35 low fat label requirements
Food and drink labelling and packaging regulations - what you must show, warnings, health and organic labels and packaging standards. ... (for example, low fat) or a health claim ... Ice cream is a frozen food made from a mixture of dairy products, containing at least 10 percent milkfat. "Reduced fat" ice cream contains at least 25 percent less total fat than the referenced product (either an average of leading brands, or the company's own brand). "Light" or "lite" ice cream contains at least 50 percent less total fat ...
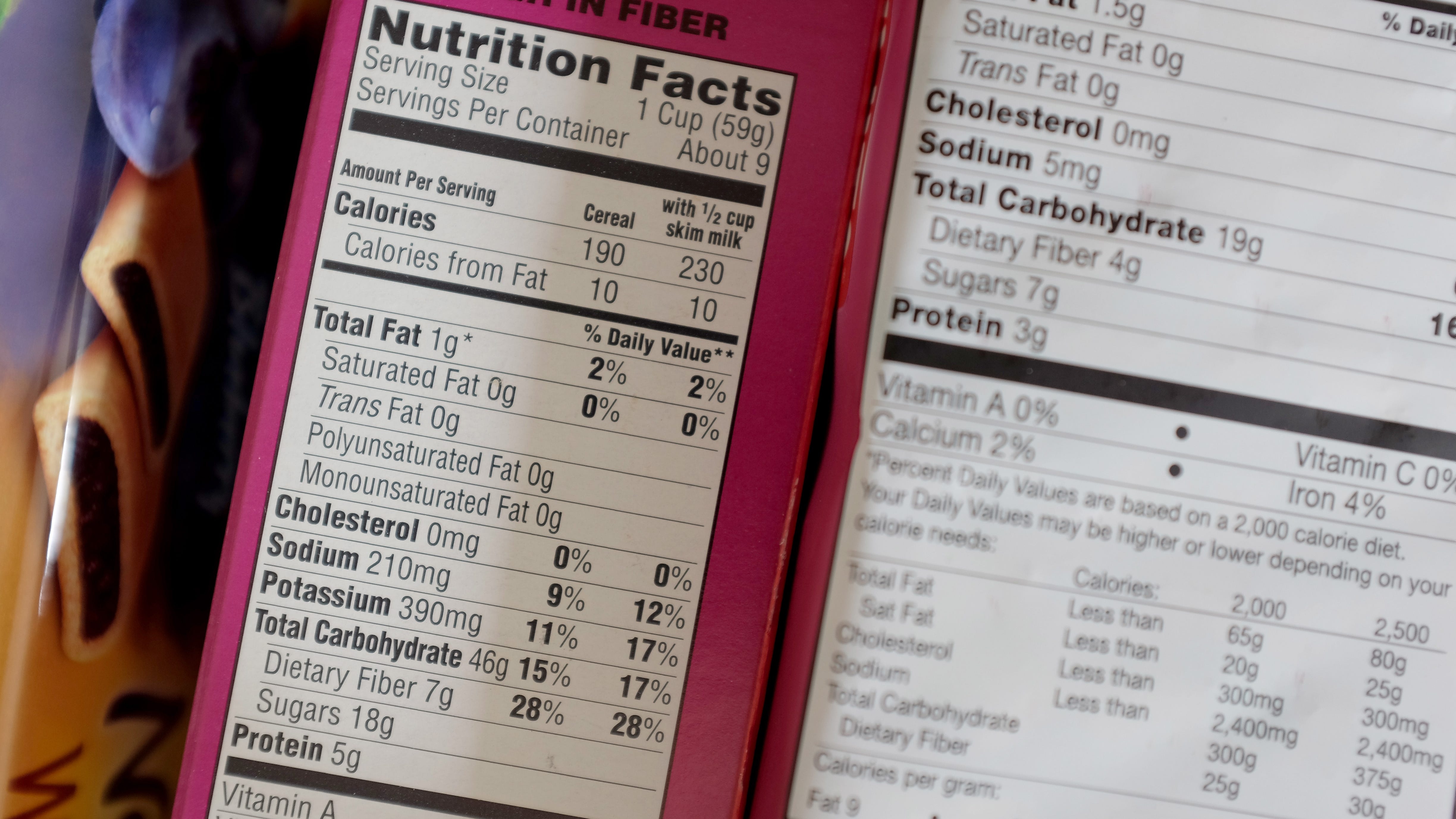
So, if a food contains fewer than 3 grams of fat per 100 calories, it is a low fat food. To determine if a food is low fat, a person can read its nutrition label.

Low fat label requirements
Section II provides an overview of the basic food labeling requirements, including the prior label approval process, establishment responsibilities, temporary label approvals, and other facets of the preapproval process. Sections III through XII address in detail each of the up to eight If you want to find products even lower in fat, look for the fat-free designation. To be labeled as fat-free, a product must have 0.5 grams of fat or less per serving. It must not have a fat-based ingredient like oil. Note that low fat does not necessarily mean a product is low in saturated fat. Manufacturers who use this claim have to make sure the product meets strict criteria before they are allowed to print 'low in fat' on the food label. A 'low fat' or 'low in fat' food must contain no more than 3g of fat per 100g of food. A liquid must contain no more than 1.5g fat per 100g. 'Reduced fat' means the food must contain at least 25 percent less fat than the regular product to which it is being compared, and at least 3g less fat per 100g of food.
Low fat label requirements. Extra lean. • On seafood or game meat products: less than 5 g total fat, less than 2 g saturated fat, and less than 95mg cholesterol per RACC and per 100 g (for meals and main dishes, meets criteria per 100 g and per labeled serving). High potency. LOW FAT. A claim that a food is low in fat, and any claim likely to have the same meaning for the consumer, may only be made where the product contains no more than 3 g of fat per 100 g for solids or 1,5 g of fat per 100 ml for liquids (1,8 g of fat per 100 ml for semi-skimmed milk). FAT-FREE In order to use the words “low-fat” on your product label, you have to meet a few stringent guidelines set by the FDA. As a rule, your product must contain 3 grams or less of total fat per Reference Amount Customarily Consumed (RACC), a standard set by the FDA as a guideline for manufacturers to gauge serving sizes. If the serving size for ... (C) As required in § 101.13(e)(2), if the food meets these conditions without the benefit of special processing, alteration, formulation, or reformulation to lower cholesterol content, it is labeled to clearly refer to all foods of that type and not merely to the particular brand to which the label attaches (e.g., "low fat cottage cheese, a low cholesterol food").
Answers may include: reduced-fat, low-fat, no-fat, low salt, reduced salt, no salt, high fibre, low sugar, no sugar, diet. Fat Low-fat: Less than 3g fat/100g food (or 1.5g/100g liquid) Reduced-fat: At least 25% less fat than the regular product Fat free: No more than 0.15g total fat/100g food Light/Lite:The characteristic that makes the food 'light' must be stated on the label (regardless of whether the term refers to a nutrient or another characteristic of the food). Sugar 6.1.8 Low fat. Food must have 3 g or less fat per RACC in accordance with 21 CFR§101.62 as compared to an appropriate reference food. 6.1.9 Nonfat/skim/fat free. Food must have less than 0.5 g of fat per RACC in accordance with 21 CFR§101.62 as compared to an appropriate reference food. 6.2 Labeling. Low Fat. The requirements for nutrition claim like "low fat" are made to cater for the local dietary intake pattern. Food products which carry this claim shall comply with the requirement as stated under our national nutrient claims guidelines found in the "Handbook on Nutrition Labelling" (published by Singapore's Health Promotion Board), if they are meant for sale in Singapore. The purpose of this guidance is to advise manufacturers who wish to use the implied nutrient content claim "healthy" to label their food products as provided by our regulations.
Low-fat labels are just one of the invisible cues that can make us reach for more. Wansink said that large containers or serving dishes also subconsciously coax us to eat more more calories than ... If a food claims to be …. It means that one serving* contains …. Fat free. Less than 0.5 g fat and no ingredient that is fat. Low fat. 3 g of fat or less (and not more than 30% of calories from fat for meals and main dishes) Reduced fat or less fat. At least 25% less fat than the regular product. Low in saturated fat. When a claim is made on a food that contains more than 13 g total fat, 4 g saturated fat, 60 mg cholesterol, or 480 mg sodium per RACC, per labeled serving, or, for foods with small RACC, per 50 g, a disclosure statement is required as part of claim (i.e., “See nutrition information for ___ content” with the blank filled in with nutrient(s) that exceed the prescribed levels). 4. The content of trans-fat (fatty acid) shall be listed in the Nutrition Information if ingredients contain hydrogenated fat and (or) partial hydrogenated fat, or it/they are used in the production process. 5. As to the nutritional components with no specified NRV, only content shall be claimed. 3. Optional Labeling Items 1.
Sep 16, 2009 — LOW-CALORIE no more than 40 calories for a given reference amount (except sugar substitutes); LOW-CHOLESTEROL 20 milligrams or less cholesterol ...
Low saturated fat as defined in § 101.62 (c) (3) 90 mg or less cholesterol per LS 5. At least 10 percent of the RDI or DRV per LS of two nutrients (for a main dish product) or of three nutrients...
Low Calorie Label Requirements. professional, and plagiarism free papers . We can't write you papers for free but we can offer you a reasonable price for a quality-oriented service. With Low Calorie Label Requirements the help Low Calorie Label Requirements of professional writers, you can improve your GPA easily and without any stress. Alice.
When levels exceed: 13g Fat, 4g Saturated Fat, 60mg Cholesterol, and 480mg Sodium per reference amount, per labeled serving or, for food with small reference amounts, per 50 g, disclosure statement...
A label may contain the terms "light" or "lite" if a food that derives 50% or more of its calories from fat has its fat content reduced by 50% or more per reference amount customarily consumed, or if a food that derives less than 50% of its calories from fat has the number of calories reduced by at least one-third per reference amount customarily consumed.18
The group is expected to recommend stricter labeling requirements to help consumers make smarter food choices. ... "During the low-fat craze, people ran out and bought low-fat Snackwell cookies ...
(a) General requirements. A claim about the level of fat, fatty acid, and cholesterol in a product may only be made on the label or in labeling of products if: (1) The claim uses one of the terms defined in this section in accordance with the definition for that term; (2) The claim is made in accordance with the general requirements for nutrient content claims in § 381.413; and
The food contains: (a) less than 0.5 gof fat per reference amountand serving of stated size; or. (b) less than 0.5 gof fat per serving of stated size, if the food is a prepackaged meal. Must comply with requirementsand conditionsfor making a nutrient content claim.
The FDA guidelines for using a low-calorie NCC are simple enough to understand and adhere to, but you need to be familiar with the Recommended Amount Customarily Consumed(RACC) for your particular product. This amount, which is a number set by the FDA to help food manufacturers determine portion sizes for their nutrition facts panel, will help you determine if your product fits within the low-calorie parameters. Once you’ve determined the RACC for your particular product, you can use online nutritional analysis software to instantly calculate the calories for the RACC. In order to be considered low-calorie, it must fit within the following guidelines: Low-Calorie: A maximum of 40 calories per RACC is considered low. If the RACC for your particular food product is less than 50 grams, calories can’t exceed 40 per 50-gram serving. For entire meals and main dishes, the calories cannot exceed 120 per 100 grams. Of course, there are other calorie-related NCCsof interest to consumers, incl...
Fat is an important part of your diet, but figuring out how much to eat can be confusing. Over the last 50 years, many people have moved from a moderate fat to a low fat diet, based on ...
A claim that a food is fat-free, and any claim likely to have the same meaning for the consumer, may only be made where the product contains no more than 0.5g of fat per 100g or 100ml. However,...
For a solid food product to claim as "low fat", it must contain not more than 3g of total fat per 100g of food but for a liquid product to claim as "low fat", it must contain not more than 1.5g of total fat per 100mL of food so Brand D milk cannot claim itself as "low fat".
Manufacturers who use this claim have to make sure the product meets strict criteria before they are allowed to print 'low in fat' on the food label. A 'low fat' or 'low in fat' food must contain no more than 3g of fat per 100g of food. A liquid must contain no more than 1.5g fat per 100g. 'Reduced fat' means the food must contain at least 25 percent less fat than the regular product to which it is being compared, and at least 3g less fat per 100g of food.
If you want to find products even lower in fat, look for the fat-free designation. To be labeled as fat-free, a product must have 0.5 grams of fat or less per serving. It must not have a fat-based ingredient like oil. Note that low fat does not necessarily mean a product is low in saturated fat.
Section II provides an overview of the basic food labeling requirements, including the prior label approval process, establishment responsibilities, temporary label approvals, and other facets of the preapproval process. Sections III through XII address in detail each of the up to eight

























0 Response to "35 low fat label requirements"
Post a Comment