41 label the parts of the holoenzyme structure.
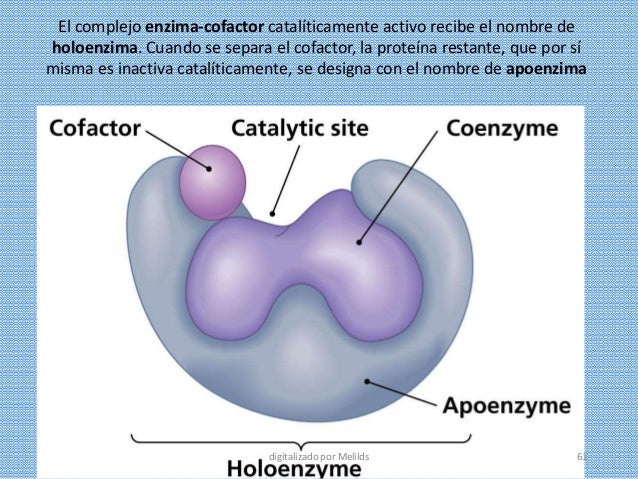
Holoenzyme: Definition & Overview - Video & Lesson ... An apoenzyme needs to become a holoenzyme (apoenzyme + cofactor) in order to function. The function of a holoenzyme is to change substrate into product, just like an enzyme does, but holoenzymes... Solved Label the parts of the holoenzyme structure. Drag ... Ans)Label the parts of the holoenzyme structure. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. holoenzyme is a complete active enzyme which is helo … View the full answer Transcribed image text: Inorganic cofactor Active site Coenzyme (organic cofactor) Apoenzyme (protein) Holoenzyme Previous question Next question
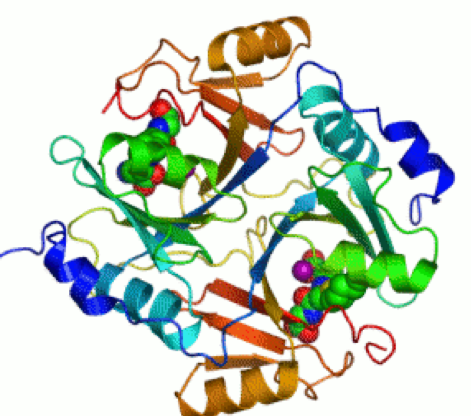
Cryo-EM Structure of the Human Ribonuclease P Holoenzyme ... Bacterial RNase P consists of a single RNA subunit and a sole C5 protein, while the archaeal holoenzyme contains one RNA and four protein subunits [91,92].

Label the parts of the holoenzyme structure.
PDF Stepwise assembly of the human replicative polymerase ... This structure, known as the holoenzyme, is able to slide freely along the DNA template, which allows the polymerase to promote the addition of nucleotides in a highly efficient manner. Protein complexes called clamp loaders are responsible for attaching the holoenzyme to the DNA template, and also for detaching it. Structural Basis of Transcription Initiation: An RNA ... The crystal structure of Thermus aquaticus RNA polymerase holoenzyme (α 2 ββ′ωσ A) complexed with a fork-junction promoter DNA fragment has been determined by fitting high-resolution x-ray structures of individual components into a 6.5-angstrom resolution map.The DNA lies across one face of the holoenzyme, completely outside the RNA polymerase active site channel. Chapter 25 Flashcards - Quizlet Verified answer. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Which of the following best describes veins? a. thick walled, small lumens, low pressure, lack valves b. thin walled, large lumens, low pressure, have valves c. thin walled, small lumens, high pressure, have valves d. thick walled, large lumens, high pressure, lack valves.
Label the parts of the holoenzyme structure.. Learning Through Art: Dna Structure Can You Correctly ... The structure of DNA is a double helix comprised of 4 nucleotides. Each nucleotide has the following: A phosphate group (P) and a sugar molecule (backbone of DNA) One of 4 bases; A=adenine, T=thymine, C=cytosine, or G=guanine To form the double helix, these nucleotides pair together using the base-pairing rules. More › More Courses ›› View Course Structure of a bacterial RNA polymerase holoenzyme open ... In bacteria, the RNA polymerase (RNAP) holoenzyme binds and unwinds promoter DNA, forming the transcription bubble of the open promoter complex (RPo). We have determined crystal structures, refined to 4.14 Å-resolution, of RPo containing Thermus aquaticus RNAP holoenzyme and promoter DNA that includes the full transcription bubble. RNA polymerase - Wikipedia A sigma (σ) factor binds to the core, forming the holoenzyme. After transcription starts, the factor can unbind and let the core enzyme proceed with its work. The core RNA polymerase complex forms a "crab claw" or "clamp-jaw" structure with an internal channel running along the full length. Gags Biochemistry (structure & Functions) CF9 30 Label The Parts Of The Holoenzyme Structure. - Labels Information List Lipids (structure & function) Glycosaminoglycans And Proteoglycans - A Quick Revision | Our ... Lipids (structure & function) 35 Can You Label The Way Nucleotides Pair Up In Replicating Dna ... 'cell structure and function' on SlideShare
The Core Subunit Structure in RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme ... The core subunit arrangement α2-β-β′ within DNA-dependent RNA polymerase holoenzyme α2ββ′σ from Escherichia coli was investigated by neutron small-angle scattering using label triangulation. The qu... Restructuring of an RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme Elongation ... In the holoenzyme complex th with core enzyme, r70 binds the -35 and -10 elements of the ifi predominant class of bacterial promoters: region 4 of a70 rec- ar ognizes the -35 element (1, 2) as double-stranded (ds)DNA, and B, region 2 of o'70 recognizes the -10 element as both dsDNA and to single-stranded (ss)DNA (2-6). Holoenzyme - The School of Biomedical Sciences Wiki Holoenzyme is a catalytically active enzyme that consists of apoenzyme and cofactor. Cofactors can make reactions that cannot be done by standard twenty amino acids. Cofactors are divided in two groups: metals ( Zn 2+, Mg 2+, Ni 2+ , Mo, Se, Mn, K + ), coenzymes . Use of the same coenzyme usually means that enzymes catalyse similar mechanisms . Crystal structure of the 500-kDa yeast acetyl-CoA ... The two-fold axis of the dimer is vertical (black line). c - e, Overall structure of ScACC holoenzyme, viewed from the side ( c ), down the BC domain dimer ( d ), and down the CT domain dimer ( e...
The architecture of Tetrahymena telomerase holoenzyme | Nature The long-awaited structure of a telomerase holoenzyme, from Tetrahymena, has been obtained by electron microscopy; affinity labelling of subunits and modelling with NMR and crystal structures of ... The EM structure of human DNA polymerase γ reveals a ... Structure of the pol γ holoenzyme complex. (A) An area of an image of template-primer-bound pol γ stained with uranyl acetate is shown using a 3-μm defocus raw micrograph to provide improved clarity. (B) Representative projections (1), corresponding class averages (2) and CTF-corrected raw images (3) used for reconstruction. The box size is 223 Å. Solved Label the parts of the T cell receptor. Drag the ... Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (31 ratings) Transcribed image text: Label the parts of the T cell receptor. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Structure of the Autoinhibited Kinase Domain of CaMKII and ... Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-II (CaMKII) is unique among protein kinases for its dodecameric assembly and its complex response to Ca2+. The crystal structure of the autoinhibited kinase domain of CaMKII, determined at 1.8 Å resolution, reveals an unexpected dimeric organization in which the calmodulin-responsive regulatory segments form a coiled-coil strut that blocks peptide and ...
PDF Molecular Insights into the Structure and Function of the ... Molecular Insights into the Structure and Function of the Telomerase Holoenzyme in Tetrahymena thermophila By Heather Upton A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Molecular and Cell Biology in the Graduate Division of the University of California, Berkeley Committee in charge:
The core subunit structure in RNA polymerase holoenzyme ... The core subunit arrangement of alpha 2-beta-beta' within DNA-dependent RNA polymerase holoenzyme alpha 2 beta beta' sigma from Escherichia coli was investigated by neutron small-angle scattering using label triangulation. The quaternary structure of multisubunit biomolecules can be studied by this new method if total reconstitution works in a ...
DNA Polymerase III Holoenzyme - an overview ... The holoenzyme comprises two dimerized β subunits (β 4 ), a dimeric core Pol III (α 2 ε 2 θ 2) and a single γ complex (γ 1 τ 2 δ 1 δ′ 1 χ 1 ψ 1) that loads the β processivity clamp onto the DNA template. The physical and genetic evidence supporting dimerization of DNA polymerase III fits nicely with a structural model for replication.
Crystal structure of the α6β6 holoenzyme of propionyl ... The structure of the α6β6PCC holoenzyme contains a central β6hexamer core, in the shape of a short cylinder with a small hole along its axis (Fig. 1a). This hexameric core can be considered as a trimer of β2dimers, with each dimer being formed by one subunit from each layer of the structure (Fig. 1b).
Label the parts of the animal cell Flashcards | Quizlet Label the parts of the animal cell. Structure and support for the cell. A gel-like material that surrounds all parts of the cell within the membrane. Nice work!
Localization and quaternary structure of the PKA RI holoenzyme The full-length RIβ(2):C(2) crystal structure allows us to visualize all the domains of the PKA holoenzyme complex and shows how isoform-specific assembly of holoenzyme complexes can create ...
structure | Deliciously Grey Here, the holoenzyme (core + sigma) binds specifically to a promoter by interaction between the sigma factor and the -10 and -35 regions of the promoter DNA. The structure is visualized in Fig. 1, with a reminder that the DNA double helix extends outwards in both directions. Figure 1. Holoenzyme interaction with promoter DNA.
Anatomy and Physiology Summer Work - Screen 22 on FlowVella - Presentation Software for Mac iPad ...
holoenzyme | Deliciously Grey Here, the holoenzyme (core + sigma) binds specifically to a promoter by interaction between the sigma factor and the -10 and -35 regions of the promoter DNA. The structure is visualized in Fig. 1, with a reminder that the DNA double helix extends outwards in both directions. Figure 1. Holoenzyme interaction with promoter DNA.
Enzymes - Structure, Classification, and Function Enzymes are a linear chain of amino acids, which give rise to a three-dimensional structure. The sequence of amino acids specifies the structure, which in turn identifies the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Upon heating, enzyme's structure denatures, resulting in a loss of enzyme activity, that typically is associated with temperature.
RNA polymerase holoenzyme: structure, function and ... Several structural elements not visible in the core structure were resolved in the holoenzyme structure [36 ••], including the β′ amino-terminal nonconserved domain (β′163-452) that forms a large extension of the β′ pincer, and the β′ Zinc-finger domain (β′53-81) located between amino-terminal and carboxy-terminal domains (ND and CD) of σ.
The EM structure of human DNA polymerase gamma reveals a ... Simple visual inspection of the dumb-bell-shaped holoenzyme structure suggested that the upper lobe appears to permit a good fit to the crystal structure of the human or mouse accessory subunit dimer (Carrodeguas et al, 2001; Fan et al, 2006). The lower part adopts a shape resembling the catalytic subunit shown in Figure 1.



0 Response to "41 label the parts of the holoenzyme structure."
Post a Comment