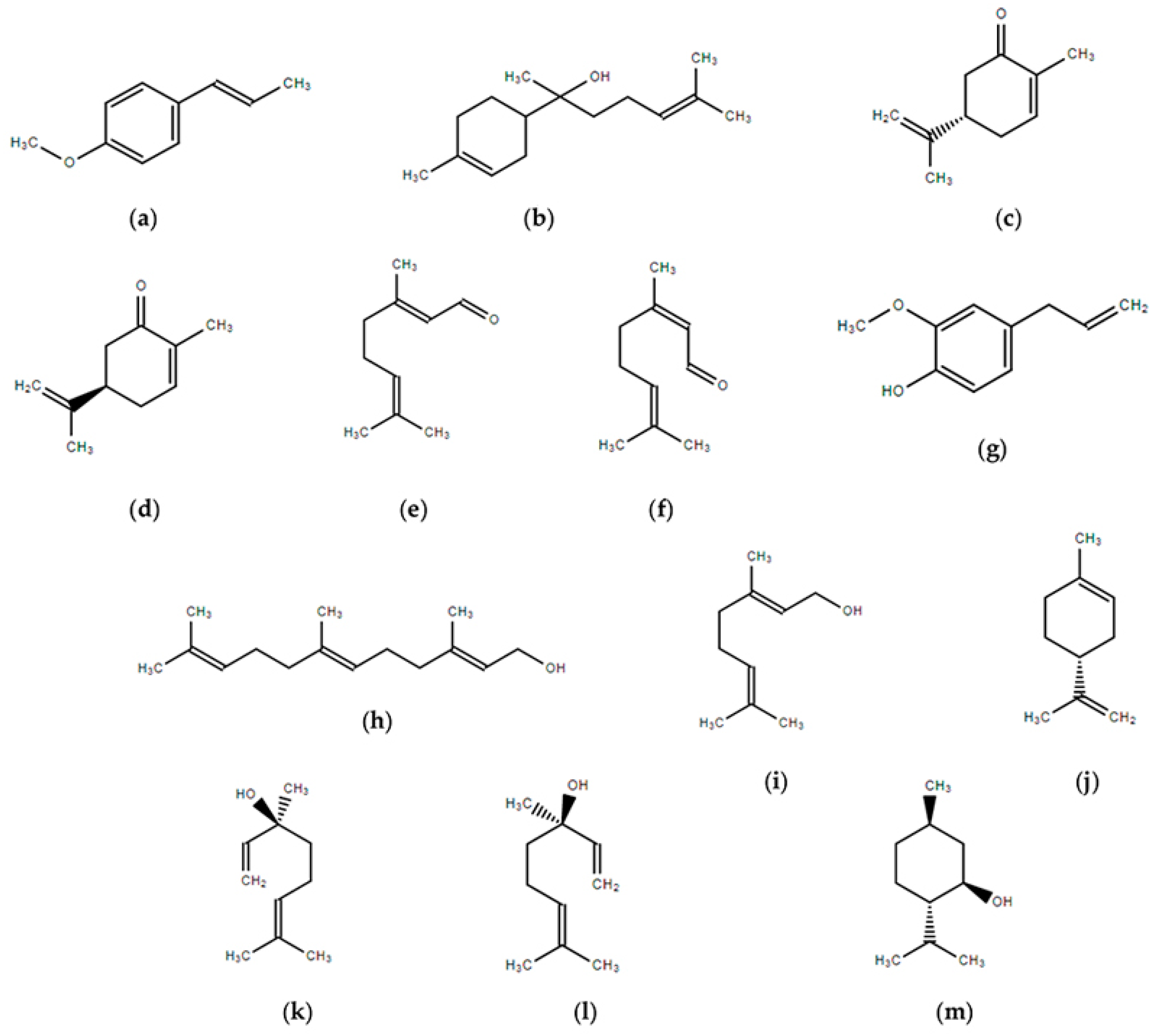

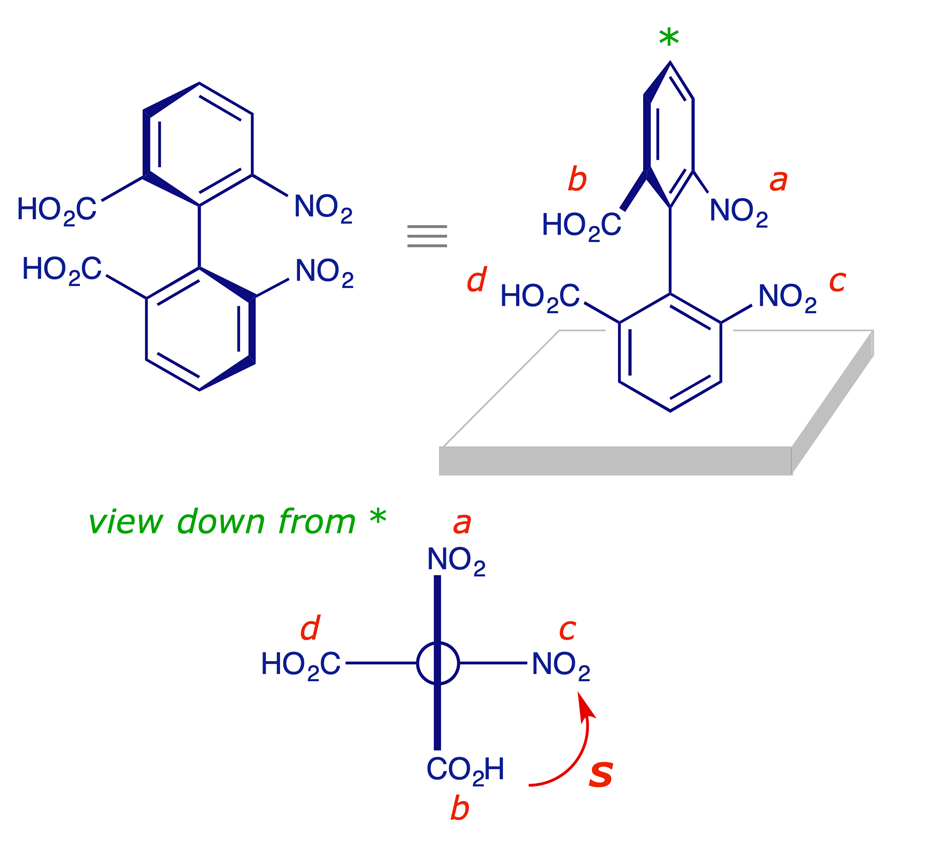
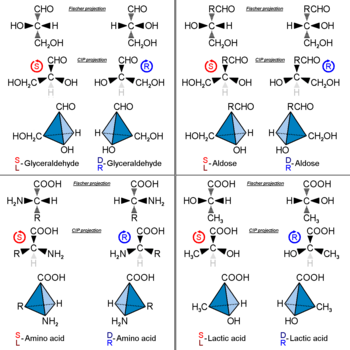
















0 Response to "35 Label The Following Compound As R Or S"
Post a Comment