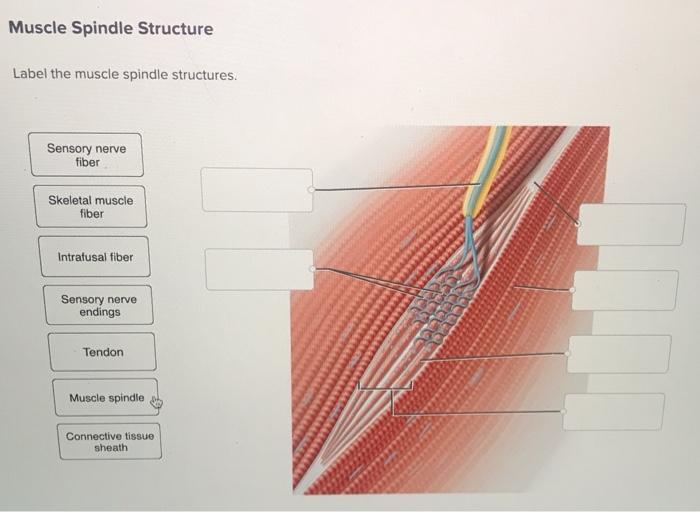
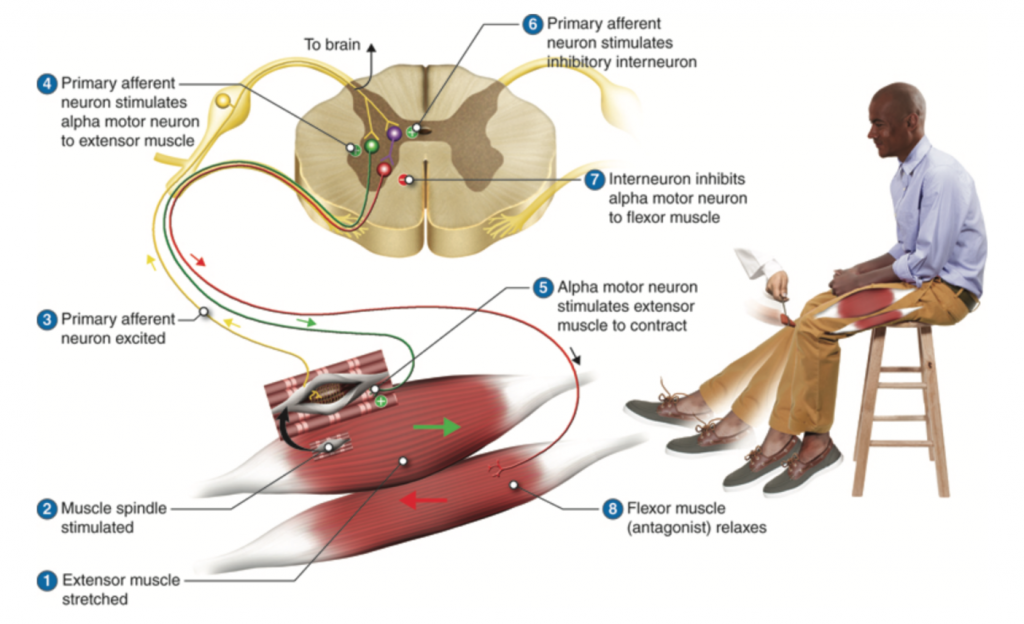
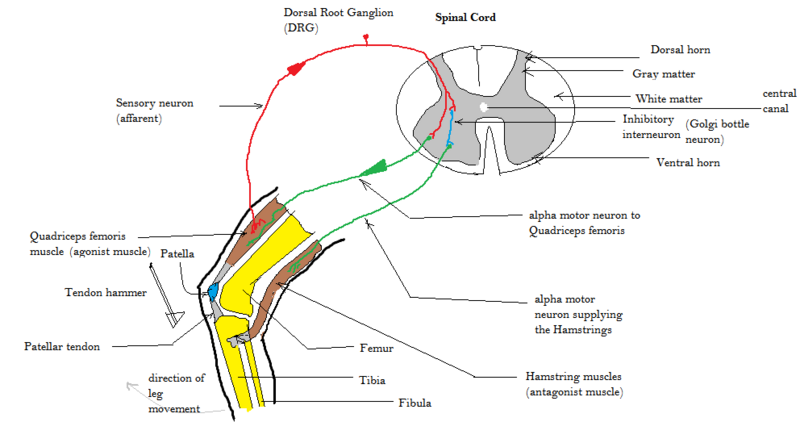
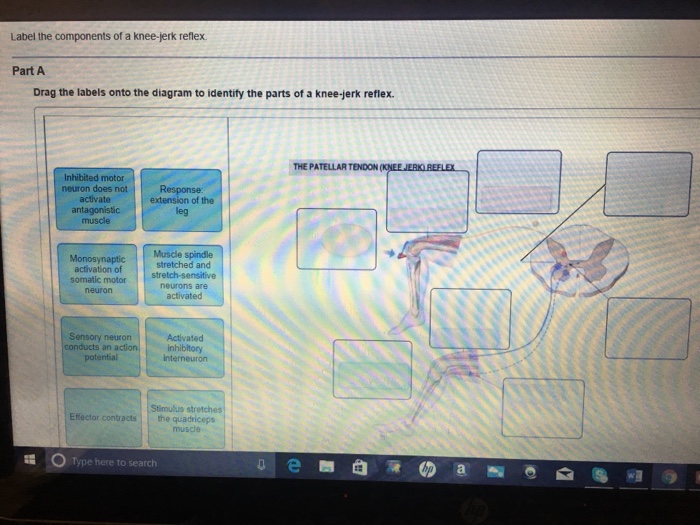
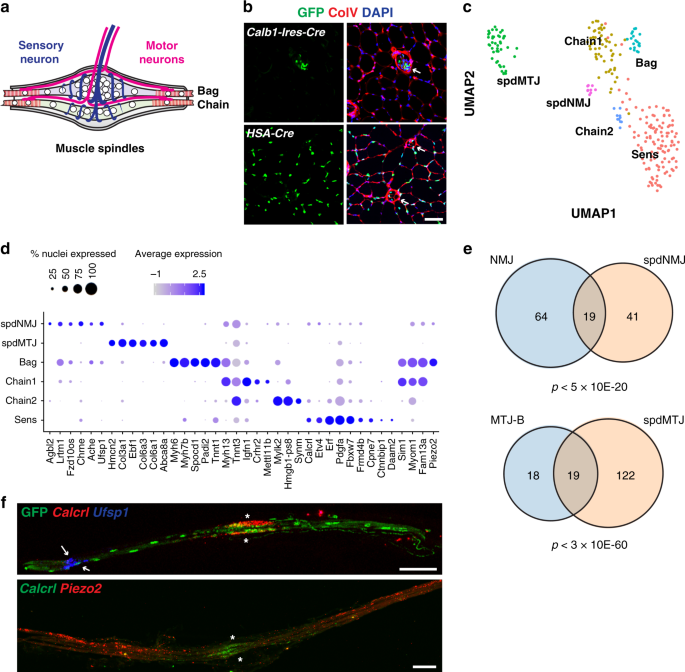
40 label the structures involved in muscle spindle function.
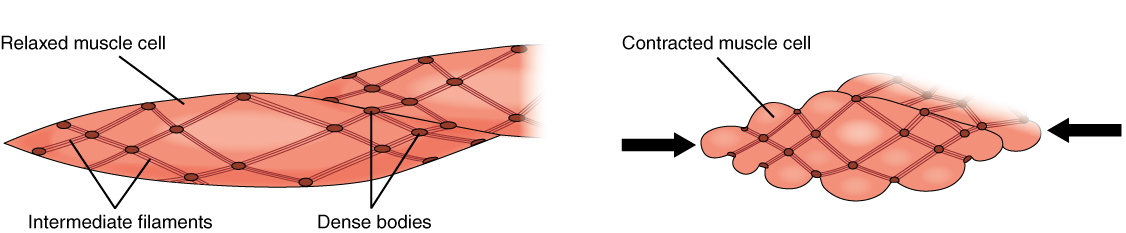
Smooth muscle cells are also relatively large, but are long and spindle shaped. Red blood cells and sperm are both exam- ples of small cells. Red blood cells appear round, while sperm cells are streamlined with long flagella. Cell shape is often directly related to function. Epithelial cells fit tightly together and cover large areas. Synaptic‐like vesicles (SLVs) in muscle spindle annulospiral endings. (A) The upper drawing is a reconstruction of a serially sectioned cat muscle spindle showing the incoming myelinated afferent axon arriving from below, as it then branches and eventually loses its myelin sheath to deliver a series of characteristically annulospiral endings wrapping around intrafusal muscle fibres.
Each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue that enclose it, provide structure to the muscle, and compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle (Figure 10.2.1). Each muscle is wrapped in a sheath of dense, irregular connective tissue called the epimysium , which allows a muscle to contract and move powerfully while ...
Label the structures involved in muscle spindle function.
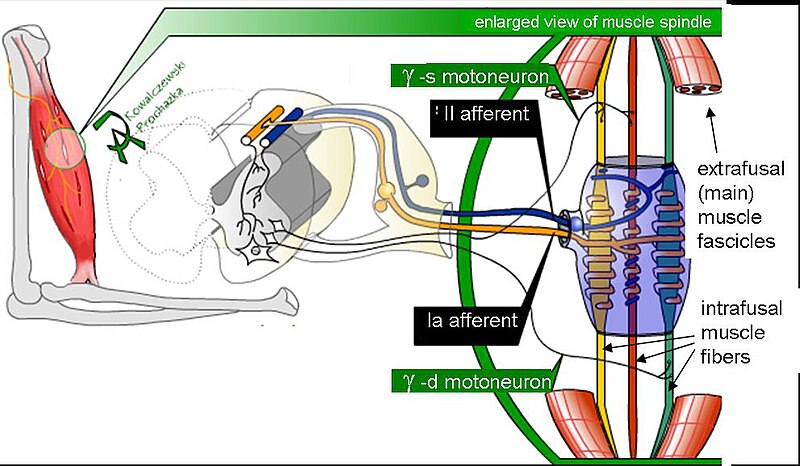
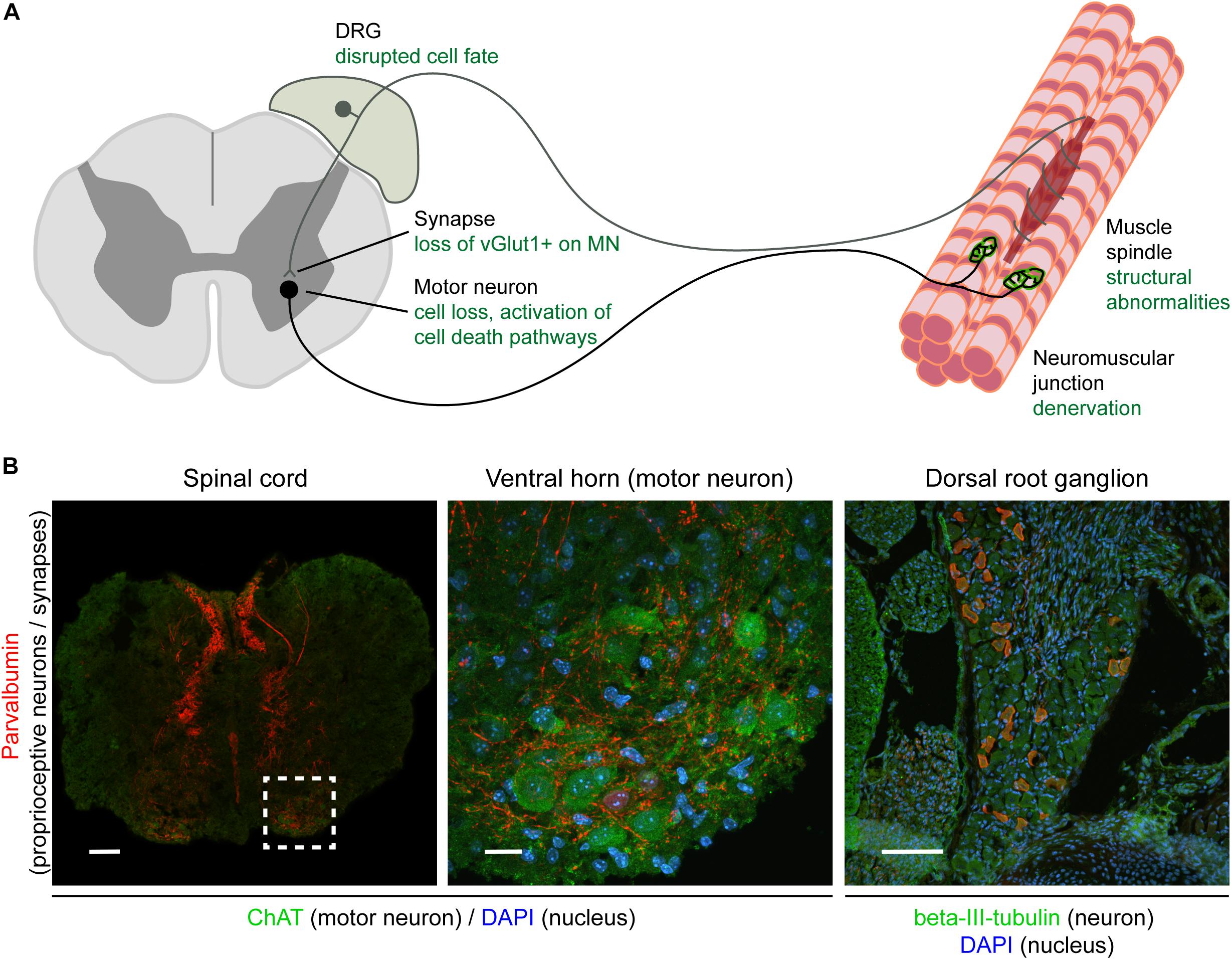
Cell Structures involved in Mitosis - Spindle Fibres, Centriole, Centrosomes, Sister Chromatids, Centromeres Spindle Fibres In Mitosis, Spindle Fibres form at opposite poles of the cell and meet at the equator. Collectively, they form a spindle-shaped structure which attach to Centromeres Centrioles The muscle spindle is an unusual receptor because it has a motor innervation (the fusimotor system), through which its responsiveness can be controlled by the brain. This article focuses on the underlying anatomy of the muscle spindle/fusimotor system and theories about its roles in normal function and neurological disease. A local potential depolarizes the axolemma of the trigger zone to threshold. 2. Voltage-gated sodium ion channels activate, sodium ions enter, and the axon section depolarizes. 3. Sodium ion channels inactivate, and voltage-gated potassium ion channels activate, so sodium ions stop entering and potassium ions leave, beginning repolarization. 4.
Label the structures involved in muscle spindle function.. This change is the function of the ciliary muscles of the ciliary body. Complete the sentences describing the structures involved in proprioception. The stretch receptors found in skeletal muscle near their tendons are called muscle spindles. Muscle spindles consist of functionally different central and peripheral parts. The central part is sensory where it is sensitive to stretching. On the other hand, the peripheral part is contractile and is innervated by the gamma-motor neuron. upper middle trunks lower roots (ventral rami): upper subscapular lower subscapular thoracodorsal medial cutaneous nerves of the arm and forearm long thoracic medial pectoral lateral pectoral nerve to subclavius suprascapular dorsal scapular posterior divisions anterior divisions lateral cords posterior medial axillary musculo- cutaneous radial … The double labeling technique was used to assess a possible co-innervation of both structures by the TMnu, which are known to provide sensory innervation to the masseter muscle spindles [ 13, 5 ].
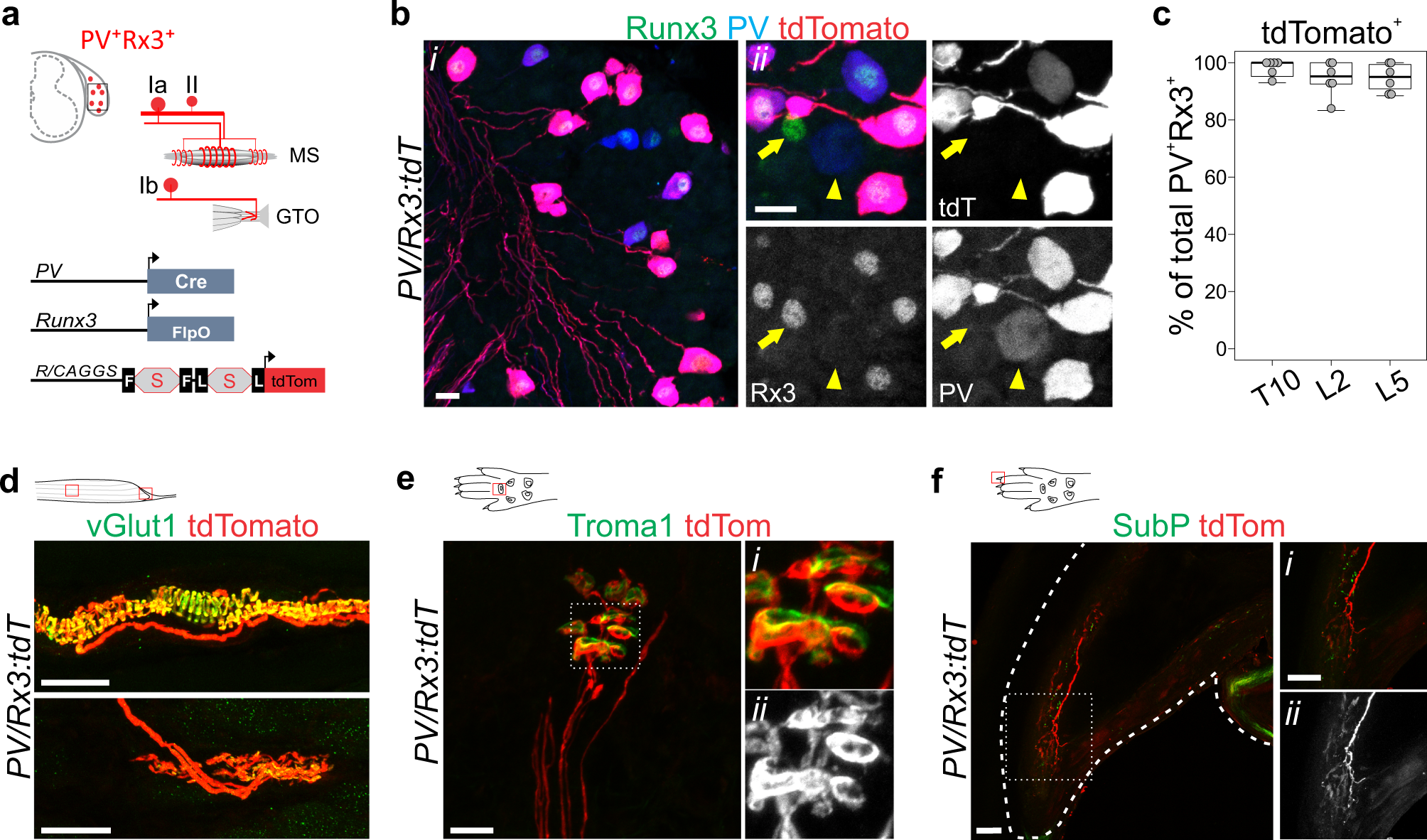
A smooth muscle is composed of cells that are narrow and spindle-shaped with a single nucleus that is located centrally. The cells of smooth muscles are made up of fibres of myosin and actin that run through the cells and are backed by a framework of various proteins, wherein the filaments are arranged in a stacked pattern across the cell. Muscle spindles are small sensory organs with an elongated shape, involved in proprioception. Image 2: Mammalian muscle spindle showing typical position in a muscle (left), neuronal connections in spinal cord (middle) and expanded schematic (right). The spindle is a stretch receptor with its own motor supply consisting of several intrafusal muscle fibres. Label the structures involved in muscle spindle function. Some boxes are used more than once. Muscle spindles are sensory receptors that are located in muscle. Their job is to detect changes in muscle length and the speed of change in muscle length. Below is an image of a muscle spindle. When muscles lengthen, the spindles are stretched. This stretch activates the muscle spindle which in turn sends an impulse to the spinal cord.
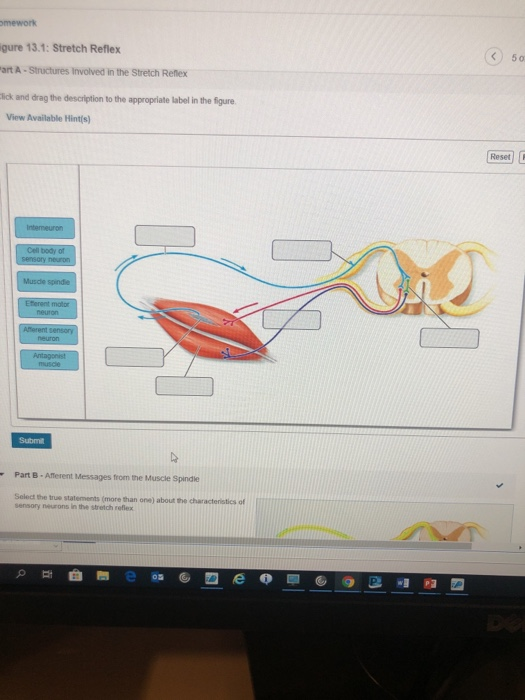
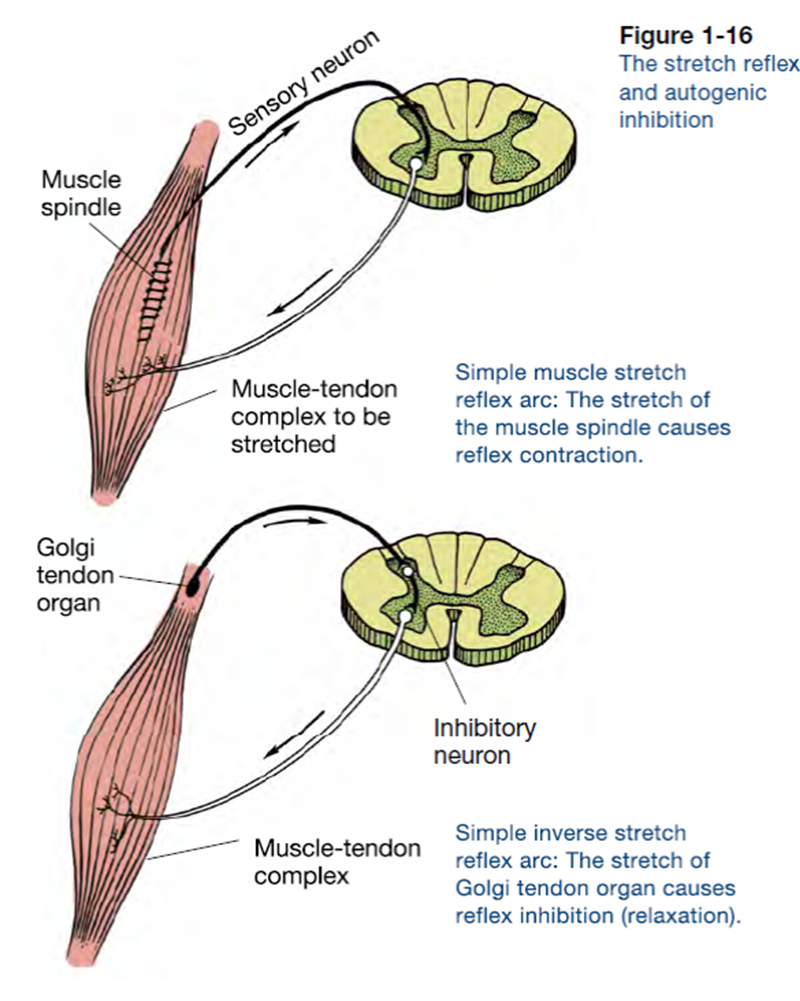
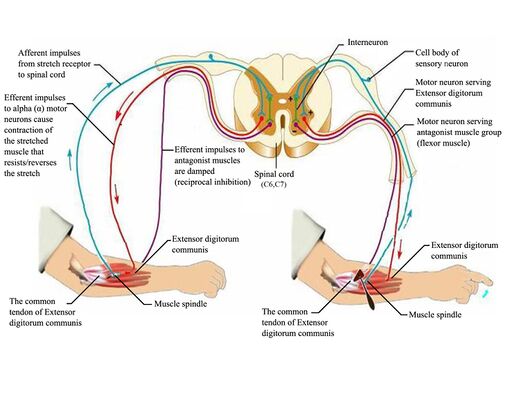
Anatomy of the Stretch Reflex. Located within the belly of the muscle, between and parallel to the main muscle fibers, are muscle spindles. These muscle spindles are made up of spiral threads called intrafusal fibers, and nerve endings, both encased within a connective tissue sheath. Biceps femoris muscle (posterior view) Embedded within a muscle are the muscle spindles. Muscle spindles are composed of a few intrafusal fibres (nuclear bag and nuclear chain are the subtypes), which in fact lack the contractile proteins of normal muscle (actin and myosin), they are non contractile, and they serve as receptive surfaces. In the last part of this coaching activity you will turn your attention to the crossed extensor reflex. You will first order the events that take place during this reflex. Then you will identify the type (s) of synapses found in this reflex arc. Finally, you will test your knowledge by applying what you have learned to a different/new reflex. Muscle Spindle and Golgi Tendon Organ Golgi Tendon Organ The golgi tendon organ is a proprioceptor, sense organ that receives information from the tendon, that senses TENSION. When you lift weights, the golgi tendon organ is the sense organ that tells you how much tension the muscle is exerting.
Epithelial tissues: location, structure and function of epithelial tissues. Epithelia line surfaces, form glands and act as receptor cells in sensory organs (Fig. 1).Epithelial tissues line internal and external surfaces, such as the external surface of the skin or the internal lining of the intestine.
are 3 . Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers by undivided structures called —4— If a cell undergoes mito- sis but not cytokinesis, the product is S The structure that acts as a scaffolding for chromosomal attachment and movement is called the 6 ._1_ is the period of cell life when the cell is not involved in division. Three cell popula-
Within the muscle, bundles of muscle fibers or cells, known as fascicles, are bound together by another layer of connective tissue known as the perimysium. Every muscle fiber or cell within a fascicle is itself encased in a layer of connective tissue called endomysium
Label the structures involved in muscle spindle function. * Alpha motor neurons activate extrafusal muscle fibers * Gamma motor neurons activate intrafusal fibers * Both Extrafusal & Intrafusal muscle fibers contract * Stretch receptor activation in center of spindle remains Constant
Diagram and label the structures involved. (Hint: Keep it simple; for example, you could draw a rectangle and label it "right leg muscle" and another for the left, and don't worry about drawing all neurons involved, just enough to show you understand the basics.
Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers by are undivided structures called 4 . If a cell undergoes mito- sis but not cytokinesis, the product is 5 . The structure that acts as a scaffolding for chromosomal attachment and movement is called the 6 7 is the period of cell life when the cell is not involved in division. Three cell popula-
Transcribed image text: Drag the labels onto the diagram of muscle spindle function. Reset Muscle shortens Strelch receptors in the spinde are activated throughout the contraction Muscle length Gamma mator neurons activate intrafusal fibers Intrafusal fibers do not slacken so firing rate remains constant. Alpha motor neurons activate extrafusal muscle bers Action potentials of spindle sensory neuron Muscle shortens Time Sensitivity to muscle stretch is maintained over the range of muscle ...
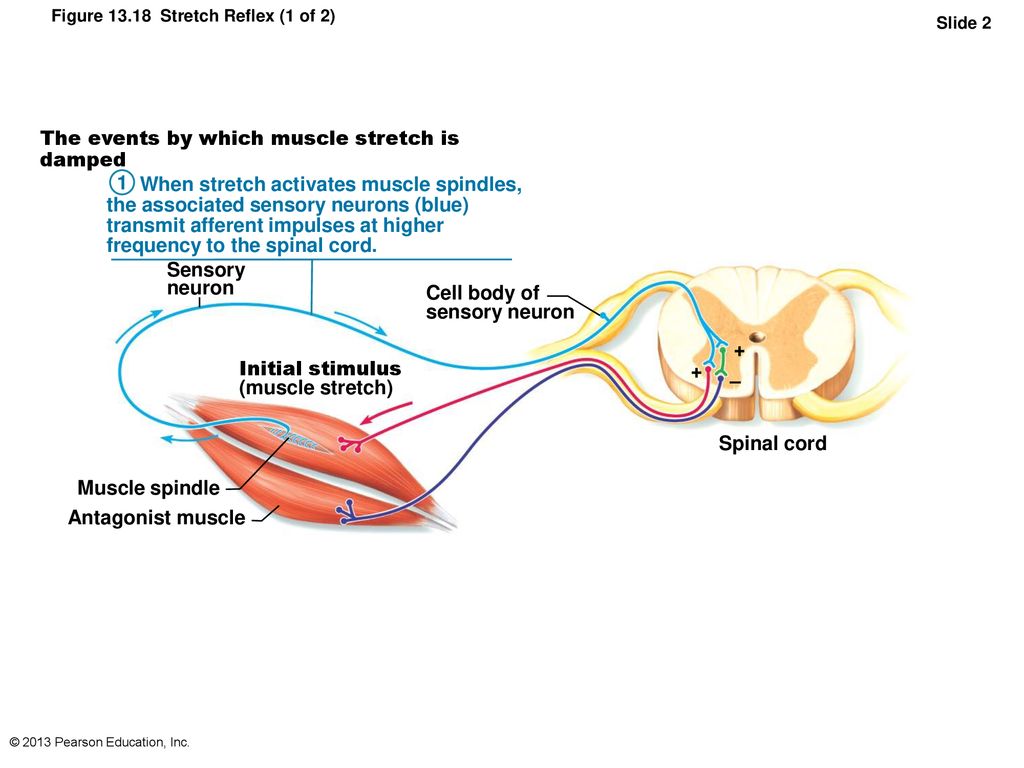
The pathway can be described as a 'reflex arc' which is made up of 5 components: A receptor - muscle spindle An afferent fibre - muscle spindle afferent An integration centre - lamina IX of spinal cord An efferent fibre - α-motoneurones An effector - muscle
A local potential depolarizes the axolemma of the trigger zone to threshold. 2. Voltage-gated sodium ion channels activate, sodium ions enter, and the axon section depolarizes. 3. Sodium ion channels inactivate, and voltage-gated potassium ion channels activate, so sodium ions stop entering and potassium ions leave, beginning repolarization. 4.
The muscle spindle is an unusual receptor because it has a motor innervation (the fusimotor system), through which its responsiveness can be controlled by the brain. This article focuses on the underlying anatomy of the muscle spindle/fusimotor system and theories about its roles in normal function and neurological disease.
Cell Structures involved in Mitosis - Spindle Fibres, Centriole, Centrosomes, Sister Chromatids, Centromeres Spindle Fibres In Mitosis, Spindle Fibres form at opposite poles of the cell and meet at the equator. Collectively, they form a spindle-shaped structure which attach to Centromeres Centrioles















:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nucleus-of-skeletal-muscle-fiber/3fBKxdMoyUFj8fsymsuRrw_134Nucleus_of_skeletal_muscle_fiber_magnified.png)


0 Response to "40 label the structures involved in muscle spindle function."
Post a Comment