36 Label The Cells And Molecules Involved In Cell-mediated Immunity
Oct 29, 2021 · Eventually, SARS-CoV-2-specific CD4+ (T H) and CD8+ (Tc) cells, present in peripheral blood circulation, undergo a rapid decline (half-life = 3–5 months) owing to infiltration into lung tissue and virus-induced lysis , suggesting the non-permanence of the T cell-mediated immunity following natural infection and/or vaccination. Nevertheless. Regulatory T cells (Treg cells), also known as suppressor T cells, are crucial for the maintenance of immunological tolerance. Their major role is to shut down T cell-mediated immunity toward the end of an immune reaction and suppress auto-reactive T cells that escaped the process of negative selection in the thymus.
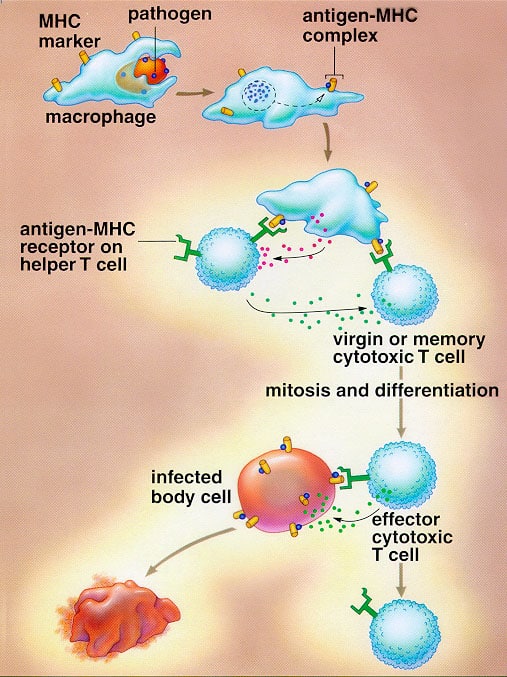
Put the steps involved in cell-mediated immunity in order. 1. In the lymph nodes, cytotoxic T cells encounter dendritic cells displaying epitope on MHC-I. The tc cell is activated. 2. The active cytotoxic T cell (CTL) leaves the lymph node looking for infected host cells displaying the same epitope on their MCL-I.
Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity
Put the steps involved in cell-mediated immunity in order. Part B - Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity Stopped Here Pr. 13. MicroFlix Activity: Immunology -- Summary of Adaptive Immunity Includes cilia, mucous membranes, dendritic cells May 24, 2021 · T cell exhaustion presents one of the major hurdles to cancer immunotherapy. Among exhausted CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, the terminally exhausted subset contributes directly to tumor cell. Immunology is a branch of biology that deals with the study of immune systems of all living organisms. It is an expansive science and is still being studied extensively. Immunology is the reason why vaccines exist, and it is one of the essential veins of biology. The following quiz covers some basic concepts of this subject. So take the quiz and find out.
Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity. 30 Label The Cells And Molecules Involved In Cell Mediated Immunity. The cell mediated response begins when a pathogen is engulfed by an antigen presenting cell in this case a macrophage. The literature concerned with the types of cells that participate in the humoral and cell mediated immune response has been reviewed. T cells develop in the thymus and are responsible for cell-mediated immunity. B cells develop in the bone marrow in mammals and are responsible for the production of circulating antibodies. lymphoid organ. Organs involved in the production or function of lymphocytes, such as thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, and tonsils. lysis Other signaling molecules synthesized in the GI tract, such as methane and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), have a great impact on intestinal function. Microbial metabolites may affect contractile activity, neuromuscular function, and calcium concentration within the myenteric plexus, all being involved in visceral perception, motility, as well. The cell-mediated immunity (CMI) The antibody-mediated immunity (Humoral Immnity) Not completely independent evidenced by (1) Ab-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC) use Abs as receptors to recognize and target cells for killing (2) Chemotactic peptides generated by the activation of Cꆦin response to Ag-Ab complexes can contribute to assembling the
Immunology is a branch of biology that deals with the study of immune systems of all living organisms. It is an expansive science and is still being studied extensively. Immunology is the reason why vaccines exist, and it is one of the essential veins of biology. The following quiz covers some basic concepts of this subject. So take the quiz and find out. <label>AIM</label>The aim of this paper is to clarify the critical role of GPCR signaling in T cell immunity.<label>METHODS</label>The G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the most common targets in current pharmaceutical industry, and represent the largest and most versatile family of cell surface communicating molecules. Question: MicroFlix Activity: Immunology - Cell-Mediated Immunity Part B - Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help MHC-1 Perforin CTL Rhinovirus epitopo Granzyme CDB Dendritic cell TCR. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated T-cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that can for example serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses, or to stimulate T cells ex vivo and transfer into patients.
May 24, 2021 · T cell exhaustion presents one of the major hurdles to cancer immunotherapy. Among exhausted CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, the terminally exhausted subset contributes directly to tumor cell. Jul 07, 2021 · T follicular helper (T FH) cells are crucial for B cell-mediated humoral immunity 1.Although transcription factors such as BCL6 drive the differentiation of T FH cells 2,3, it is unclear whether. Feb 15, 2019 · In addition to a pivotal role in humoral immunity, the importance of this pathway is evident in cell-mediated immunity with several molecules in the clinic aimed at modulating this pathway. The non-humoral contributions of CD40 axis to the immune response will be described next. 3. CD40/CD40L pathway in cell-mediated immunity3.1. T cells Immunology is a branch of biology that covers the study of immune systems in all organisms. Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and diseases; malfunctions of the immune system in immunological disorders (such as autoimmune diseases, hypersensitivities, immune deficiency, and transplant rejection); and the.
T- cells are the mediators of cell mediated immune response. T cells originate in bone marrow and mature in thymus. T cells interaction with other immune cells is via a receptor called T-Cell receptor (TCR), which can only interact with antigenic peptides bound to Class II MHC molecules on the surface of antigen presenting cells (APCs).
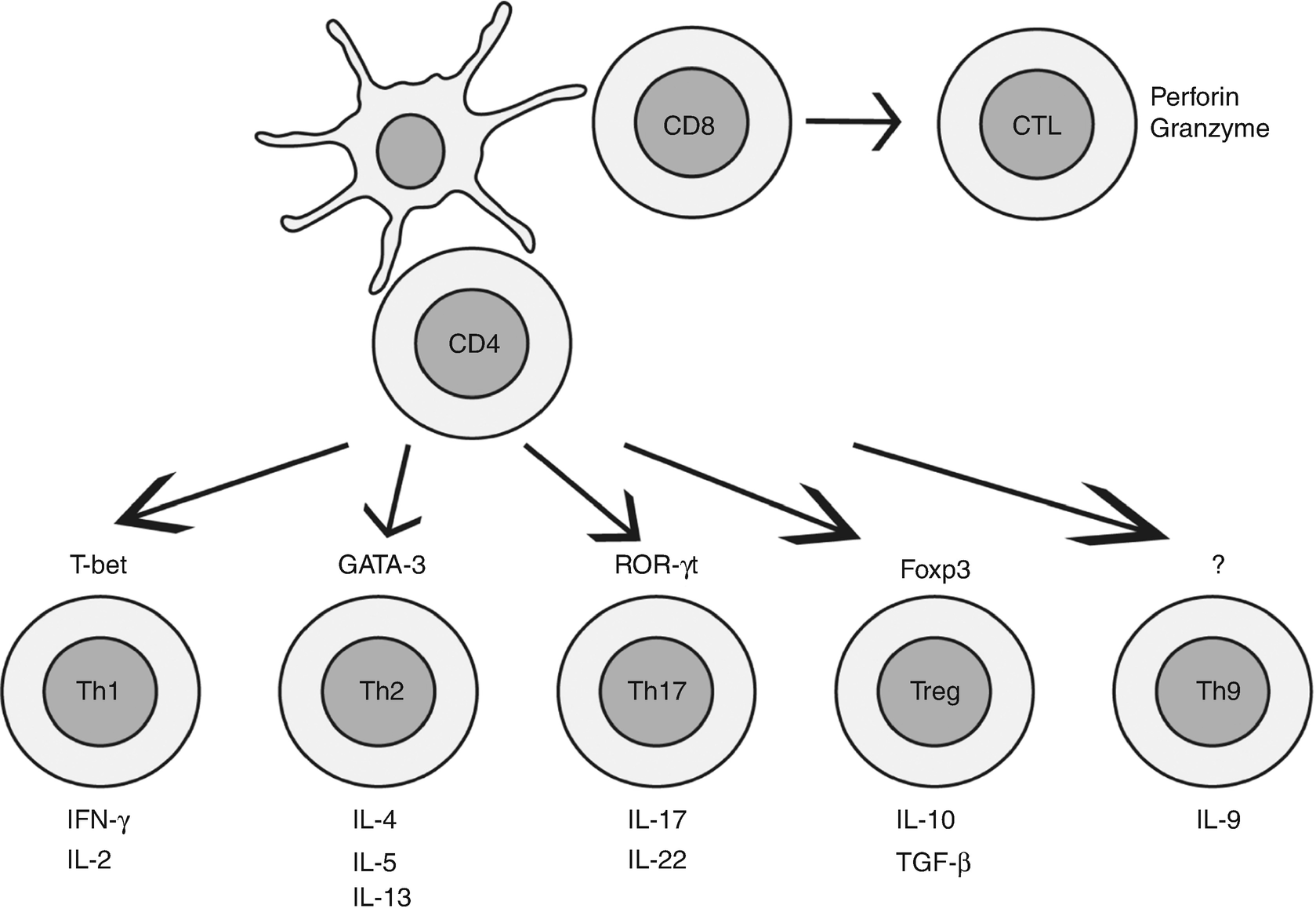
2 major groups of cells are involved. 1) Lymphocytes: B lymphocytes or B cells and T lymphocytes or T cells are the major players in adaptive immune response. In adults, these cells are derived from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow. T cells mediate cell mediated immunity whereas B cells are behind antibody mediated or humoral immunity.
Main Difference - Humoral Immunity vs Cell mediated immunity. Humoral immunity and cell mediated immunity are two types of adaptive immunity. Adaptive immunity generates an antigen-specific immune response.During adaptive immunity, the antigen is first recognized through receptors of the lymphocytes, and immune cell clones are produced to attack that particular antigen.
Biology. Biology questions and answers. Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Question: Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity.
• B7 molecules bind CD28 on T cells. CD28 signaling provides "Signal 2" to T cells and is necessary for T cell activation. • CD28 costimulation is mediated, in part, by increasing IL-2 secretion.
Aug 01, 2002 · Exosomes are saucer-shaped vesicles of 30–100 nm in diameter, which are delimited by a lipid bi-layer and which float at a density of 1.13–1.19 g ml −1 in sucrose gradients. These vesicles.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (73 ratings) correct order 1.) In the lymph nodes, cytotoxic T cells encounter dendritic cells displa.. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Part A- Correctly sort the steps involved in cell-mediated immunity Put the steps involved in cell-mediated immunity.
Cell-mediated immunity is directed primarily at removing virus-infected cells, but is also a very important player in defending against fungi, protozoa, intracellular bacteria, and cancers. It also plays a major role in transplant rejection. Figure 33-21. Cell mediated immune responses.
Cell mediated immune response is carried out by the T-cells or T lymphocytes (Fig. 11). So, it is also called T-cell immunity. This type of immune response is to defend against pathogens that may invade host cells. The surface of the T-cell has receptor molecule that can bind with antigens. These receptor molecules are made of a variable unit.
Jan 01, 2014 · Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), also called antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, is an immune mechanism through which Fc receptor-bearing effector cells can recognize and kill antibody-coated target cells expressing tumor- or pathogen-derived antigens on their surface.
Aug 25, 2020 · Natural Killer (NK) cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells are two types of immune cells that can kill target cells through similar cytotoxic mechanisms. With the remarkable success of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered T (CAR-T) cells for treating haematological malignancies, there is a rapid growing interest in developing CAR-engineered NK (CAR-NK) cells for cancer therapy.
Nov 24, 2020 - One type of immunity is cell-mediated immunity which employs lymphocytes that directly attack/destroy foreign cells or diseased host cells. It is a means of ridding pathogens residing inside human cells where they are inaccessible to antibodies. The mechanism of cell-mediated immunity is shown above. #HealthFitness
5. The following statements are labels for the cell mediated process in Model 1. • ____ A piece of the pathogen is presented on the surface of the phagocyte. • ____ The helper T-cell disperses a chemical signal to activate other immune response systems. • ____ The helper T-cell binds to the piece of pathogen presented on the phagocyte.
Label The Cells And Molecules Involved In Cell Mediated Immunity. Cell mediated immunity cmi is an immune response that does not involve antibodies but rather involves the activation of macrophages and nk cells the production of antigen specific cytotoxic t lymphocytes and the release of various cytokines in response to an antigen.
lysosomes, and MIICs. MRs colocalized with CD1b tion molecules involved in "first line defense" to adap-molecules, suggesting that the MR could deliver LAM tive, T cell-mediated immune responses. to late endosomes for loading onto CD1b. LAM and CD1b colocalized in organelles that may be sites of lipoglycan antigen loading.
In cell-mediated therapies like CAR-T cell therapy, immune cells are extracted from the patient, genetically engineered to recognize tumor specific antigens, and returned to the patient. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer (NK) cells , lymphokine-activated killer cells , cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells.
The cell mediated response begins when a pathogen is engulfed by an antigen presenting cell in this case a macrophage. Label the cells and molecules involved in cell mediated immunity. G t cells are classified by their clusters of differentiation cd which serve as receptors. They are infected by viruses. They can mature and attack infected cells.
Sep 14, 2021 · Lymph nodes (LNs) are frequent sites of metastasis. Molodtsov, Khatwani et al. find that melanoma-specific CD8+ T cells persist as functional resident memory (Trm) populations within skin-draining LNs, and these Trm cells prevent melanoma growth upon tumor seeding in LNs. A LN Trm transcriptional signature predicts survival in melanoma patients, highlighting the relevance of LN Trm function in.
During inflammation, white blood cells (such as neutrophils and macrophages) rapidly travel from the blood into the tissues to kill invading organisms and remove injured cells. Other white blood cells involved in nonspecific immunity are monocytes (which develop into macrophages), eosinophils, basophils, and natural killer cells.
T and B cells, in contrast to the cells involved in innate immunity, can target specific antigens presented to them by antigen-presenting cells. Platelets, small anucleate cells produced by megakaryocytes, are required for hemostasis. Overview Functions of blood [1] [2] Transport of: Oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to tissues
Jul 12, 2021 · 1. Cytokine Storm Syndrome Occurs during Viral Infection and Inflammation. During an immune response, the cytokine storm phenomenon arises when homeostasis is not returned, and the pro-inflammatory pathways are without regulation and are hyperactive [1,2,3].Rather than being thought of as a specific disease, the cytokine storm syndrome is considered to be a culminating endpoint to.
In recent reports, activation of NK cells has been shown to induce memory cell-like functions (3, 8, 10, 11). These observations call for reevaluation of the role of the NK cell in adaptive immunity. NK cells were initially shown to be involved in contact hypersensitivity in a mouse model of hapten induced dermatitis (10).
Put the steps involved in cell-mediated immunity in order. Part B - Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity Stopped Here Pr. 13. MicroFlix Activity: Immunology -- Summary of Adaptive Immunity Includes cilia, mucous membranes, dendritic cells
Label the cells and molecules involved in cell mediated immunity. In the case of the humoral immune response the interaction of the antigen reactive cells with the antigen leads to the release or transfer of information to the antibody forming cell resulting in the synthesis and secretion of antibody molecules.
A non-classical MHC molecule that presents antigenic peptides derived from classical class I MHC is: HLA-B. HLA-DM. HLA-E. HLA-Q.
The major function of cell-mediated immunity is to kill an infected body cell. This function is carried out by the CTL. On the other hand, the T H -cells help in activation of other cells. The function of T s and T D cells are less well-known. The CTLs bind with the help of CD8 protein to the infected body cells which express the antigenic.
Cell-cell interactions in cell-mediated immunity - activation of macrophages in response to endogenous antigens in vesicles. Macrophages play a central role in the immune system. As shown in Figure 9, macrophages are involved in: Initial defense as part of the innate immune system. Antigen presentation to Th cells.
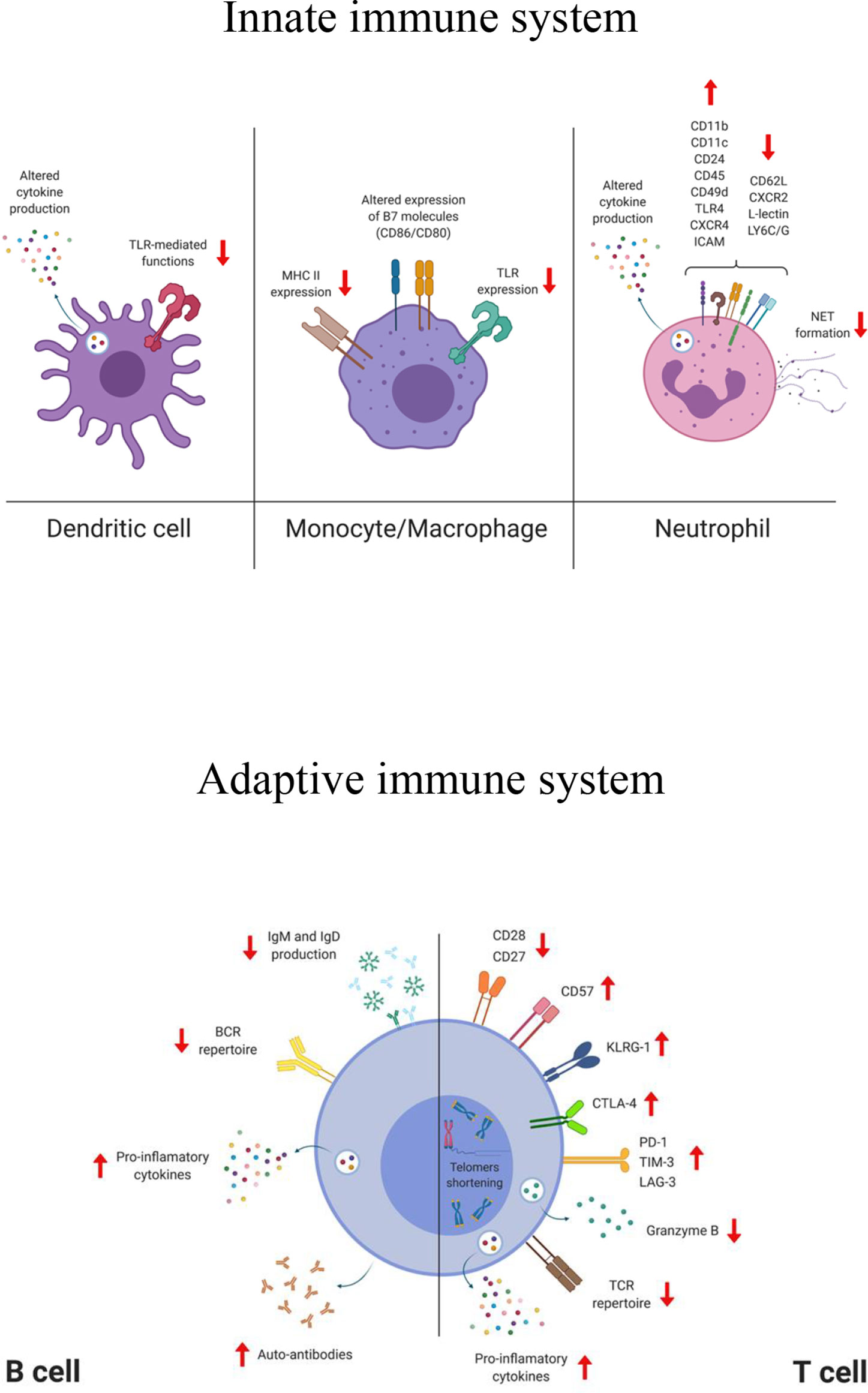
The vast majority of research that highlights peripheral immune perturbations in the context of cancer has focused on this increase in immature and immunosuppressive myeloid populations; however, this expansion also often co-occurs with alterations to many other peripheral immune lineages (Fig. 1).Our group recently used mass cytometry to comprehensively profile the phenotype and frequency of.
The cell-mediated immune response identifies and destroys infected cells, preventing the bacteria or virus from spreading any further. Cell-mediated immunity provides a double layer of security.
26 Synopsis A. Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity. e B-cell receptors C Cellular immunity is mediated by auxiliary T cells, cytotoxic T cells, natural killer cells, and macrophages. T and B Lymphocytes A single antigen molecule may be composed of many individual _____ Cellular adaptive immunity is carried out by _____.
6. Label the cells and molecules involved in cell-mediated immunity 7. What is apoptosis? a. The receptor on a cytotoxic T-cell that recognizes MHC molecules b. The proliferation of cytotoxic T-cells c. The process of programmed cell death d. A protein molecule that forms a pore in the membranes of infected cells 8. What is the function of the.
Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immune Responses. The immune system distinguishes two groups of foreign substances. One group consists of antigens that are freely circulating in the body. These include molecules, viruses, and foreign cells. A second group consists of self cells that display aberrant MHC proteins. Aberrant MHC proteins can originate.










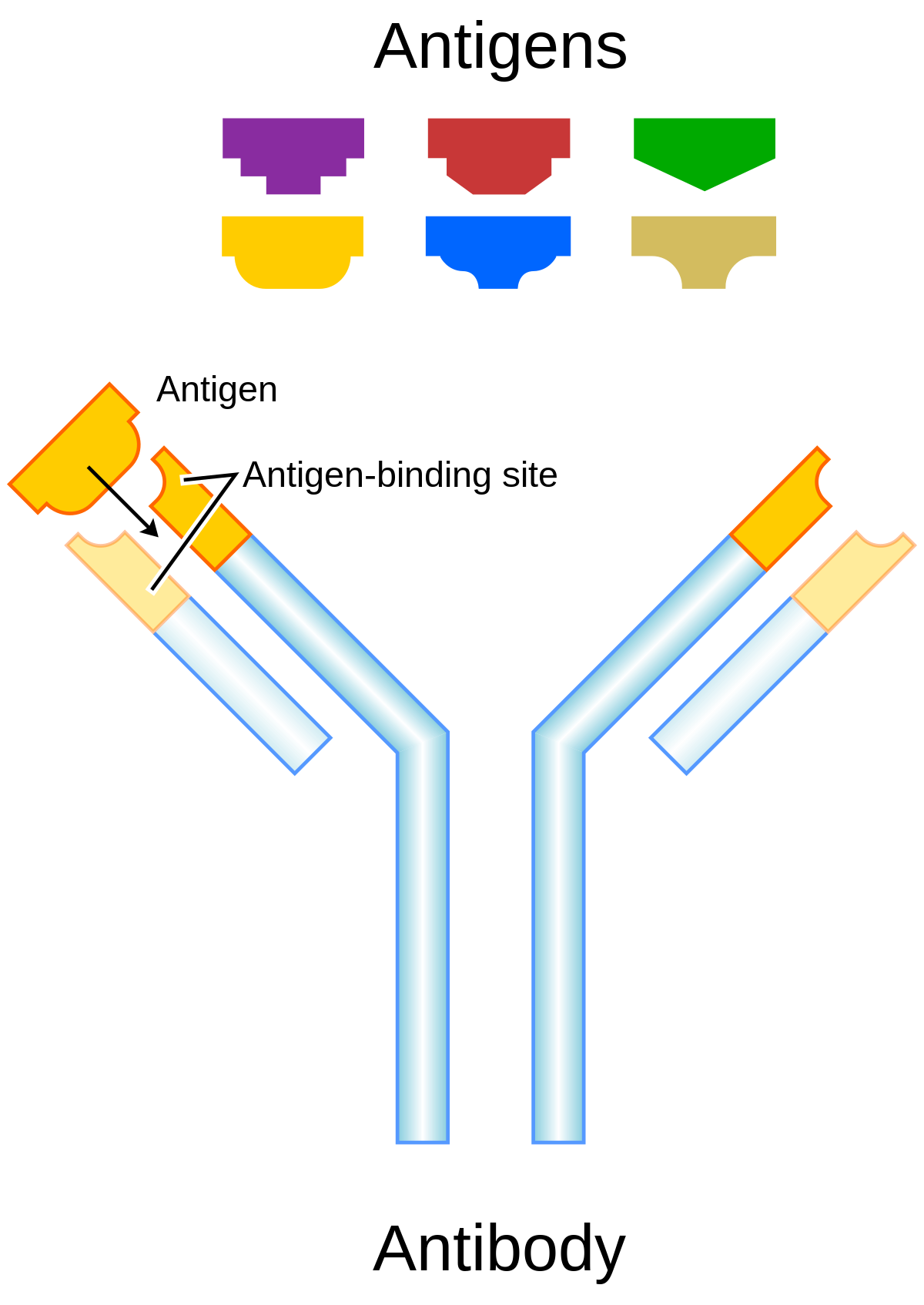










0 Response to "36 Label The Cells And Molecules Involved In Cell-mediated Immunity"
Post a Comment