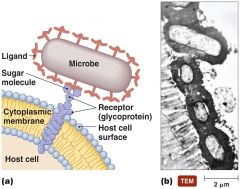
34 Label The Structures Involved In Pathogen Adhesion To Host Cells.
Altered porins in the cell wall block passage of antibiotic through the cell wall. A microbe develops a transport mechanism in the plasma membrane that rapidly pumps antibiotic out of the bacterial cell. An enzyme that destroys the antibiotic is produced. Target site is modified, so that an antibiotic is unable to bind to its target. Mycoplasma genitalium is a newly recognized pathogen associated with sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). MgPa, the adhesion protein of Mycoplasma genitalium, is the main adhesin and the key factor for M. genitalium interacting with host cells. Currently, the long-term survival mechanism of M. genitalium in the host is not clear. In this study, a T7 phage-displayed human urothelial cell (SV.
They are able to detect structures on the surfaces of foreign cells that are not found in the host. C. They detect foreign, unfamiliar chemical substances released by the invading cells.. Identify the structures involved in adhesion of a pathogen to a host cell.... Label each map with the correct epidemiological description.

Label the structures involved in pathogen adhesion to host cells.
Virulence Factors for Adhesion. As discussed in the previous section, the first two steps in pathogenesis are exposure and adhesion. Recall that an adhesin is a protein or glycoprotein found on the surface of a pathogen that attaches to receptors on the host cell. Adhesins are found on bacterial, viral, fungal, and protozoan pathogens. Bacterial cell surface glycans are quintessential drug targets due to their critical role in colonization of the host, pathogen survival, and immune evasion. The dense cell envelope glycocalyx contains distinctive monosaccharides that are stitched together into higher order glycans to yield exclusively bacterial structures that are critical for. Virus-infected cells and foreign pathogens such as bacteria and fungi will not express the MHC I specific to the host organism, which will fail to inhibit the NK cell's killing responses. If both types of receptors are being stimulated, the receptor that experiences a higher degree of relative stimulation will determine the NK cell behavior.
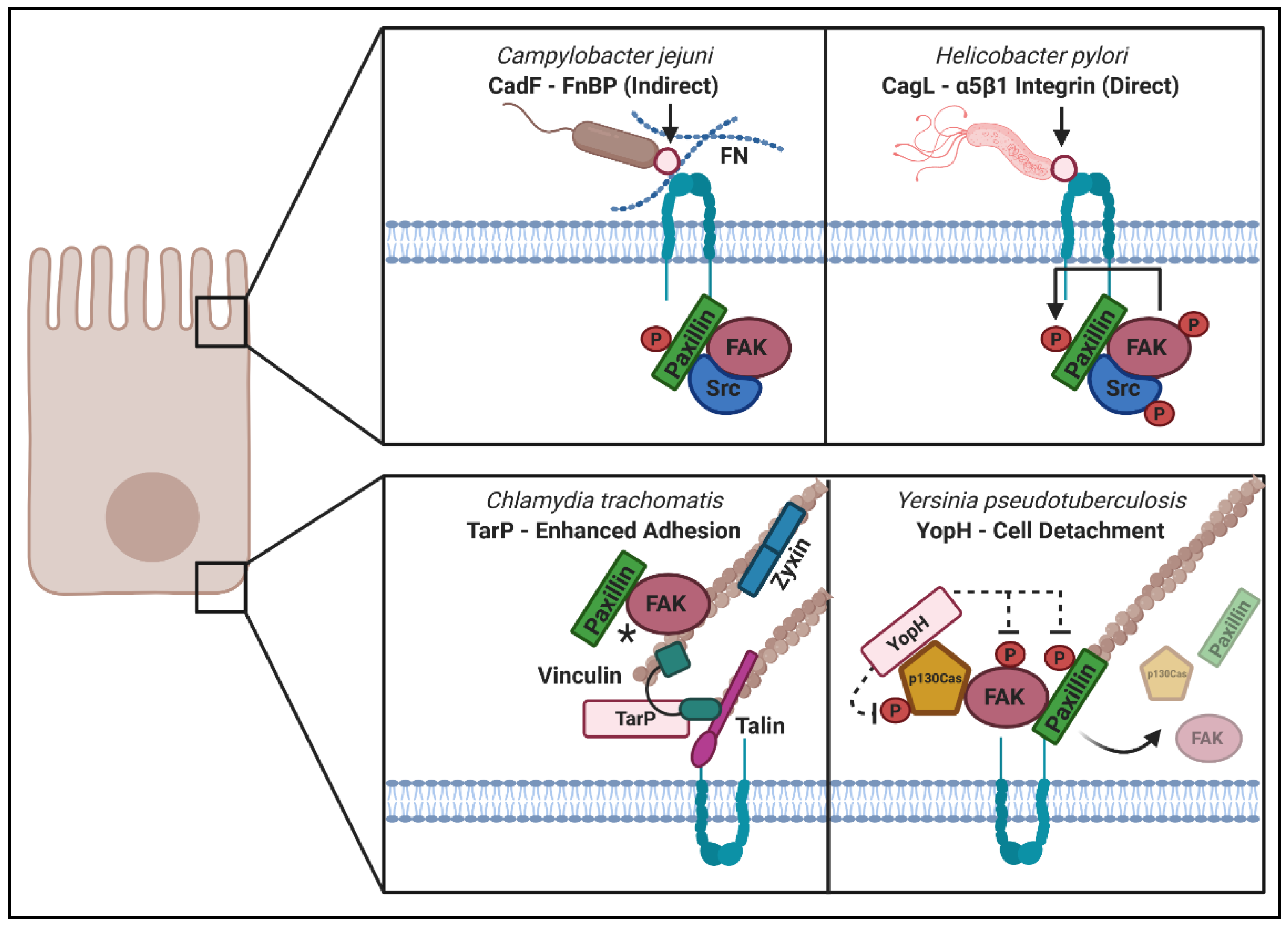
Label the structures involved in pathogen adhesion to host cells.. 1.1. Microbial Adhesion, Colonization and Host Infection. The severity of an infectious disease depends on the level of invasiveness and the extent of host cell and tissue damage caused by the pathogen involved [].A varying degree of virulence can be observed across different pathogens and among different strains of a single pathogen [].Virulence is a complicated concept in microbial. During later stages, the biofilm is mature, forming characteristic "mushroom" structures due the polysaccharides (4). Finally, some cells start to detach and the biofilm (shown in yellow) will disperse (5). Adapted from Vasudevan, 2014, J Microbiol Exp 1(3): 00014. DOI: 10.15406/jmen.2014.01.00014. The role of biofilms in pathogenesis Bacterial Adhesion and Entry into Host Cells. Successful establishment of infection by bacterial pathogens requires adhesion to host cells, colonization of tissues, and in certain cases, cellular invasion—followed by intracellular multiplication, dissemination to other tissues, or persistence. Bacteria use monomeric adhesins/invasins or. Enteropathogenic E.coli (EPEC) is a human pathogen that causes acute and chronic pediatric diarrhea. The hallmark of EPEC infection is the formation of attaching and effacing (A/E) lesions in the intestinal epithelium. Formation of A/E lesions is mediated by genes located on the pathogenicity island locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE), which encode the adhesin intimin, a type III secretion.
The results point to LPS and, in particular, to the length of the polysaccharide fraction as an important L. pneumophila determinant involved in the process of adhesion to the host cell. Introduction Legionella pneumophila is an intracellular pathogen and the main causative agent of Legionnaires' disease - a severe and often fatal pneumonia. In medical situations, they are major determinants of bacterial virulence because they allow pathogens to attach to (colonize) tissues and, sometimes, to resist attack by phagocytic white blood cells. As surface structures on the bacterial cell, the functions of fimbriae overlap with those of capsules discussed below. Virulence Factors for Adhesion. As discussed in the previous section, the first two steps in pathogenesis are exposure and adhesion. Recall that an adhesin is a protein or glycoprotein found on the surface of a pathogen that attaches to receptors on the host cell. Adhesins are found on bacterial, viral, fungal, and protozoan pathogens. The study revealed that the LPS of L. pneumophila serogroup 1 is a major determinant of the cell wall, which anchors bacteria in the host cell membrane. The important role of the O-antigen structure in recognition and uptake by host cells has been indicated by investigations of Escherichia coli (O'Donoghue et al., 2017). OMVs devoid of the O.
Hence, bacteria are found adhered to host’s epithelial cells due to direct adhesion to host cells or binding to secretory products that coat host cells or bacteria. For example, teeth are rapidly colonised by bacteria. Besides, bacteria also adher to phagocyte cells of the host and trigger immune system and may or may not be phagocytosed. Through all these virulence mechanisms and immune evasion techniques, pathogens have evolved strategies to survive in the host. Of course, the interaction of a pathogen with a host is a dynamic situation, so that advances made by the pathogen are countered by the host. Thus, the expansion of cytotoxic T cells (Tc) in the host can lead to escape. Host cells and environments for Mtb. TB is transmitted from an infected to a susceptible person in airborne particles, called droplet nuclei. Transmission occurs when a person inhales droplet nuclei containing Mtb, and the droplet nuclei traverse the mouth or nasal passages, upper respiratory tract and bronchi to reach the alveoli of the lungs. Virus-infected cells and foreign pathogens such as bacteria and fungi will not express the MHC I specific to the host organism, which will fail to inhibit the NK cell's killing responses. If both types of receptors are being stimulated, the receptor that experiences a higher degree of relative stimulation will determine the NK cell behavior.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (27 ratings) Transcribed image text: Label the structures involved in pathogen adhesion to host cells. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
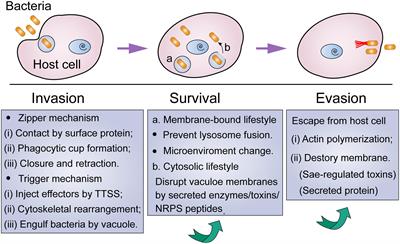
Antibodies and phagocytic cells will not penetrate live host cells To avoid host immune defenses, pathogens can enter a cell through endocytosis and form a phagosome. This phagosome is protective for the pathogen because antibodies and phagocytic cells will not penetrate live host cells to attack.
involved in host-pathogen interactions, e.g. by promoting bacterial adhesion to host cells, stabilizing toxins, and transporting other virulence factors. Moreover, OMVs of various bacterial pathogens have been found to elicit immune responses in infected hosts (Ellis and Kuehn, 2010; Kulp and Kuehn, 2010; Kulkarni and Jagannadham, 2014).
Describe 2 macromolecular receptors found on eukaryotic cell surfaces involved in pathogen adhesion. carbohydrates peptide residues.. Pathogens enter the lymph or blood to reach other sites.... domain that enzymatically attacks particular host cell function or structure. B: binding subunit linked to A by disulfide bond. It is specific to a ...
Adhesion to host cells and tissues is a key feature allowing bacteria to persist in an environment under constant flux and to initiate transient or permanent symbioses with the host. This review discusses reasons why adhesion is such a seemingly indispensable requirement for bacteria-host interactions, and whether bacteria can bypass the need.
Haemophilus parasuis is part of the microbiota of the upper respiratory tract in swine. However, virulent strains can cause a systemic disease known as Glässer's disease. Several virulence factors have been described in H. parasuis including the virulence-associated trimeric autotransporters (VtaAs). VtaA2 is up-regulated during infection and is only found in virulent strains.
Virulence Factors for Adhesion. As discussed in the previous section, the first two steps in pathogenesis are exposure and adhesion. Recall that an adhesin is a protein or glycoprotein found on the surface of a pathogen that attaches to receptors on the host cell. Adhesins are found on bacterial, viral, fungal, and protozoan pathogens.
An exotoxin that has the ability to kill or damage host cells is referred to as a(n) cytotoxin.. Identify the structures involved in adhesion of a pathogen to a host cell.... Label each map with the correct epidemiological description.
Human pathogenic fungi produce three basic 'cell' types: hyphae, yeast cells, and spores. The organization and subcellular structure of these different cell types and their modes of growth and formation are reviewed. Growth and form is the consequence of how new cell surface is formed. This is generated by the delivery of vesicles to the surface which provides new membrane and the enzymes.
They range in size from large cells such as Bacillus anthracis (1.0 to 1.3 µm X 3 to 10 µm) to very small cells such as Pasteurella tularensis (0.2 X 0.2 to 0.7 µm) Mycoplasmas (atypical pneumonia group) are even smaller, measuring 0.1 to 0.2 µm in diameter. Bacteria therefore have a surface-to-volume ratio that is very high: about 100,000.
Bacterial adhesion is a critical initiation step in bacterial colonization and persistence, both for pathogens and commensals. Bacteria express various adhesive surface structures such as capsule, fimbriae or pili, and several surface proteins (for examples the reader is referred to Klemm et al. []).Typically the adhesive structures are not expressed at the same time as the flagellum, so that.
The presence of these proteins has been associated with virulence of some pathogens, due to its potential to invade the host epithelial cells. However, the presence of FBPs could be beneficial on probiotic bacteria as they could increase their adhesion ability to host cells favouring the exclusion of pathogens (Lehri et al. 2015; Hymes et al.
adhesion of the pathogen to host cells. A pathogen's ability to colonize and invade host tissues strictly depends on this process. Thus, interference with adhesion (anti-adhesion therapy) is an efficient way to prevent or treat bacterial infections. As a basis to present different strategies to interfere
Group A Streptococcus (GAS) is a human-specific pathogen responsible for a wide range of diseases, ranging from superficial to life-threatening invasive infections, including endometritis, and autoimmune sequelae. GAS strains express a vast repertoire of virulence factors that varies depending on the strain genotype, and many adhesin proteins that enable GAS to adhere to host cells are.
Bacterial cell surface glycans are quintessential drug targets due to their critical role in colonization of the host, pathogen survival, and immune evasion. The dense cell envelope glycocalyx contains distinctive monosaccharides that are stitched together into higher order glycans to yield exclusively bacterial structures that are critical for.
Phagocytosis is series of steps where the pathogens and the immune cells interact during an invasion. This starts with the adhesion process between the host and pathogen cells, and is followed by the engulfment of the pathogens. Many analytical methods that are applied to characterize phagocytosis based on imaging the host-pathogen confrontation assays rely on the fluorescence labeling of cells.
Grading Policy Figure 14.5a You will name the structures involved in pathogen adhesion. Part A Label the structures involved in pathogen adhesion to host cells. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
Mechanisms of bacterial adhesion to host cells. Adhesion of bacteria to host surfaces is a crucial aspect of host colonization as it prevents the mechanical clearing of pathogens and confers a selective advantage towards bacteria of the endogenous flora. Accordingly, bacteria have evolved a very large arsenal of molecular strategies allowing.




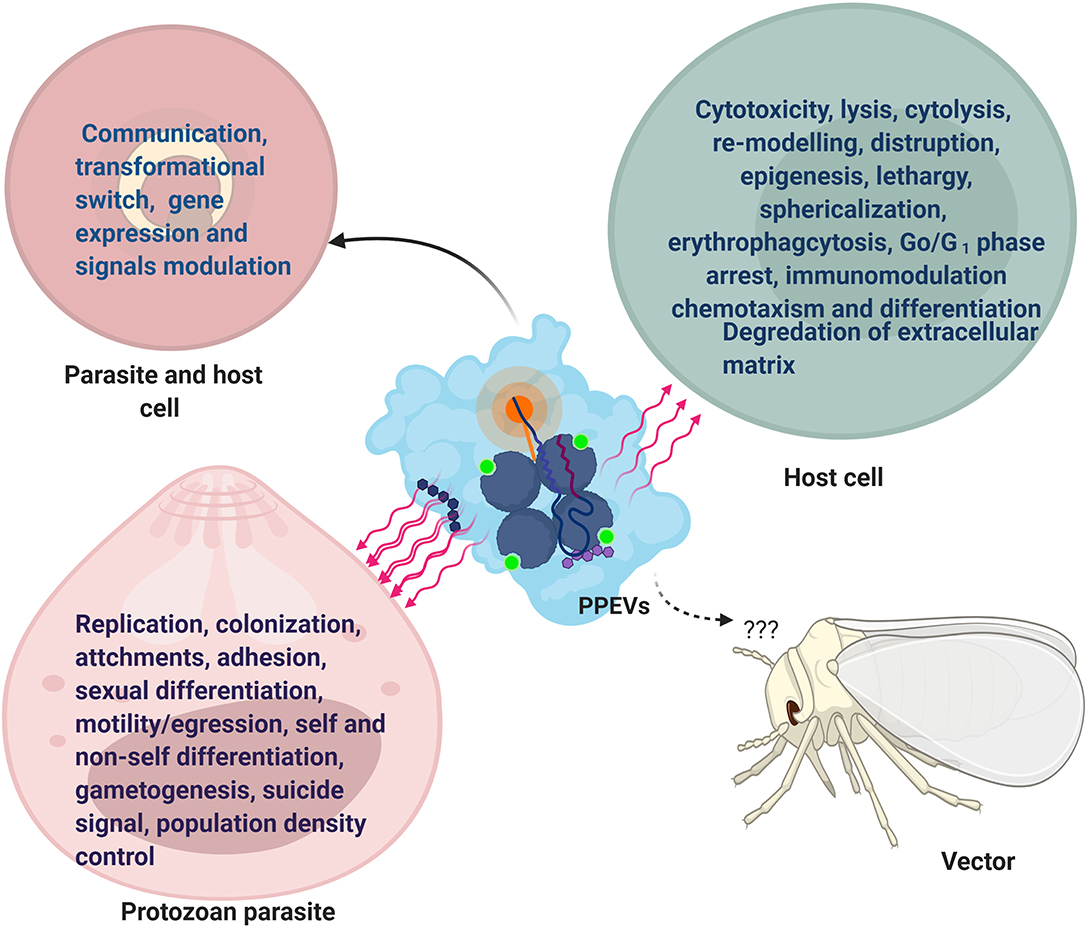
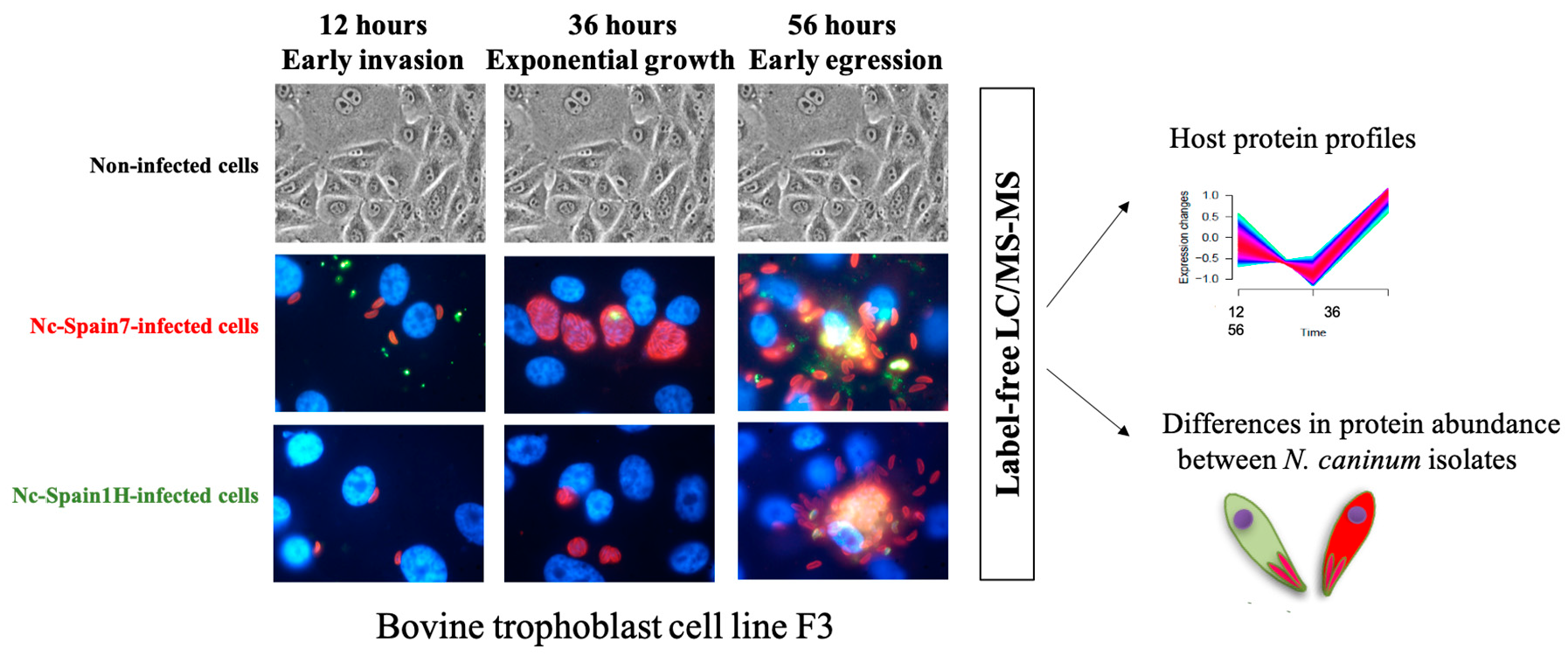

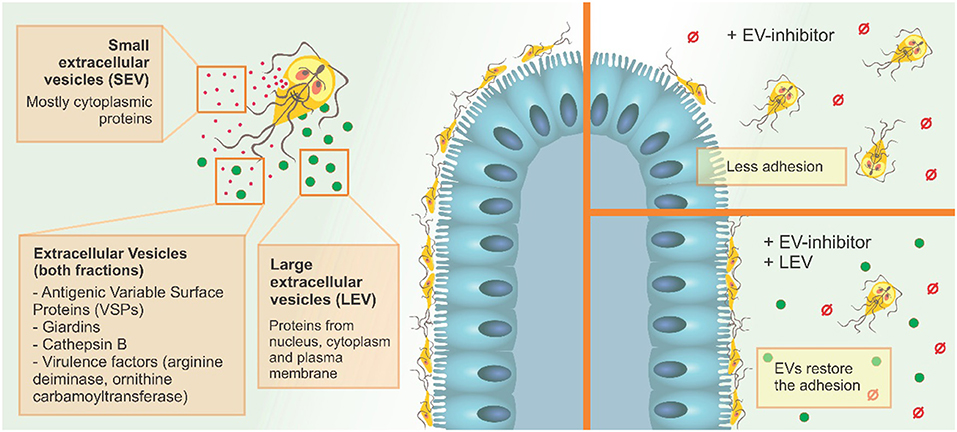


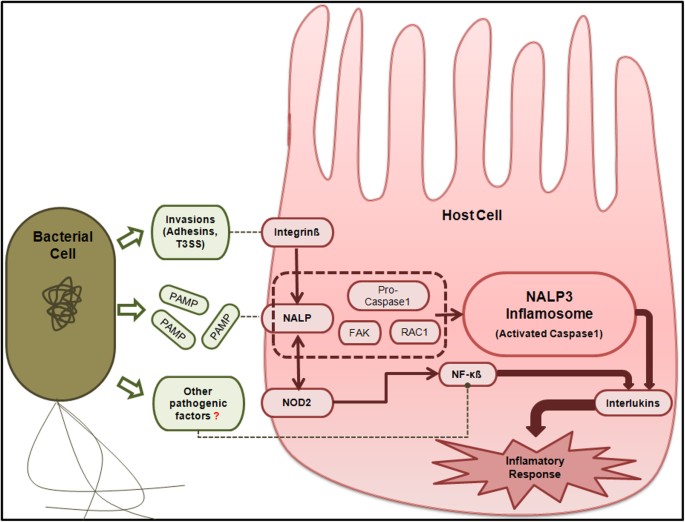


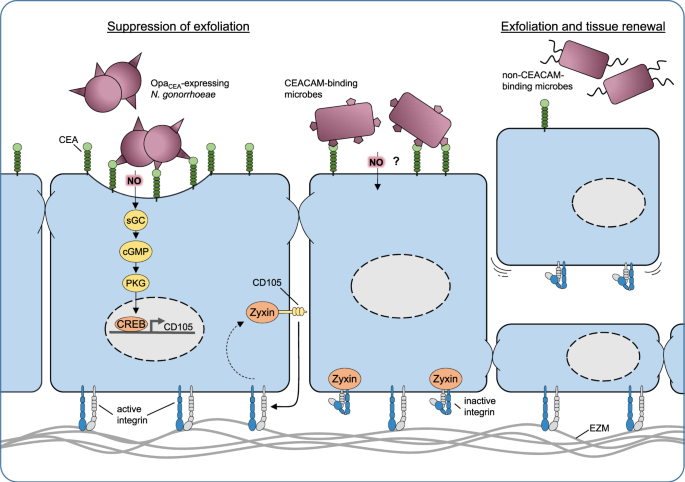




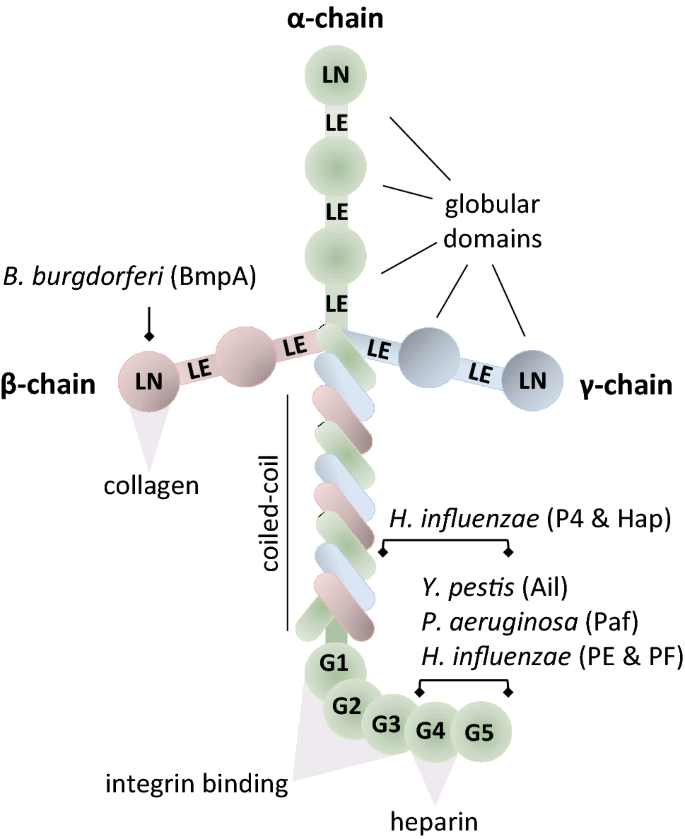
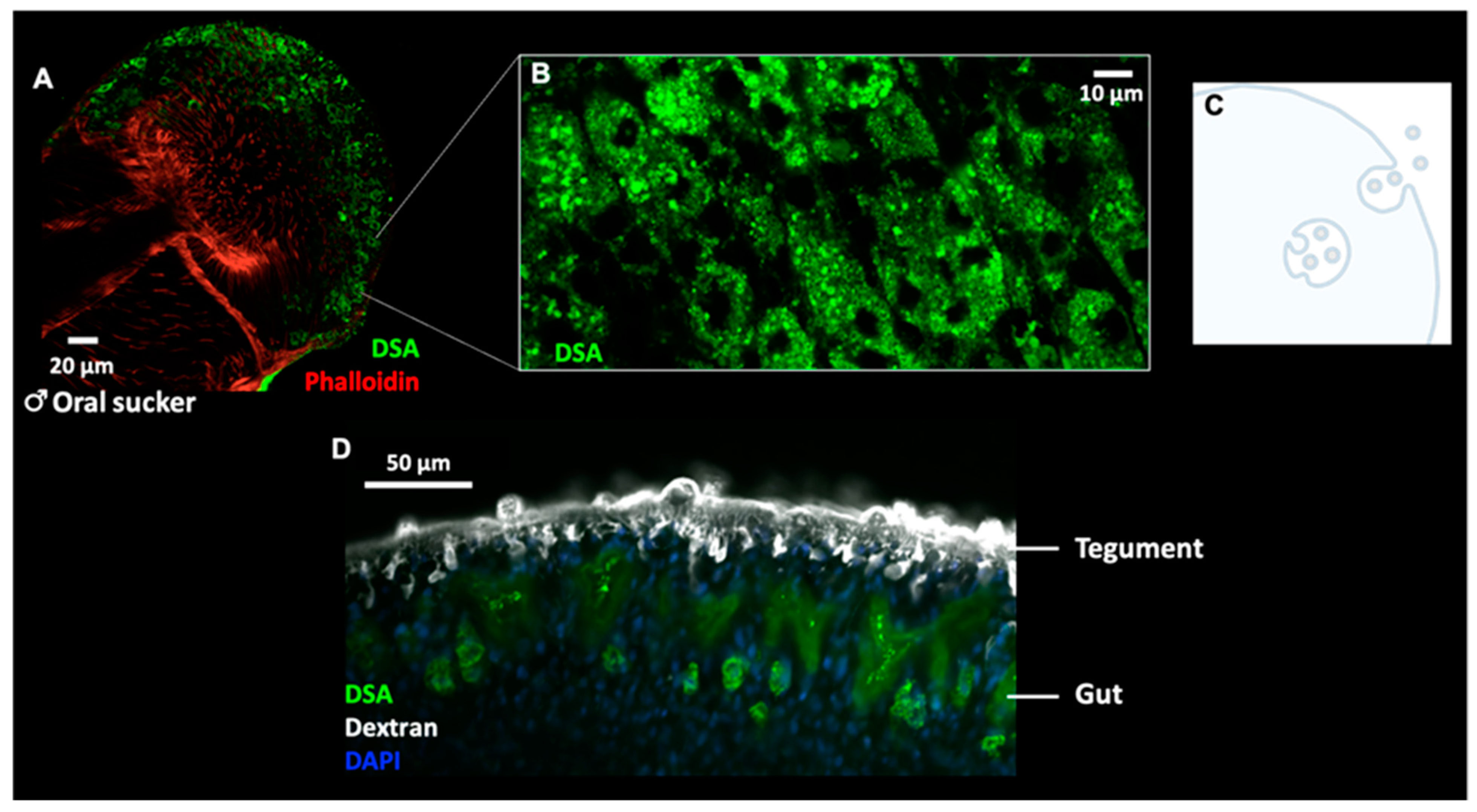
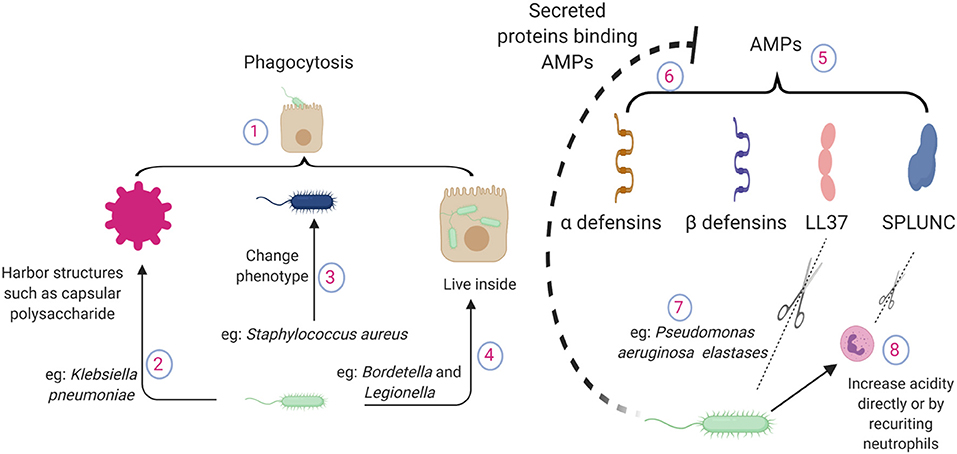
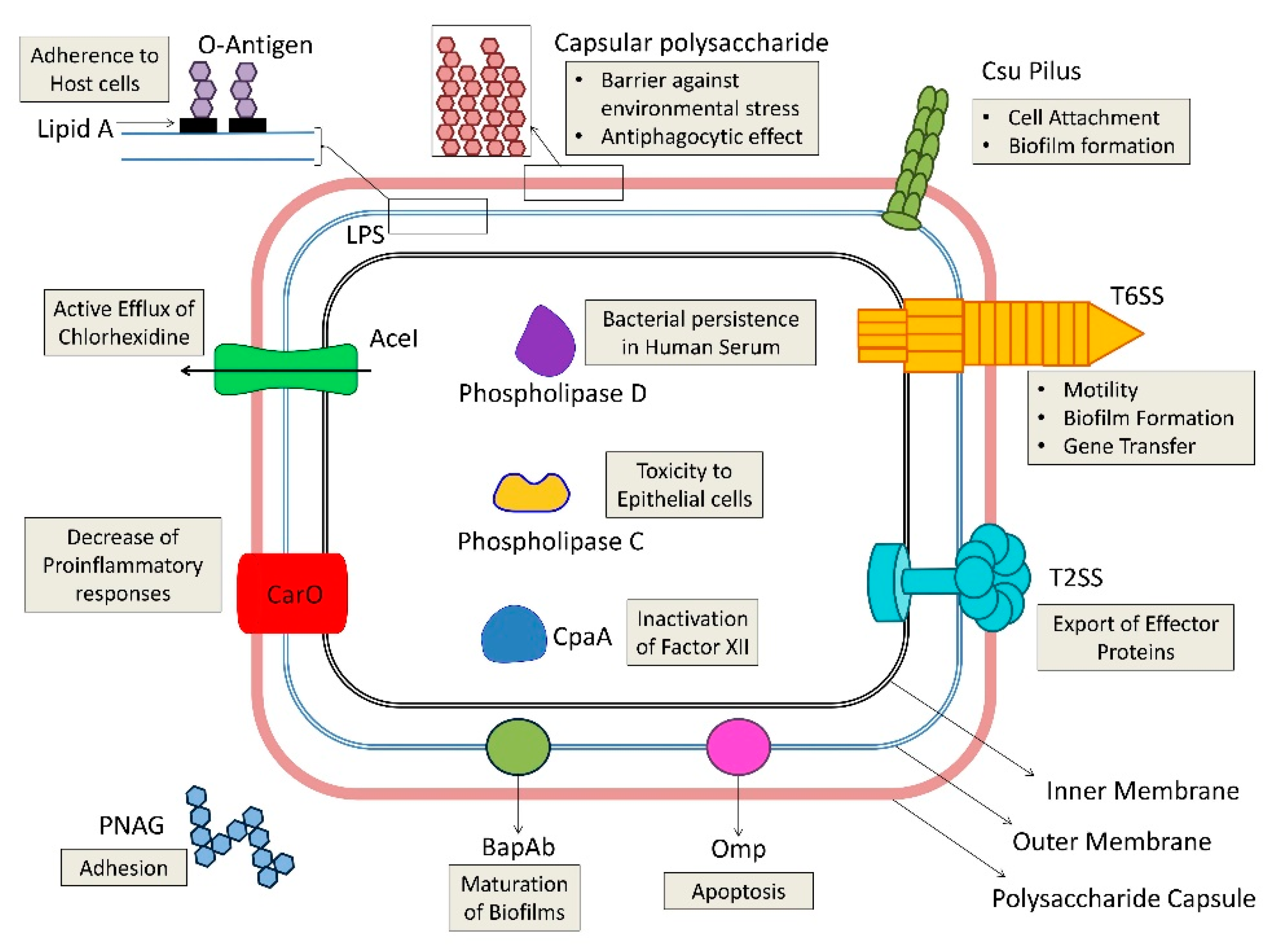
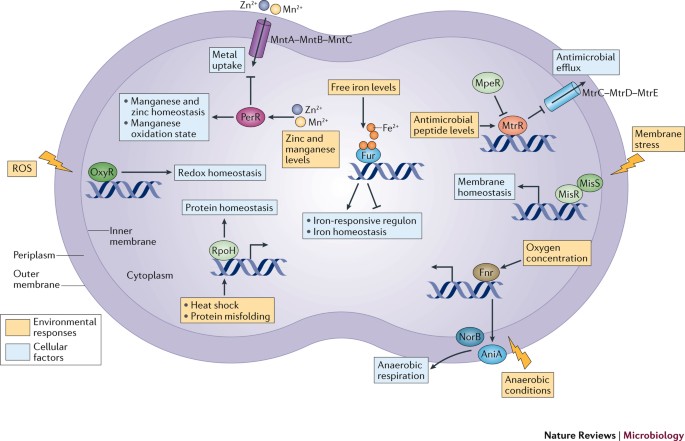

0 Response to "34 Label The Structures Involved In Pathogen Adhesion To Host Cells."
Post a Comment