45 the neuronal membrane is at its resting potential at label
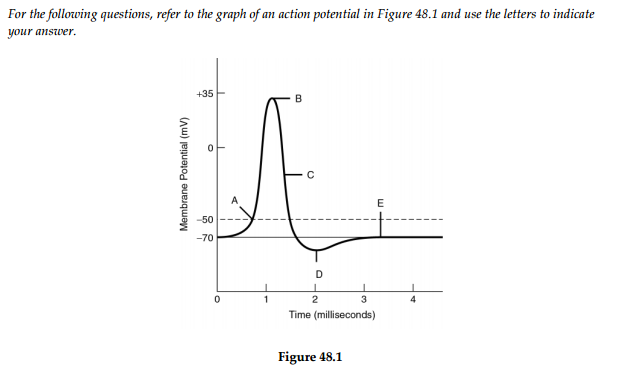
7.7: Membrane Potential - Chemistry LibreTexts (Clockwise From Upper Left) 1) The charges are equal on both sides; therefore the membrane has no potential. 2)There is an unbalance of charges, giving the membrane a potential. 3) The charges line up on opposite sides of the membrane to give the membrane its potential. The neuronal membrane is at its resting potential at label ... The neuronal membrane is at its resting potential at label ________. Answer Answer: E Neurons are cells that facilitate communication from one part of the body to another and signals are send as mean of communication which can be achieved through electrical potentials. Thus, cell membrane around the neuron usually create ionic potentials
Resting Membrane Potential - Nernst - Generation ... In electrically inactive neurones, this is known as the resting membrane potential. Its typical value lies between -50 and -75 mV. In this article, we will explore how the resting membrane potential is generated, how to calculate its approximate value and how changes in resting membrane potential may lead to significant pathology. Overview

The neuronal membrane is at its resting potential at label
Neural Communication | Introduction to Psychology The semipermeable nature of the neuronal membrane somewhat restricts the movement of these charged molecules, and, as a result, some of the charged particles tend to become more concentrated either inside or outside the cell. Between signals, the neuron membrane's potential is held in a state of readiness, called the resting potential. Membrane potential (resting membrane potential) (article ... A resting (non-signaling) neuron has a voltage across its membrane called the resting membrane potential, or simply the resting potential. The resting potential is determined by concentration gradients of ions across the membrane and by membrane permeability to each type of ion. Chapter 48 Flashcards | Quizlet 11) Although the membrane of a "resting" neuron is highly permeable to potassium ions, its membrane potential does not exactly match the equilibrium potential for potassium because the neuronal membrane is also A) fully permeable to sodium ions. B) slightly permeable to sodium ions. C) fully permeable to calcium ions. D) impermeable to sodium ions.
The neuronal membrane is at its resting potential at label. Neuron Flashcards | Quizlet Although the membrane of a "resting" neuron is highly permeable to potassium ions, its membrane potential does not exactly match the equilibrium potential for potassium because the neuronal membrane is also A) fully permeable to sodium ions. B) slightly permeable to sodium ions. C) fully permeable to calcium ions. D) impermeable to sodium ions. Solved Neurons: The Resting Membrane Potential Draw a ... Neurons: The Resting Membrane Potential Draw a neuron and label its basic structural features. • Explain the basis of the resting membrane potential (RMP). In a simple synapse neurotransmitter chemicals are ... 7) Although the membrane of a ʺ resting ʺ neuron is highly permeable to potassium ions, its membrane potential does not exactly match the equilibrium potential for potassium because the neuronal membrane is also _____. How Neurons Communicate | Boundless Biology resting potential: the nearly latent membrane potential of inactive cells Nerve Impulse Transmission within a Neuron For the nervous system to function, neurons must be able to send and receive signals. These signals are possible because each neuron has a charged cellular membrane (a voltage difference between the inside and the outside).
Labeled Neuron Diagram - Science Trends In its resting state, the concentration of sodium ions outside the neuron is about 10 times greater than inside the neuron and the concentration of potassium ions if greater inside the cell. In this resting state, the membrane potential is equal to about -70mV, which is called the resting membrane potential. Action Potential of Neurons - dummies The electrical difference across the membrane of the neuron is called its resting potential. The resting potential is created by a transport protein called the sodium-potassium pump. This protein moves large numbers of sodium ions (Na +) outside the cell, creating the positive charge. nervous system - The neuronal membrane | Britannica Resting potential The electrical potential across the nerve membrane can be measured by placing one microelectrode within the neuron (usually in the soma) and a second microelectrode in the extracellular fluid. The microelectrode consists of a sharp-tipped glass capillary tube filled with conducting solution. Chapter 48 Test Bank Flashcards | Chegg.com 11)Although the membrane of a "resting" neuron is highly permeable topotassium ions, its membrane potential does not exactly match the equilibriumpotential for potassium because the neuronal membrane is also. A)fully permeable to sodium ions. B)slightly permeable to sodium ions. C)fully permeable to calcium ions. D)impermeable to sodium ions.
Biology Chap. 37 Flashcards - Quizlet 7) Although the membrane of a "resting" neuron is highly permeable to potassium ions, its membrane potential does not exactly match the equilibrium potential for potassium because the neuronal membrane is also A) fully permeable to sodium ions. B) slightly permeable to sodium ions. C) fully permeable to calcium ions. D) impermeable to sodium ions. 7.2: Resting, Graded and Action Potential - Medicine ... Eventually, the extra K+ ions diffuse out of the cell through the potassium leakage channels, bringing the cell from its hyperpolarized state, back to its resting membrane potential. Figure 7.11. The formation of an action potential can be divided into five steps: (1) A stimulus from a sensory cell or another neuron causes the target cell to ... After the depolarization phase of an action potential the ... Though the membrane of a ʺ resting ʺ neuron is highly permeable to potassium ions , its membrane potential does not exactly match the equilibrium potential for potassium because the neuronal membrane is. A ) ... The neuronal membrane is at its resting potential at label. A ) ... PDF Part I: Maintaining the Resting Potential A membrane exhibiting membrane potential is said to be polarized. When the neuron is not sending a signal, the (resting) voltage ranges from -60 to -80 mV (millivolts). The membrane potential at rest is called the neuron's resting potential. For this lab activity, we will consider a neuron with a resting potential of -70 mV.
For a neuron with an initial membrane potential at 70 mV ... (a) the neuronal membrane is at its resting potential at label at e (b) the membraneʹs permeability to sodium ions is at its maximum at b (c) the membrane potential is closest to the equilibrium potential for potassium at label d (d) the minimum graded hyperpolarization needed to operate the voltage -gated sodium and potassium channels is …
Solved The neuronal membrane is at its resting potential ... A is the answer… View the full answer Transcribed image text: The neuronal membrane is at its resting potential at label +35 0 Membrane Potential (mV) -C A E -50 -70 D 0 1 4 2 3 Time (milliseconds) OB OA E ОС Previous questionNext question COMPANY About Chegg Chegg For Good College Marketing Corporate Development Investor Relations Jobs
Solved Question 9 1 pts Membrane potential (mv) -50 -100 ... The neuronal membrane is at its resting potential at label A) 1 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5 E) 6 Question 10 1 pts Action potentials move along axons A) more slowly in axons of large than in small diameter B) by activating the sodium-potassium "pump" at each point along the axonal membrane C) in both direction at relatively the same speed D) by reversing ...
Resting Membrane Potential | Biology for Majors II A neuron at rest is negatively charged: the inside of a cell is approximately 70 millivolts more negative than the outside (−70 mV, note that this number varies by neuron type and by species). This voltage is called the resting membrane potential; it is caused by differences in the concentrations of ions inside and outside the cell.
7.2 - Resting, Graded and Action Potential - Introductory ... Eventually, the extra K+ ions diffuse out of the cell through the potassium leakage channels, bringing the cell from its hyperpolarized state, back to its resting membrane potential. Figure 7.11. The formation of an action potential can be divided into five steps: (1) A stimulus from a sensory cell or another neuron causes the target cell to ...



0 Response to "45 the neuronal membrane is at its resting potential at label"
Post a Comment