40 factor label method physics
The factor-label method is also very useful in converting non-metric units into metric units. For example, in some chemistry problems you might be called upon to convert the energy of a food that ... Aug 07, 2021 · Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine. IPEM's aim is to promote the advancement of physics and engineering applied to medicine and biology for the public benefit. Its members are professionals working in healthcare, education, industry and research.
Q factor formulas. The basic Q or quality factor formula is based upon the energy losses within the inductor, circuit or other form of component. From the definition of quality factor given above, the Q factor can be mathematically expressed in the Q factor formula below: Q = E Stored E Lost per cycle.

Factor label method physics
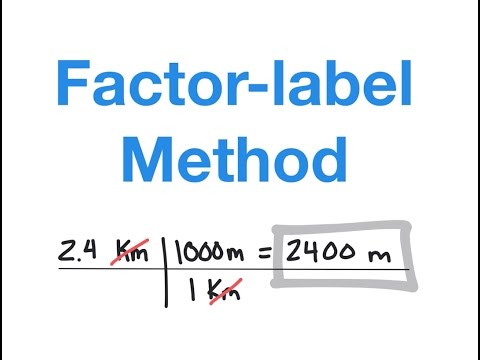
Let’s use this method for determining the force between the plates of a parallel-plate condenser. If we imagine that the spacing of the plates is increased by the small amount $\Delta z$, then the mechanical work done from the outside in moving the plates would be \begin{equation} \label{Eq:II:8:12} \Delta W=F\,\Delta z, \end{equation} where ... May 10, 2020 · Step 1: Convert the data vector into a factor. The factor() command is used to create and modify factors in R. Step 2: The factor is converted into a numeric vector using as.numeric(). When a factor is converted into a numeric vector, the numeric codes corresponding to the factor levels will be returned. The factor-label method for converting units. The factor-label method is the sequential application of conversion factors expressed as fractions and arranged so that any dimensional unit appearing in both the numerator and denominator of any of the fractions can be cancelled out until only the desired set of dimensional units is obtained.
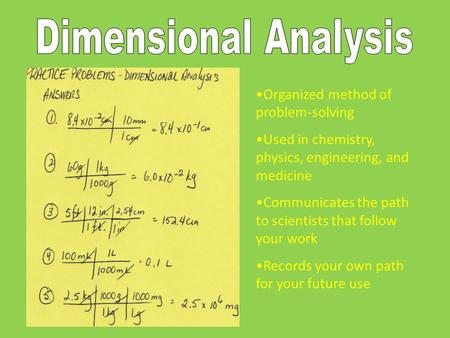
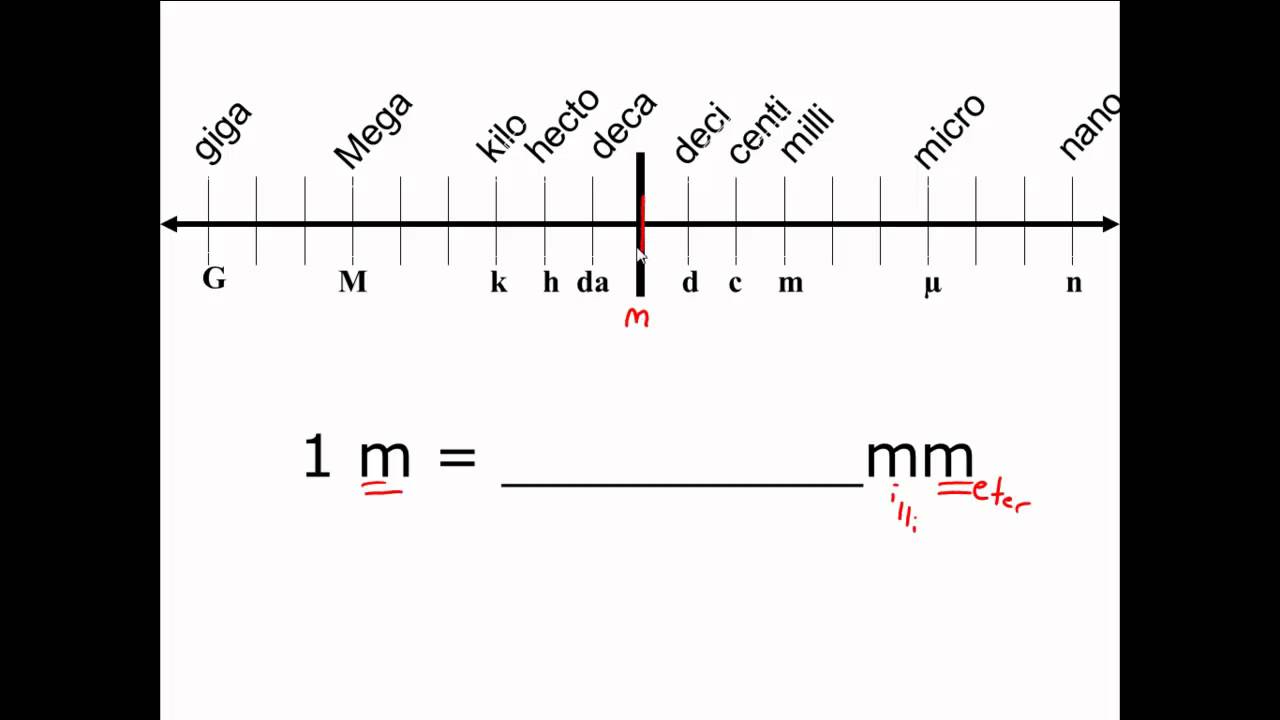
Factor label method physics. Sep 13, 2018 · Therefore, when we breathe out, all the carbon dioxide we exhale has already been accounted for.We are simply returning to the air the same carbon that was there to begin with. Remember, it's a carbon cycle, not a straight line - and a good thing, too!. Update information: This rebuttal was updated on September 12, 2018 to swap the graphic showing a - … Physics 12 skill FACTOR-LABEL METHOD FOR CONVERTING UNITS A very useful method of converting one unit to an equivalent unit is called the factor-label method of unit conversion. You may be given the speed of an object as 25 km/h and wish to express it in m/s. To make this conversion, you must change km to m and h to s. Factor Label Method is a systematic way of converting units in science. On the left hand side are the most informative you tube videos about factor label method. On the right hand side are the PowerPoint notes, graphic organizer, and worksheets we did in class. Answer key for the worksheet may be requested in class when the worksheets are first ... Jul 26, 2019 · In the science of optics, the magnification of an object like a lens is the ratio of the height of the image you can see to the height of the actual object being magnified. For instance, a lens that makes a small object appear very big has a high magnification, while a lens that makes an object appear small has a low magnification. An object's magnification is generally given by …
Videos Anatomy and Physiology AP Biology AP Chemistry AP Environmental Science AP Physics Biology Chemistry Earth Science Educational NGSS - Next Generation Science Standards Physics Statistics & Graphing; ... Factor-Label Method. Mr. Andersen shows you how to use the factor label method to solve complex conversions. Home / About / Videos ... Oct 02, 2015 · The following appears on p. 3 of Permanent Magnets and Magnetism, D.Hadfield, ed., (London, Iliffe Books Ltd, 1962) in its Chap. 1, Introduction and History by E.N. da C. Andrade: “William Gilbert, whose De Magnete Magneticisque Corporibus et de Magno Magnete Tellure Physiologia Nova, usually known simply as De Magnete, published in 1600, may be … Lesson 1.5 - The Factor-Label Method. The factor-label method is a procedure for converting a quantity from one unit to another. This procedure calls for multiplying the original quantity by a fraction made up of a conversion factor. The fraction is made up of the two terms in the conversion factor. 1.5 - The Factor-Label Method. The factor-label method is a procedure for converting a quantity from one unit to another. This procedure calls for multiplying the original quantity by a fraction made up of a conversion factor. The fraction is made up of the two terms in the conversion factor. Since the two terms are, in essence, the same ...
Dimensional analysis is also called a Unit Factor Method or Factor label method, because a conversion factor is used to evaluate the units. For example, suppose we want to know how many meters there are in 4 km. Normally we calculate as. 1 km = 1000 meters. 4 km = 1000 × 4 = 4000 meters (Here the conversion factor used is 1000 meters) In physics and engineering, the quality factor or Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how underdamped an oscillator or resonator is. It is approximately defined as the ratio of the initial energy stored in the resonator to the energy lost in one radian of the cycle of oscillation. Q factor is alternatively defined as the ratio of a resonator's centre frequency to its bandwidth ... Factor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors.For example, it is possible that variations in six observed variables mainly reflect the variations in two unobserved (underlying) variables. The Q factor implies energy losses within a resonant device that might be anything from a mechanical pendulum, an entity in a mechanical structure, or from an electrical circuit, such as a resonant circuit.. Q factor shows the energy loss due to the quantity of energy contained in the design. Thus, the larger the Q factor, the lower the rate of energy loss, and hence the slower the oscillations.
The factor-label method tells us that units (such as pounds, miles, quarts, or millimeters) can be multiplied, divided, and cross-cancelled just like numbers. A unit can be cross-cancelled only with the identical unit, and one must be in a numerator, and the other in the denominator.
Dimensional Analysis (also called Factor-Label Method or the Unit Factor Method) is a problem-solving method that uses the fact that any number or expression can be multiplied by one without changing its value. It is a useful technique. The only danger is that you may end up thinking that chemistry is simply a math problem - which it definitely ...
The factor-label method for converting units. The factor-label method is the sequential application of conversion factors expressed as fractions and arranged so that any dimensional unit appearing in both the numerator and denominator of any of the fractions can be cancelled out until only the desired set of dimensional units is obtained.
May 10, 2020 · Step 1: Convert the data vector into a factor. The factor() command is used to create and modify factors in R. Step 2: The factor is converted into a numeric vector using as.numeric(). When a factor is converted into a numeric vector, the numeric codes corresponding to the factor levels will be returned.
Let’s use this method for determining the force between the plates of a parallel-plate condenser. If we imagine that the spacing of the plates is increased by the small amount $\Delta z$, then the mechanical work done from the outside in moving the plates would be \begin{equation} \label{Eq:II:8:12} \Delta W=F\,\Delta z, \end{equation} where ...






















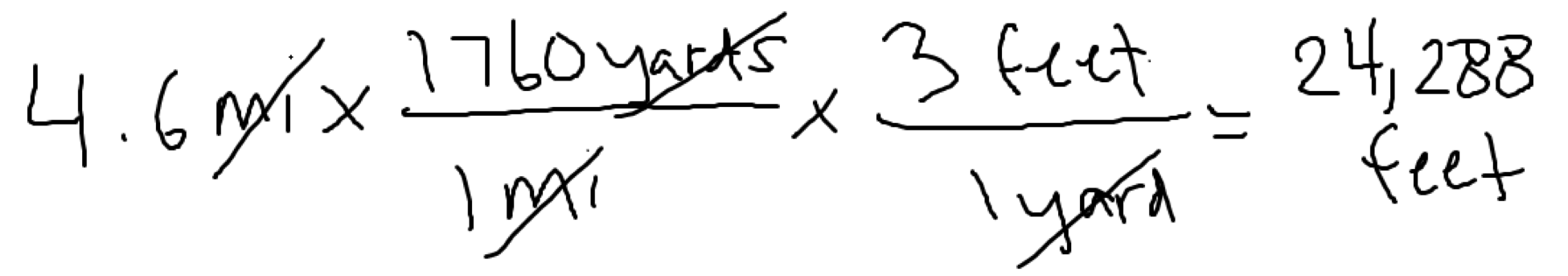







0 Response to "40 factor label method physics"
Post a Comment