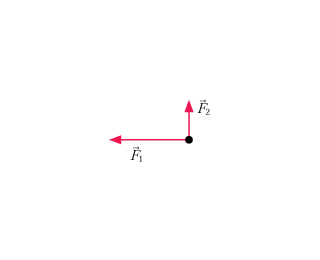
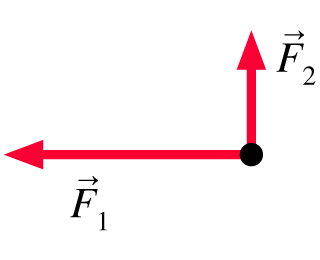
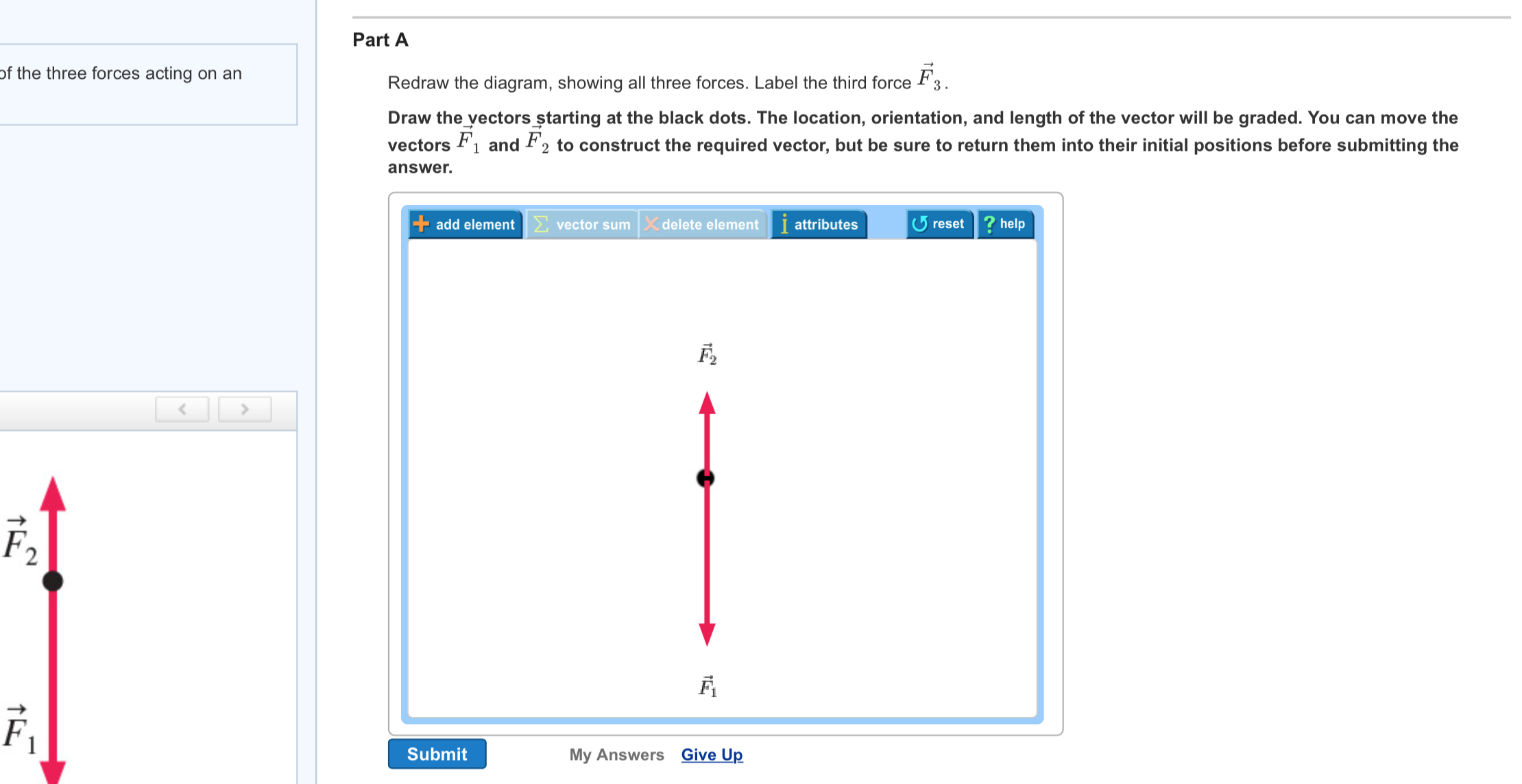
38 redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3.
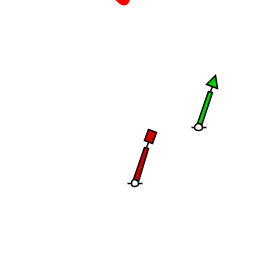
(Get Answer) - The figure shows two forces acting on an ... The figure ( Figure 1 ) below shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F ? 3. Draw the force vector with its tail at the dot. The orientation of your vectors... Draw the free-body diagram, showing all the forces acting ... Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. You can move the vectors F⃗ 1 and F⃗ 2 to construct the required vector, but be sure to return them into their initial positions before submitting ...
PDF Chapter 5. Force and Motion - Physics & Astronomy 3) Find the net force (vector sum of all individual forces) 4) Find the acceleration of the object (second Newton's law) 5) With the known acceleration find kinematics of the object
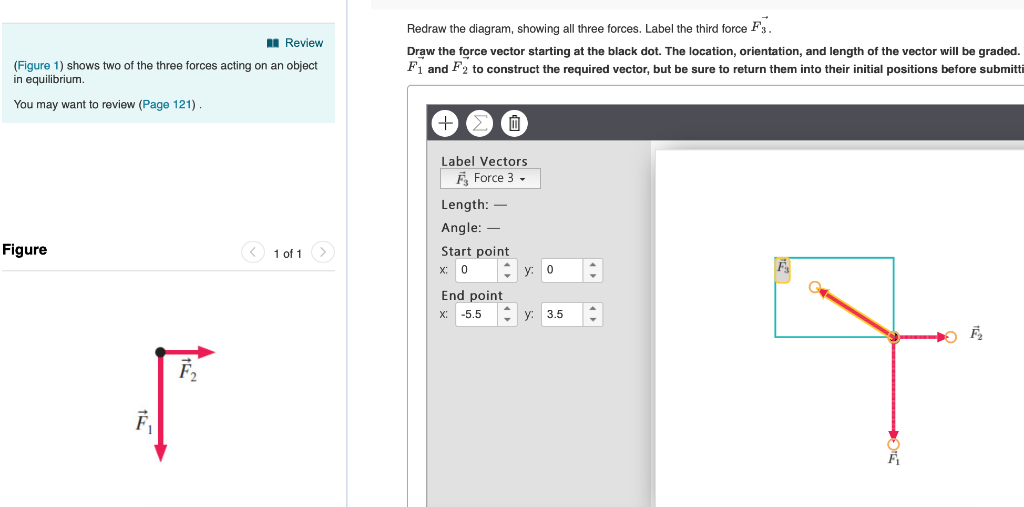
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3.
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third ... Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. You can move ...1 answer · 0 votes: Third force is shown below For equilibrium, the net force becomes zero F_1 + F_2 + F_3 = 0 F_1 (-j) + F_2 i + F_3x i + F_3y j = 0 From this F_3x = -F_2 ... Solved Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label ... Science; Physics; Physics questions and answers; Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force; Question: Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - General Physics Using ... Draw a free-body diagram; be sure to include the friction of the road that opposes the forward motion of the car. A runner pushes against the track, as shown. (a) Provide a free-body diagram showing all the forces on the runner. ( Hint: Place all forces at the center of his body, and include his weight.)
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3.. Determining the Net Force - Physics Classroom The addition of force vectors can be done in the same manner in order to determine the net force (i.e., the vector sum of all the individual forces). Consider the three situations below in which the net force is determined by summing the individual force vectors that are acting upon the objects. Resultant Force - Vector diagrams of forces: graphical ... Three forces in equilibrium (triangle of forces) The vectors of three forces acting in the same plane on a body can be drawn on a flat sheet of paper. Forces that act in the same plane are said to be coplanar. If the three forces acting on a body are in equilibrium, any one force balances out the effects of the other two forces. 1. Consider the diagram showing two force vectors: a) If ... Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force... Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. SOLVED:Show two of the three forces acting on an object in ... Problem 19 Easy Difficulty. Show two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force $\vec{F}_{3}$.
OneClass: Equilibrium of Forces: The forces F1, F2, …, Fn ... Equilibrium of Forces: The forces F 1, F 2, …, F n acting at the same point P are said to be in equilibrium if the resultant force is zero, that is, if F 1+ F 2+ … F n =0Find (a) the resultant forces acting at P, and (b) the additional force required (if any) for the forces to be in equilibrium. F 1 = 〈2, 5〉, F 2 = 〈3, −8〉 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams | University Physics Volume 1 Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... (Solved) - (Figure 1) shows two of the three forces acting ... The figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest.(Figure 1)Redraw the diagram, then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Label the new force F⃗ 3. (Remember to return all the vectors you have moved to their... Solved Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label ... Question: Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F⃗ 3F→3. Draw the vectors starting at the black dots. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. You can move the vectors F⃗ 1F→1 and F⃗ 2F→2 to construct the required vector, but be sure to return them into their initial positions ...
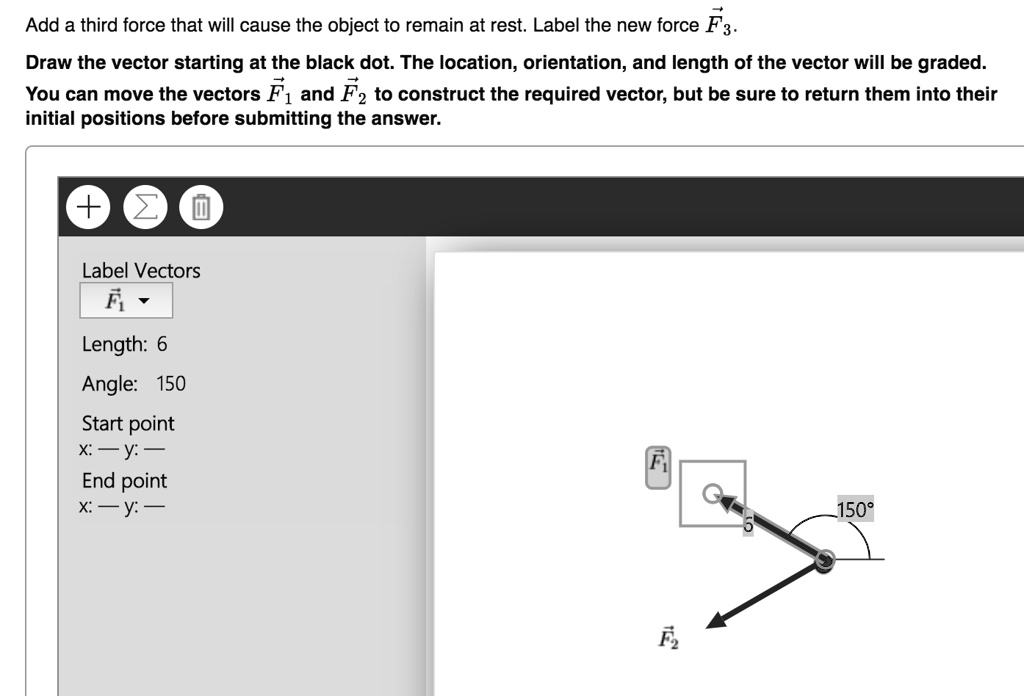
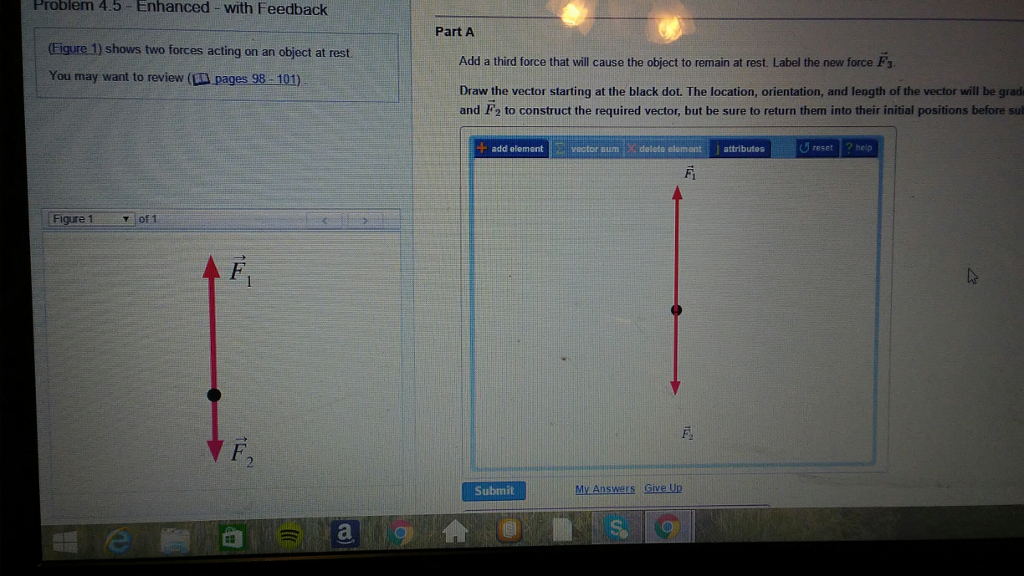
31 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain ... Label the new force f 3. Redraw the diagram then add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. Add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. The figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest. Label the new force f⃠3. Solved part A Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Question: part A Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F3 Draw the vectors starting at the black dots.1 answer · Top answer: the resulta... 31 Add A Third Force That Will Cause The Object To Remain ... Part a redraw the diagram showing all three forces. Redraw the diagram then add a third force that will cause theobject to remain at rest. Add a third force that will cause the object to remain at rest. That will cause the object to remain at rest. Label the third force f3. The figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest. Answered: FIGURE P4.6 | bartleby Figure shows two forces acting on an object at rest. Redraw the diagram, then add a third force that results in a net force of zero. Label the new force F→3 . Transcribed Image Text: FIGURE P4.6. Expert Solution.
PDF Lab 5 Forces in Equilibrium - University of Minnesota Duluth 3 into components. Set up on the force table the force ! 3 you calculated. Set a pulley for a new force ! 4 at 180 o, and a pulley for a new force ! 5 at -90 o (= +270o) as shown in Figure 4. ! Figure 4 Adjust the masses producing ! 4 and ! 5 so that all three forces put the ring in equilibrium. From considering the sum of the components, ! 4 ...
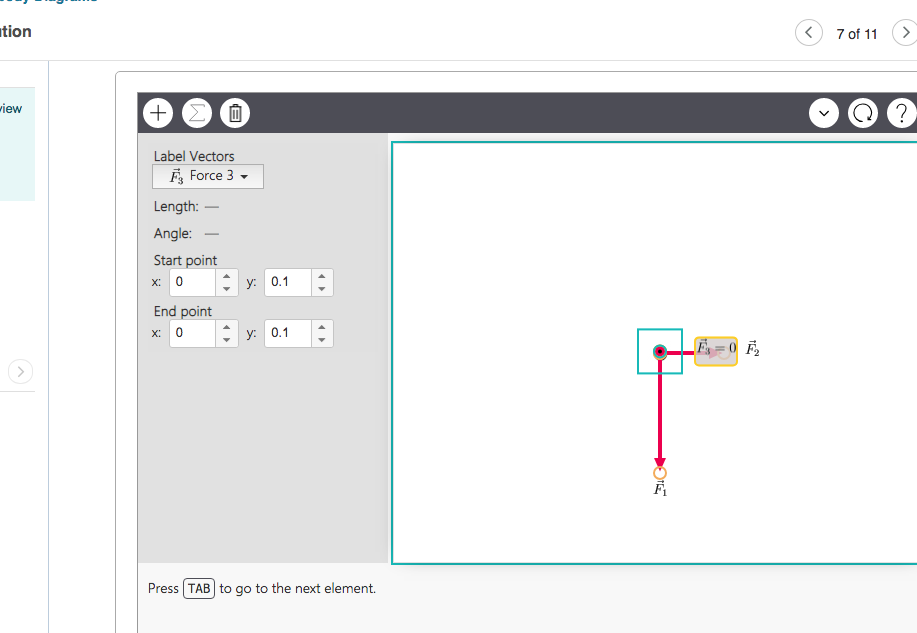
Solved (Figure 1) shows two of the three forces acting on ... Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. You can move the vectors F⃗ 1 and F⃗ 2 to construct the required vector, but be sure to return them into their initial positions before submitting the answer.
PDF Chapter 3: Rigid Bodies; Equivalent Systems of forces out what forces the body is carrying. Note: 3.1 -3.3 Introduction, Internal & External Forces For example: force of gravity, applied external force on an object. External forces on a rigid body are due to causes that are external to the body. They can cause the body to move or remain at rest as a whole.
PDF Lab 3.Adding Forces with a Force Table ary, the sum of the three applied forces is zero. You can compute the magnitude of each force from the value of the hanging masses. (F =mg. In Pullman, the magnitude of g equals 9.80 m/s2.) The direction of each force can be read from the angle marking on the force table. A diagram showing how the three force vectors sum to zero is shown in ...
Figure below shows two of the three forces acting on an ... Figure below shows two of the three forces acting on an object in equilibrium. a. Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force {eq}\vec F_3 {/eq}.
Solved Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label ... Question: Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded.
5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - General Physics Using ... Draw a free-body diagram; be sure to include the friction of the road that opposes the forward motion of the car. A runner pushes against the track, as shown. (a) Provide a free-body diagram showing all the forces on the runner. ( Hint: Place all forces at the center of his body, and include his weight.)
Solved Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label ... Science; Physics; Physics questions and answers; Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force; Question: Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third force
Redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. Label the third ... Label the third force F⃗ 3. Draw the force vector starting at the black dot. The location, orientation, and length of the vector will be graded. You can move ...1 answer · 0 votes: Third force is shown below For equilibrium, the net force becomes zero F_1 + F_2 + F_3 = 0 F_1 (-j) + F_2 i + F_3x i + F_3y j = 0 From this F_3x = -F_2 ...















0 Response to "38 redraw the diagram, showing all three forces. label the third force f⃗ 3."
Post a Comment