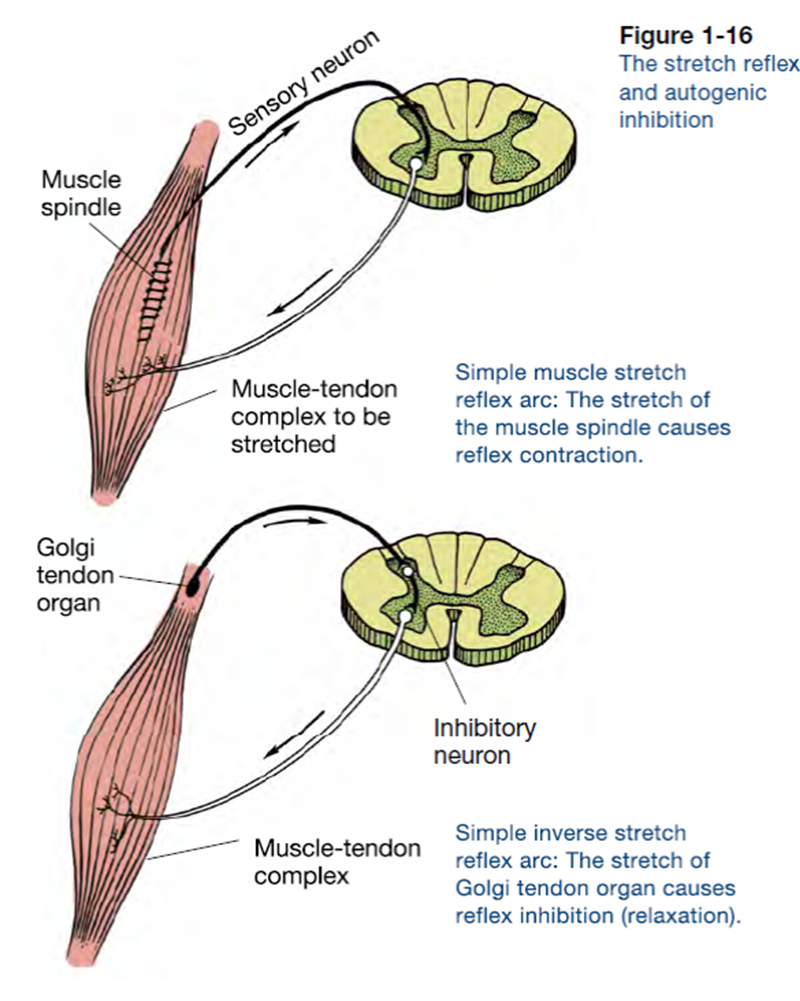
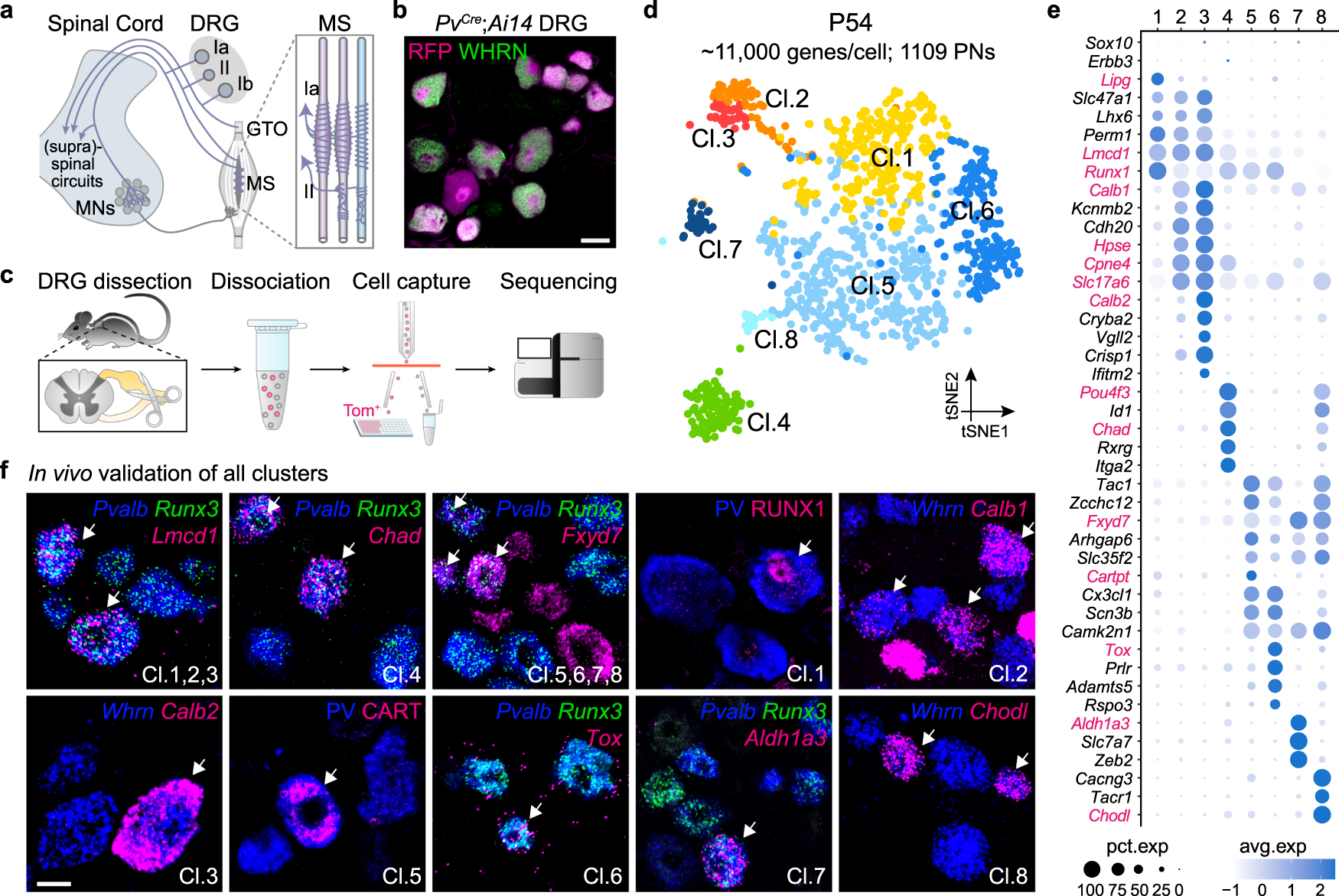
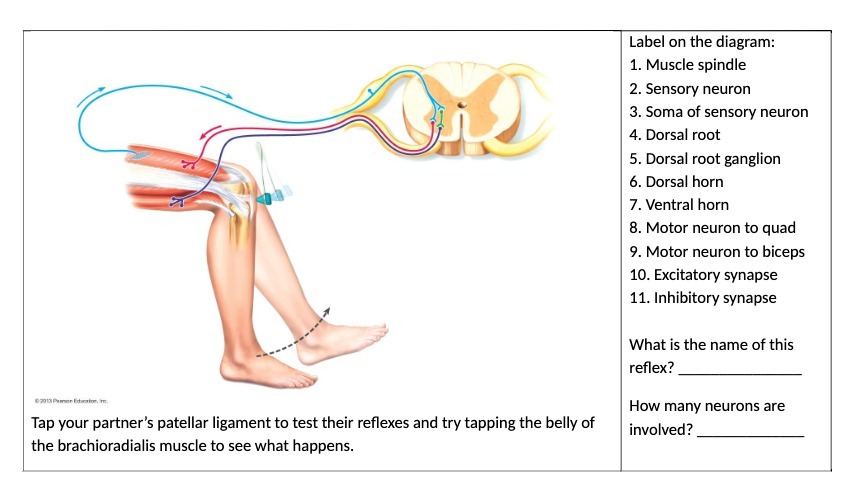
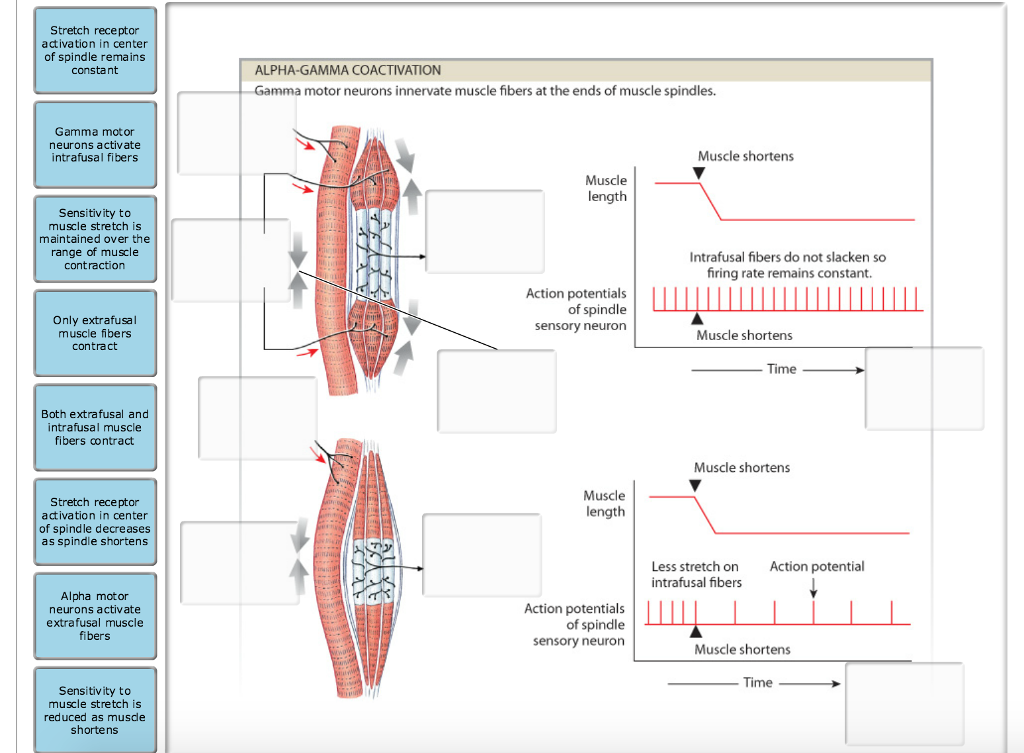
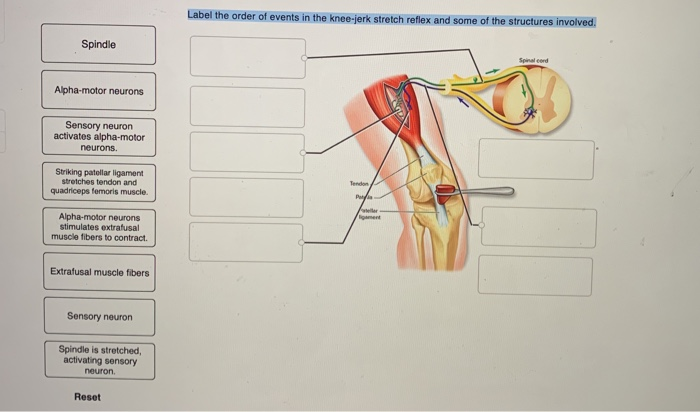
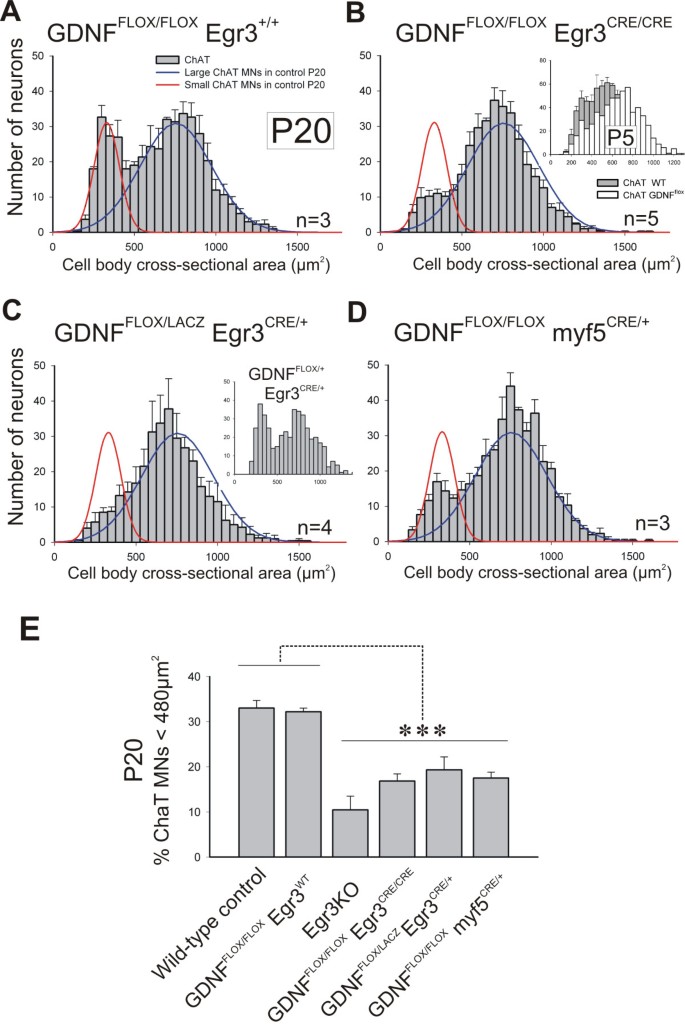
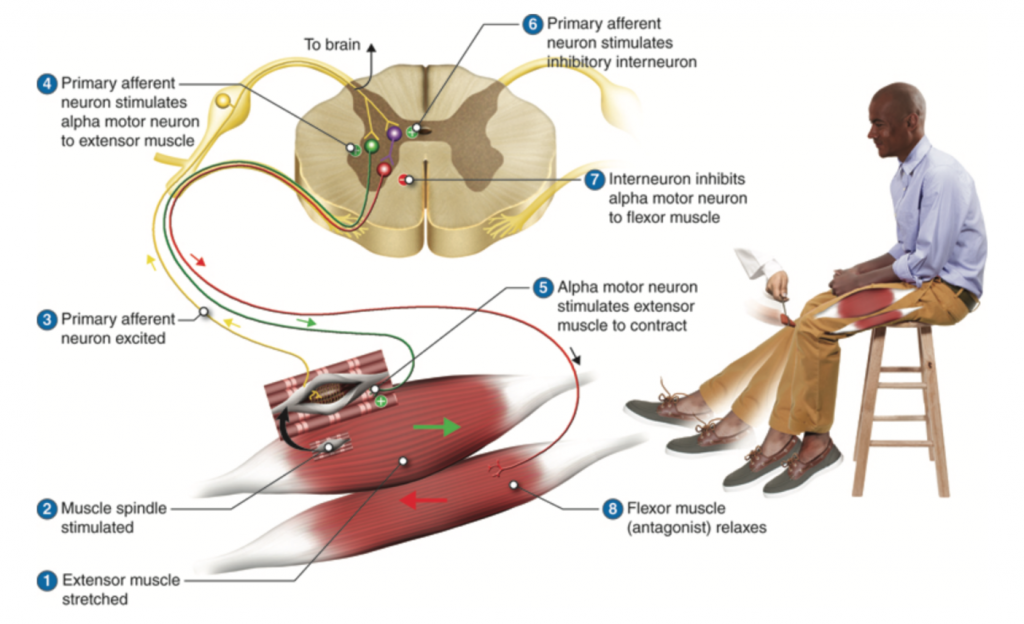
37 label the structures involved in muscle spindle function.
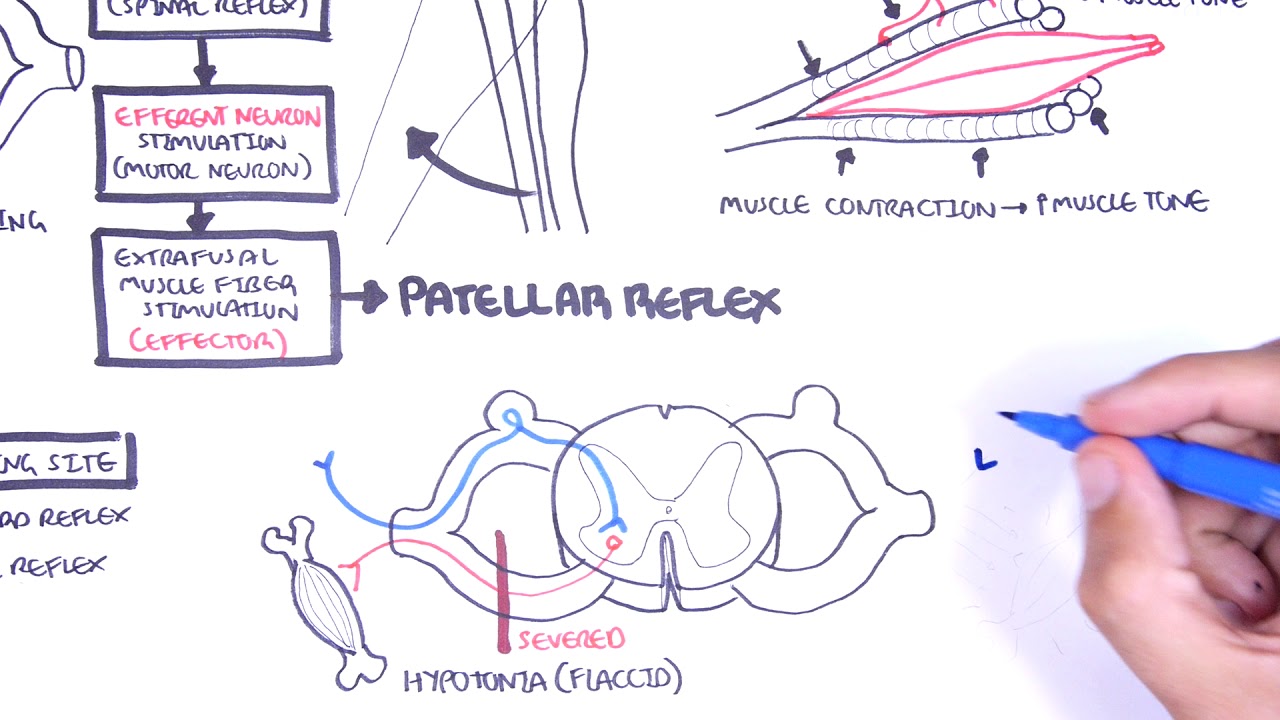
Neuromuscular junction: Parts, structure and steps - Kenhub Within the muscle, bundles of muscle fibers or cells, known as fascicles, are bound together by another layer of connective tissue known as the perimysium. Every muscle fiber or cell within a fascicle is itself encased in a layer of connective tissue called endomysium Muscle Stretch Reflex - Reflex Arc Components ... The pathway can be described as a 'reflex arc' which is made up of 5 components: A receptor - muscle spindle An afferent fibre - muscle spindle afferent An integration centre - lamina IX of spinal cord An efferent fibre - α-motoneurones An effector - muscle
NUCLEAR ENVELOPE - City University of New York Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers by are undivided structures called 4 . If a cell undergoes mito- sis but not cytokinesis, the product is 5 . The structure that acts as a scaffolding for chromosomal attachment and movement is called the 6 7 is the period of cell life when the cell is not involved in division. Three cell popula-

Label the structures involved in muscle spindle function.
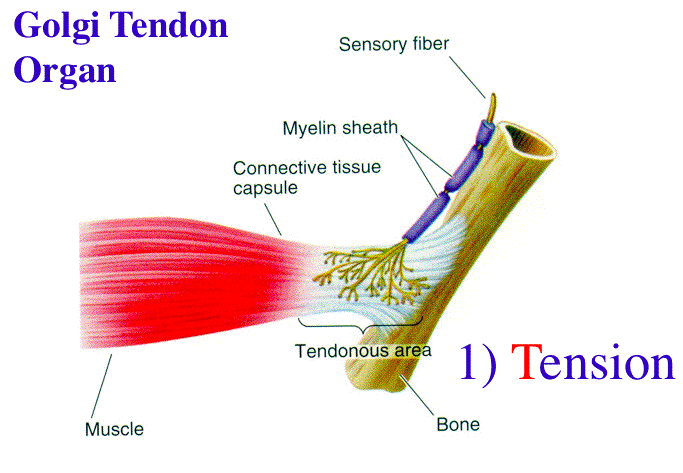
Golgi Tendon Organs and Muscle Spindles Explained | ACE The function of the GTO can be considered opposite of the muscle spindle, which serves to produce muscle contraction. Imagine a muscle spindle as if it were a thread spiraled (or wrapped around) muscle fibers near the muscle belly; as the muscle lengthens or stretches, it pulls on the spindle causing it to lose its spiral shape and also stretch. A+P Ch. 12 questions Flashcards & Practice Test - Quizlet Drag each label into the appropriate category to designate which reflex is described by the following terms or structures. Stretch Reflex - Muscle Spindles -Initiated by an increase in muscle length Withdrawal Reflex -Removes body part from painful stimulus Golgi Tendon Reflex -Receptors embedded in collagen of tendons Cell Structures involved in Mitosis - Spindle Fibres ... Cell Structures involved in Mitosis - Spindle Fibres, Centriole, Centrosomes, Sister Chromatids, Centromeres. Spindle Fibres. In Mitosis, Spindle Fibres form at opposite poles of the cell and meet at the equator. Collectively, they form a spindle-shaped structure which attach to Centromeres.
Label the structures involved in muscle spindle function.. Solved Gamma motor neurons activate innervate muscle ... Label the structures involved in muscle spindle function. Some boxes are used more than once. Muscle Spindle and Golgi Tendon Organ - University of New ... Muscle Spindle and Golgi Tendon Organ Golgi Tendon Organ The golgi tendon organ is a proprioceptor, sense organ that receives information from the tendon, that senses TENSION. When you lift weights, the golgi tendon organ is the sense organ that tells you how much tension the muscle is exerting. Muscle Spindles and the Stretch Reflex - PT Direct Muscle spindles are sensory receptors that are located in muscle. Their job is to detect changes in muscle length and the speed of change in muscle length. Below is an image of a muscle spindle. When muscles lengthen, the spindles are stretched. This stretch activates the muscle spindle which in turn sends an impulse to the spinal cord. Muscular Tissue - Structure, Functions and Types of ... Muscular tissue is a specialized tissue in animals which applies forces to different parts of the body by contraction. It is made up of thin and elongated cells called muscle fibers. It controls the movement of an organism. The cytoplasm in the muscle fibers is called sarcoplasm. It contains a network of membrane called the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Ch. 13 M & P Flashcards | Quizlet Label the structures involved in muscle spindle function. * Alpha motor neurons activate extrafusal muscle fibers * Gamma motor neurons activate intrafusal fibers * Both Extrafusal & Intrafusal muscle fibers contract * Stretch receptor activation in center of spindle remains Constant Muscle spindles - Physiopedia Muscle spindles are small sensory organs with an elongated shape, involved in proprioception. Image 2: Mammalian muscle spindle showing typical position in a muscle (left), neuronal connections in spinal cord (middle) and expanded schematic (right). 10.2 Skeletal Muscle - Anatomy & Physiology These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue that enclose it, provide structure to the muscle, and compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle ( Figure 10.2.1 ). NucleolusTrevor Wright Smooth Endoplasmic ... are 3 . Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers by undivided structures called —4— If a cell undergoes mito- sis but not cytokinesis, the product is S The structure that acts as a scaffolding for chromosomal attachment and movement is called the 6 ._1_ is the period of cell life when the cell is not involved in division. Three cell popula-
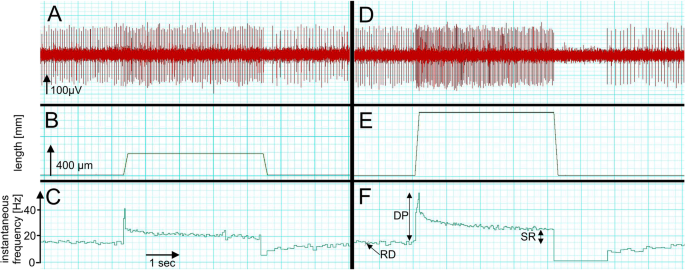
13.1 Sensory Receptors - Anatomy & Physiology 13.1 Sensory Receptors. A major role of sensory receptors is to help us learn about the environment around us, or about the state of our internal environment. Different types of stimuli from varying sources are received and changed into the electrochemical signals of the nervous system. This process is called sensory transduction. Chapter 13 Physiology Mastering A&P Flashcards | Quizlet In the last part of this coaching activity you will turn your attention to the crossed extensor reflex. You will first order the events that take place during this reflex. Then you will identify the type (s) of synapses found in this reflex arc. Finally, you will test your knowledge by applying what you have learned to a different/new reflex. Motor Units and Muscle Receptors (Section 3, Chapter 1 ... Muscle Spindles. Muscle spindles are collections of 6-8 specialized muscle fibers that are located within the muscle mass itself (Figure 1.7). These fibers do not contribute significantly to the force generated by the muscle. Rather, they are specialized receptors that signal (a) the length and (b) the rate of change of length (velocity) of the ... Lap Practical #1 EC Flashcards | Quizlet Muscles and nerves exhibit similarities in structure and nomenclature. Drag each label into the appropriate position to identify the neural structure that would correspond to the muscular image. Place the following labels in order indicating the passage of sound waves through the ear and hearing apparatus starting outside the ear.
Spinal Reflex: Anatomy and Examples | Kenhub Muscle spindles consist of functionally different central and peripheral parts. The central part is sensory where it is sensitive to stretching. On the other hand, the peripheral part is contractile and is innervated by the gamma-motor neuron.
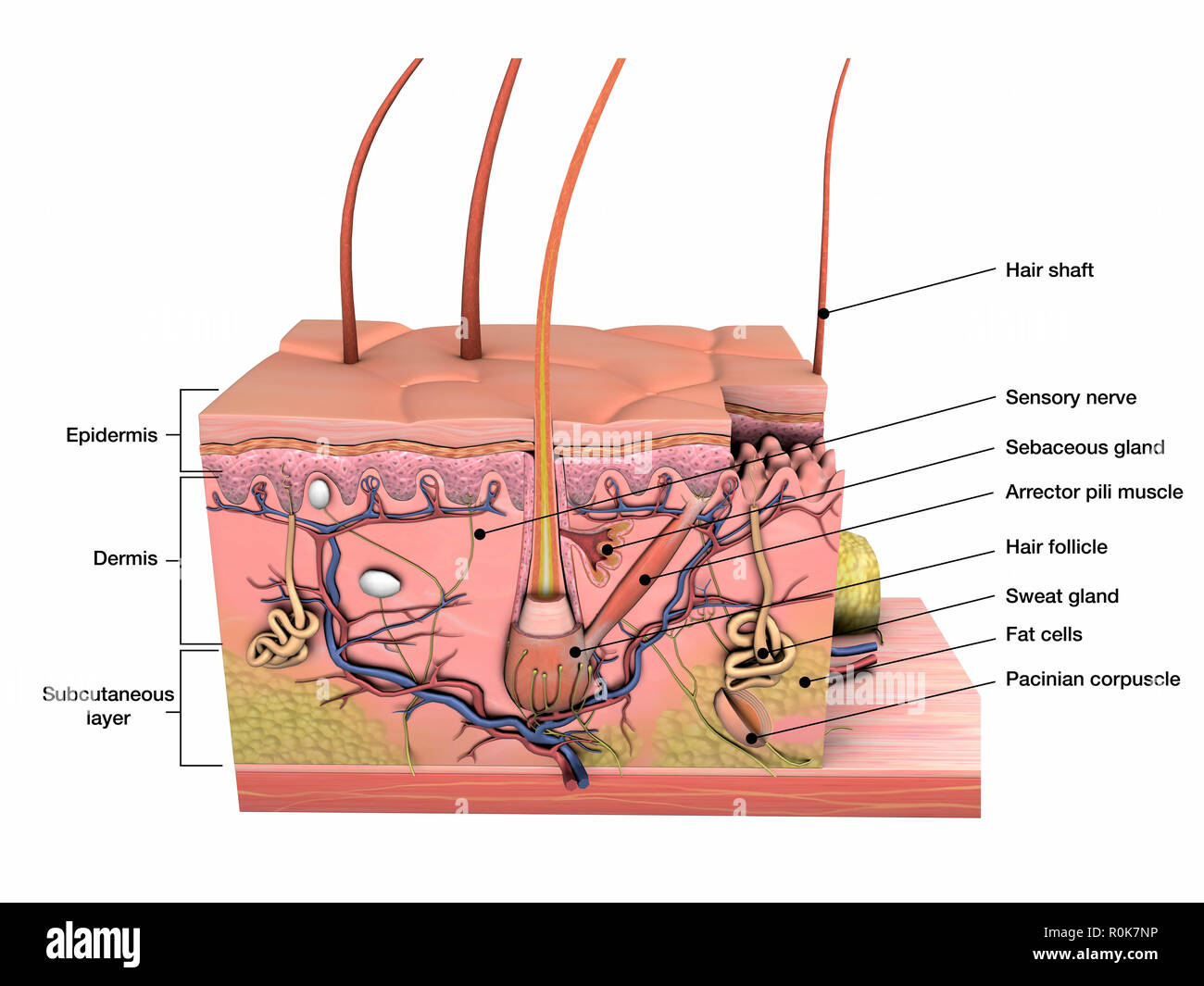
Stretch reflex: Anatomy | Kenhub Biceps femoris muscle (posterior view) Embedded within a muscle are the muscle spindles. Muscle spindles are composed of a few intrafusal fibres (nuclear bag and nuclear chain are the subtypes), which in fact lack the contractile proteins of normal muscle (actin and myosin), they are non contractile, and they serve as receptive surfaces.
PDF Human Cell Diagram, Parts, Pictures, Structure and Functions Structure and Functions The cell is the basic functional in a human meaning that it is a self-contained and fully operational living entity. Humans are multicellular organisms with various different types of cells that work together to sustain life. Other non-cellular components in the body include water, macronutrients
Intro, homeostasis, muscle & nerve physiology Intro Lecture, Homestatic Control, & Neuromuscular Function and Adaptations Introductory Lecture ... Class, make sure you can draw and label the gross structure of skeletal muscle. ... What does the muscle spindle respond do within the muscle.
Understanding the Stretch Reflex (or Myotatic Reflex) Located within the belly of the muscle, between and parallel to the main muscle fibers, are muscle spindles. These muscle spindles are made up of spiral threads called intrafusal fibers, and nerve endings, both encased within a connective tissue sheath.
Muscle Contraction - Muscle Spindle - Athabasca University The intrafusal fibers composing the muscle spindle are so small that they contribute little to the force of contraction. Some specialized muscle spindles are sensitive to the rate of change of muscle length. The density of muscle spindles is greatest in those muscles involved in precise movements such as those controlling the hand.
Skeletal Muscles - Structure, Function And Types A smooth muscle is composed of cells that are narrow and spindle-shaped with a single nucleus that is located centrally. The cells of smooth muscles are made up of fibres of myosin and actin that run through the cells and are backed by a framework of various proteins, wherein the filaments are arranged in a stacked pattern across the cell.
Exercise 4: the cell: anatomy and division review sheet ... label the cell structures using the leader lines provided. main site of ATP synthesis. ... Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers by undivided structures called _____ centromeres. ... attachment and movement is called the _____. mitotic spindle _____ is the period of cell life when the cell is not involved in division. interphase.
Cell Structures involved in Mitosis - Spindle Fibres ... Cell Structures involved in Mitosis - Spindle Fibres, Centriole, Centrosomes, Sister Chromatids, Centromeres. Spindle Fibres. In Mitosis, Spindle Fibres form at opposite poles of the cell and meet at the equator. Collectively, they form a spindle-shaped structure which attach to Centromeres.
A+P Ch. 12 questions Flashcards & Practice Test - Quizlet Drag each label into the appropriate category to designate which reflex is described by the following terms or structures. Stretch Reflex - Muscle Spindles -Initiated by an increase in muscle length Withdrawal Reflex -Removes body part from painful stimulus Golgi Tendon Reflex -Receptors embedded in collagen of tendons
Golgi Tendon Organs and Muscle Spindles Explained | ACE The function of the GTO can be considered opposite of the muscle spindle, which serves to produce muscle contraction. Imagine a muscle spindle as if it were a thread spiraled (or wrapped around) muscle fibers near the muscle belly; as the muscle lengthens or stretches, it pulls on the spindle causing it to lose its spiral shape and also stretch.








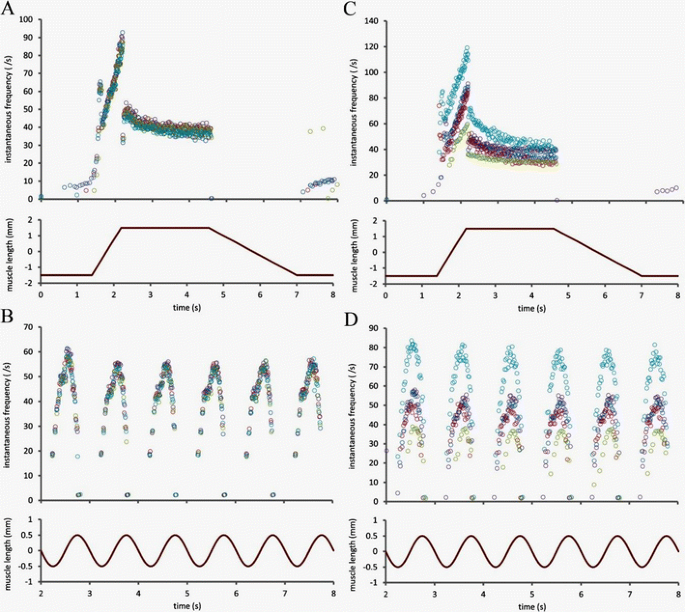


:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7173/Skeletal_muscle_01.png)

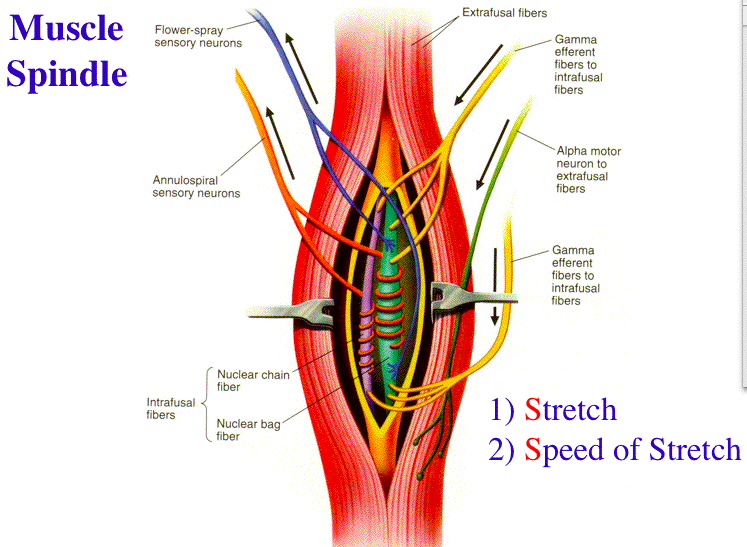



0 Response to "37 label the structures involved in muscle spindle function."
Post a Comment