39 label each part of the diagram of an atp molecule
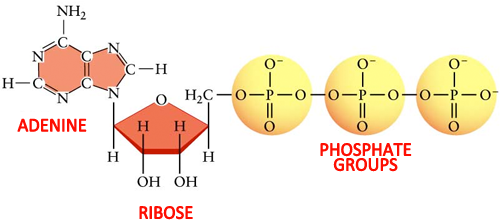
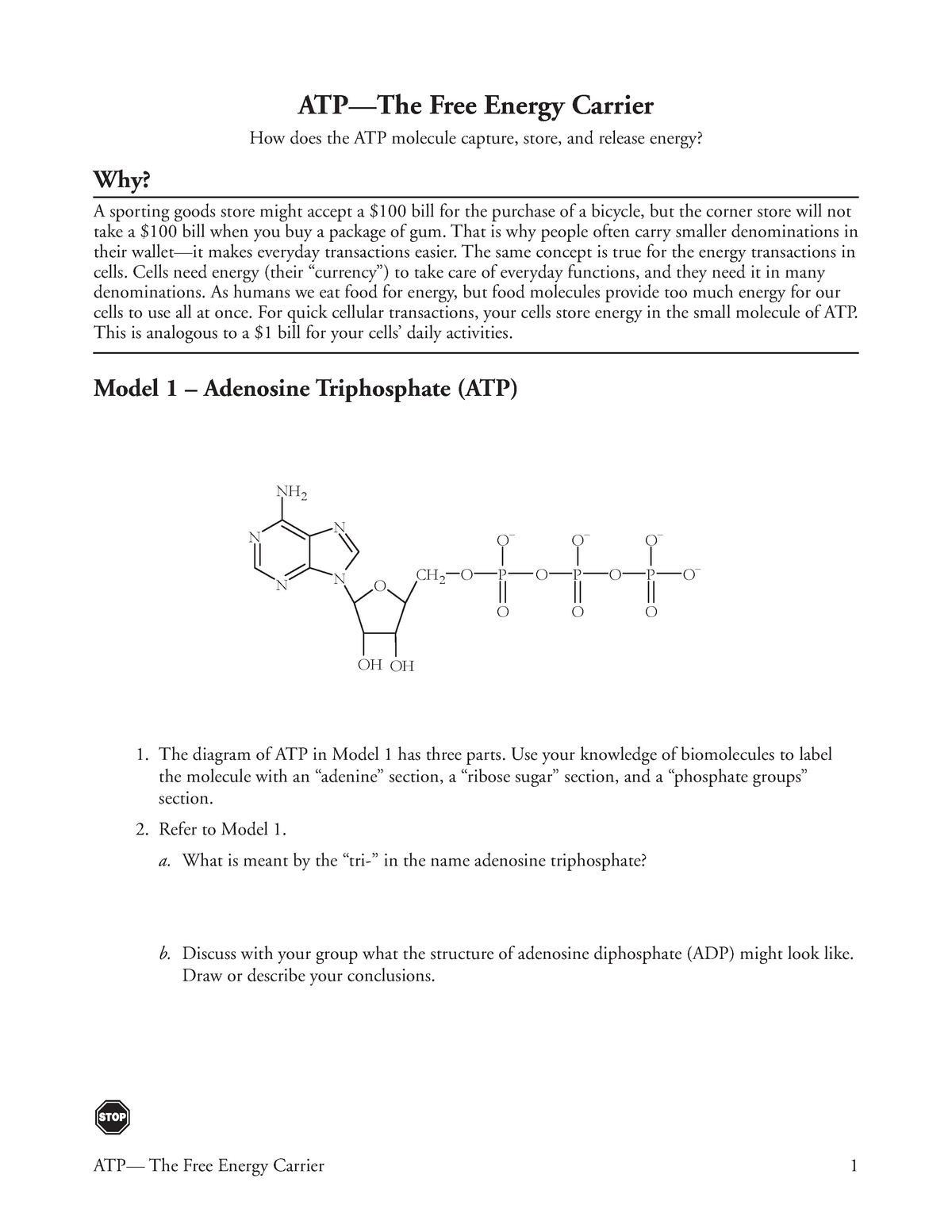
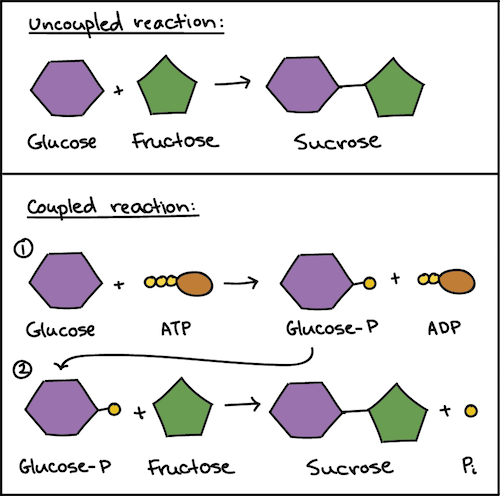
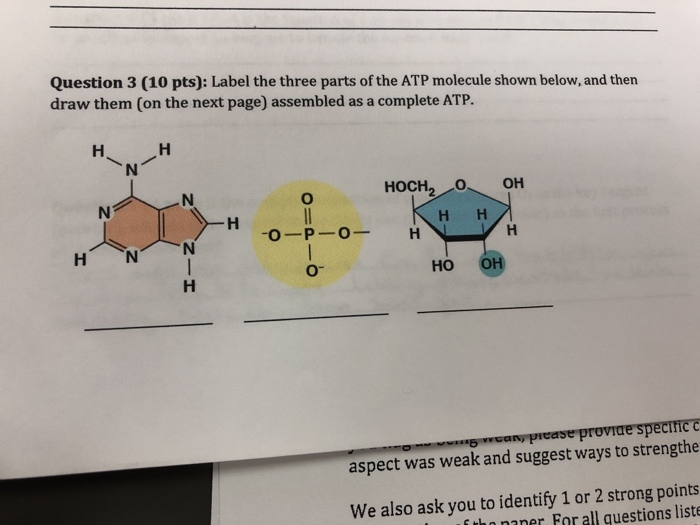
ATP_Pogil.docx - 1. The diagram of ATP in Model 1 has three parts. Use ... The diagram of ATP in Model 1 has three parts. Use your knowledge of biomolecules to label the molecule with an "adenine" section, a "ribose sugar" section, and a "phosphate groups" section. 2. Refer to Model 1. A. What is meant by the "tri-" in the name adenosine triphosphate? B. ATP Definition and Importance in Metabolism - ThoughtCo Updated on May 09, 2019. Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is often called the energy currency of the cell because this molecule plays a key role in metabolism, particularly in energy transfer within cells. The molecule acts to couple the energy of exergonic and endergonic processes, making energetically unfavorable chemical reactions able to proceed.
Ch. 18- Prep for Exam Flashcards | Quizlet The figure illustrates the oxidation of dietary fats, producing glucose, fats, ketone bodies, or ATP. Correctly label the metabolic processes occurring at each step. Name the body's main use for triglycerides. As an energy source Complete the sentences, then put the steps of lipid metabolism in order.
Label each part of the diagram of an atp molecule
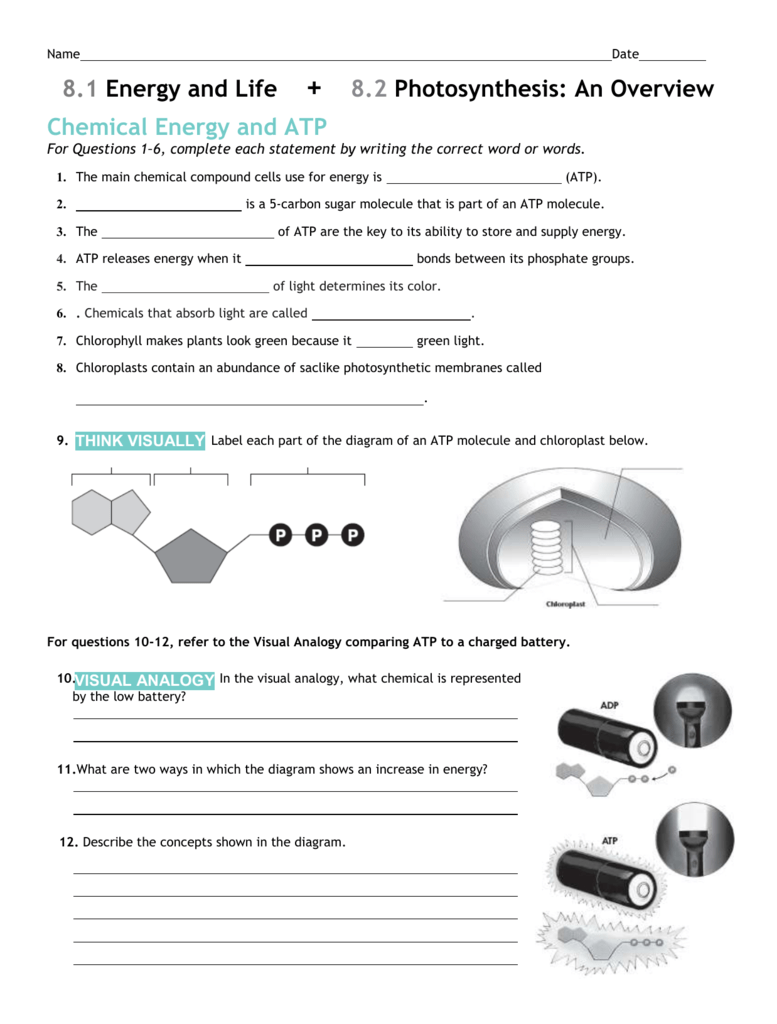
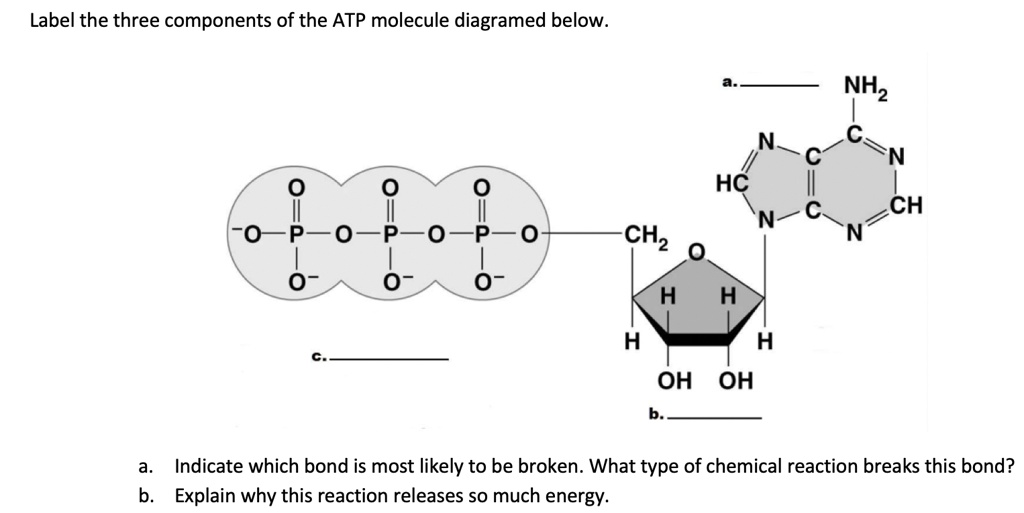
adenosine triphosphate | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Cells require chemical energy for three general types of tasks: to drive metabolic reactions that would not occur automatically; to transport needed substances across ... DOCX www3.nd.edu _____ is a 5-carbon sugar molecule that is part of an ATP molecule. The _____ of ATP are the key to its ability to store and supply energy. ATP releases energy when it _____ bonds between its phosphate groups. Most cells only store enough ATP for _____ of activity. THINK VISUALLY. 7. Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function This is a structural diagram of ATP. It is made up of the molecule adenosine (which itself is made up of adenine and a ribose sugar) and three phosphate groups. It is soluble in water and has a high energy content due to having two phosphoanhydride bonds connecting the three phosphate groups. Functions of ATP Energy Source
Label each part of the diagram of an atp molecule. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate | C10H16N5O13P3 - PubChem The total quantity of ATP in the human body is about 0.1 mole. The energy used by human cells requires the hydrolysis of 200 to 300 moles of ATP daily. This means that each ATP molecule is recycled 2000 to 3000 times during a single day. ATP cannot be stored, hence its consumption must closely follow its synthesis. Solving Hardy Weinberg Problems - YouTube Paul Andersen shows you how to solve simple Hardy-Weinberg problems. He starts with a brief description of a gene pool and shows you how the formula is deri... Adenosine Triphosphate - ATP - Bristol The ATP molecule is composed of three components. At the centre is a sugar molecule, ribose (the same sugar that forms the basis of RNA). Attached to one side of this is a base (a group consisting of linked rings of carbon and nitrogen atoms); in this case the base is adenine. The other side of the sugar is attached to a string of phosphate groups. PDF AP BIOLOGY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES - Unauthorized ATP and GTP are primary sources of energy for biochemical reactions. (a) Describe the structure of the ATP or the GTP molecule. (1 point each; 2 points maximum) • Adenosine + 3 phosphates or guanosine + 3 phosphates. • Elaborating on the phosphate bonds, e.g., unstable, negatively charged.
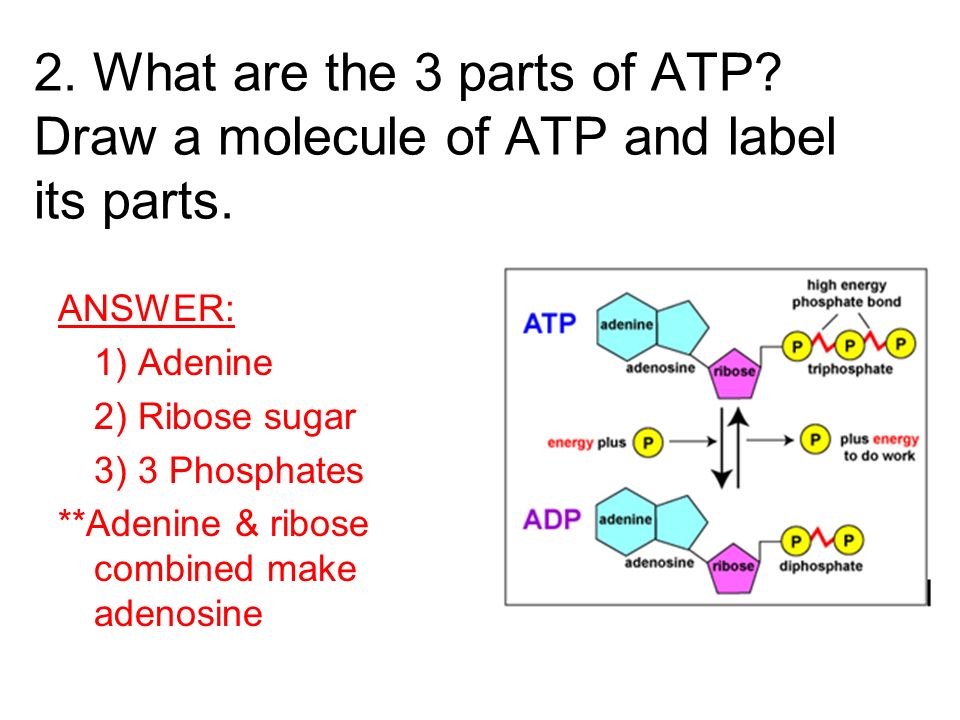
ATP and Energy (Interactive Tutorial) - learn-biology ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate ATP is a nucleotide monomer. It's composed of 3 subparts. Part 1 is the five-carbon sugar ribose. Part 2 is the nitrogenous base adenine, which is one of the letters of the genetic code. Part 3 consists of three phosphate groups (which is where the "triphosphate" part of ATP's name comes from). atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. In the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe the FANCM-family DNA helicase FmI1 directs NCO recombination formation during meiosis. u Based on these helicase motifs, a number of helicase superfamilies have been distinguished. In: Spies, M. The ClusPro web server for protein–protein docking | Nature ... Jan 12, 2017 · ClusPro is a web server that performs rigid-body docking of two proteins by sampling billions of conformations. Low-energy docked structures are clustered, and centers of the largest clusters are ... Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule | Chegg.com Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions &-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low battery? What arc two ways in which the diagram shows an increase in energy? Describe the concepts shown in the diagram.
Chapter 10 - Photosynthesis Flashcards by Emma Diaz | Brainscape b. ATP synthase releases ATP into the stroma rather than into the cytosol. c. light provides the energy to push electrons to the top of the electron chain, rather than energy from the oxidation of food molecules. d. an H + concentration gradient rather than a proton-motive force drives the phosphorylation of ATP. e. both a and c are correct. ATP Overview & Uses | What Does ATP Stand For? - Study.com ATP is short for adenosine triphosphate. ATP definition: ATP is a high-energy molecule that can be found in all types of cells, including plant cells, muscle cells, nerve cells, and more. ATP is ... Assignment Essays - Best Custom Writing Services Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply. The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules ATP consists of adenosine - composed of an adenine ring and a ribose sugar - and three phosphate groups (triphosphate). The phosphoryl groups, starting with the group closest to the ribose, are referred to as the alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) phosphates. Consequently, it is closely related to the adenine nucleotide, a monomer of RNA.
1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... ATP is a form of nucleotide structure which is mainly responsible for providing or driving the energy present in stored form from one point to another, through various chemical reactions. ( Metabolic pathways). It is mainly composed of three parts: A nitrogenous base, adenine, The sugar molecule, ribose. A chain of three phosphate group.
Solved Classify the statements about the structure of an - Chegg ATP is a nucleotide containing a base, a sugar, and phosphate groups. An ATP molecule contains three AMP molecules. ATP has three phosphate groups. High-energy phosphate bonds in ATP link the phosphate groups and the base adenine. An ATP molecule contains the nitrogenous base guanine. ATP contains ribose, a five-carbon sugar.
ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology – Photosynthesis Dec 04, 2019 · Sketch and Label the Diagram Question 1: Draw a neat and well-labeled diagram of the Chloroplast. Answer: Question 2: Draw a neat and well-labeled diagram of the apparatus you would set up to show that oxygen is given out during photosynthesis. Answer: See figure. Explain the Terms. Question: 1. ATP 2. Calvin Cycle 3. Free Energy 4. NADPH 5 ...
PDF ATP and Energy: How do cells capture, store, and release energy? then label each on the simplified model of ATP shown below a. b. c. 2. The full name for an ATP molecule is Adenosine Triphosphate. Based on the model for ATP, what is meant by the "tri" in triphosphate? 3. Predict what the structure of adenosine diphosphate and adenosine monophosphate might be. Draw or describe your prediction.
Bio102H LAB Exercise 13.pdf - Photosynthesis Animations... On Diagram 2, fill in the labels with the following descriptions. Some of the objects have multiple labels. x water (H2O) x carbon dioxide (CO2) x oxygen (O2) x G3P (sugar) x electron acceptor x electron donor x carbohydrates x energy input PART 3: LEAF STRUCTURE 1. In what plant structures does photosynthesis occur?
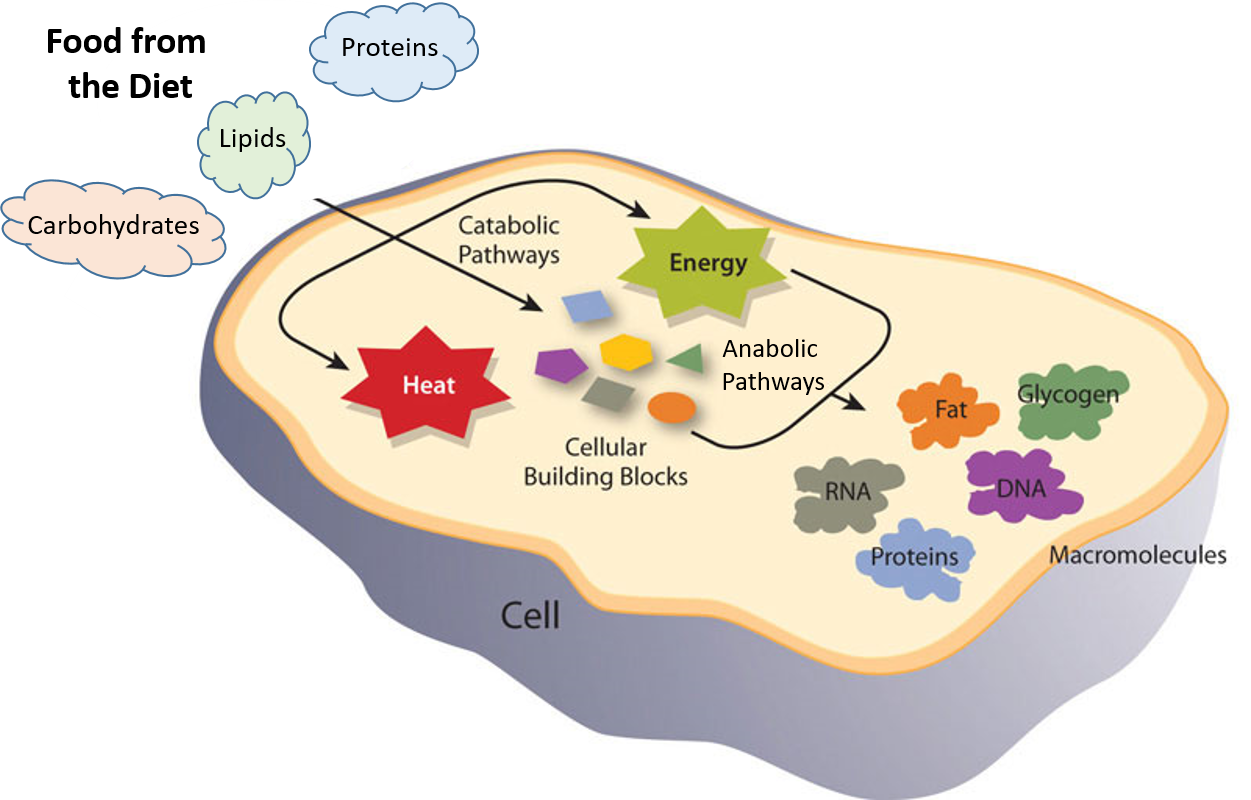
Metabolism - Wikipedia Metabolism (/ m ə ˈ t æ b ə l ɪ z ə m /, from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms.The three main purposes of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the ...
Physiology, Adenosine Triphosphate - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The body is a complex organism, and as such, it takes energy to maintain proper functioning. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate groups. ATP is commonly referred to as the "energy currency ...
The Structure of an Atom Explained With a Labeled Diagram Basic Diagram of an Atom. Most of an atom is just empty space and consists of a positively charged nucleus of protons and neutrons surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The center of an atom is the nucleus and one or more electrons surrounding the nucleus. When one says an atom is electrically neutral, it means that the number ...
Amino acid - Wikipedia This condensation reaction yields the newly formed peptide bond and a molecule of water. In cells, this reaction does not occur directly; instead, the amino acid is first activated by attachment to a transfer RNA molecule through an ester bond. This aminoacyl-tRNA is produced in an ATP-dependent reaction carried out by an aminoacyl tRNA synthetase.
How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the premier energy molecule in most living organisms. Its energy is used to push biochemical reactions forward, and it is often referred to as the "energy currency"...
ATP Diagram | Quizlet Terms in this set (9) ATP (name) adenosine triphosphate. ADP (name) adenosine diphosphate. ATP (function) a high energy molecule that transfers energy in cells. ADP (function) a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP.
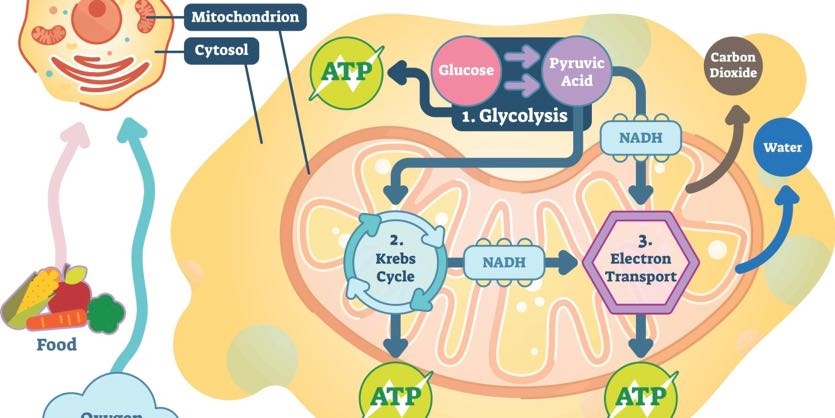
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams Cellular Respiration Equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 38*ATP. 10. Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, " biological machines " also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work. Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the ...
PHSchool.com Retirement–Prentice Hall–Savvas Learning Company PHSchool.com was retired due to Adobe’s decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support.
Structure of ATP - Learn Insta ATP molecule is composed of three phosphate molecules while ADP is composed of two phosphate molecules. ATP is composed of ribose, a five-carbon sugar, three phosphate groups, and adenine, a nitrogen-containing compound (also known as a nitrogenous base).
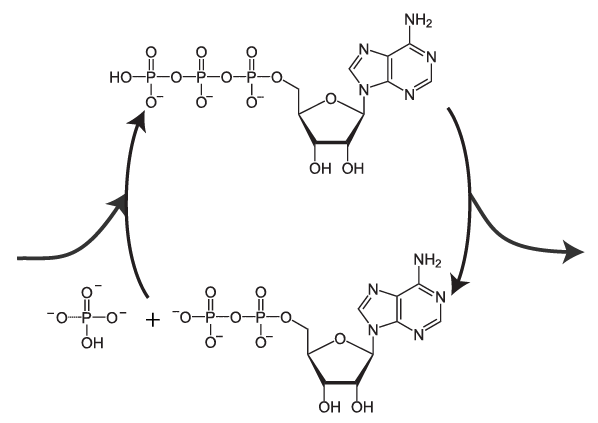
ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy ATP structure, ATP hydrolysis to ADP, and reaction coupling. ATP structure, ATP hydrolysis to ADP, and reaction coupling. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Photosynthesis: ATP and ADP Cycle - bealsscience The lower energy Adenosine DiPhosphate (ADP) is then re-energized during photosynthesis as the phosphate group is re-attached, thus completing the cycle of ATP to ADP to ATP... Below is an image of a worksheet I use in my Biology classes to help students learn the ATP Cycle to mastery. Right click the image below to download the worksheet.
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture:
ATP/ADP | Photosynthesis Quiz - Quizizz answer choices. The breaking of the bond between the 5-carbon sugar and the 1st phosphate group. The addition of a phosphate group. The removal of a phosphate group. The addition of glucose. Question 10. 30 seconds. Q. Where is the energy stored in ATP molecules.
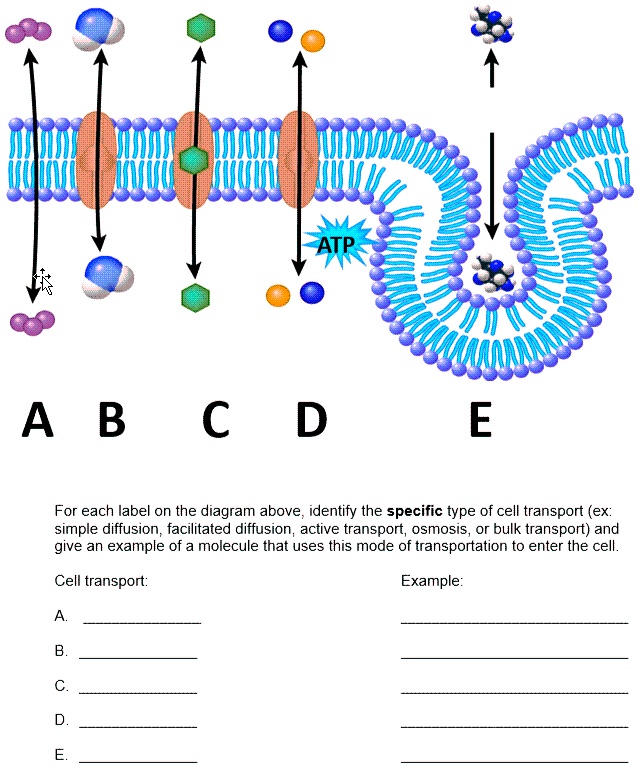
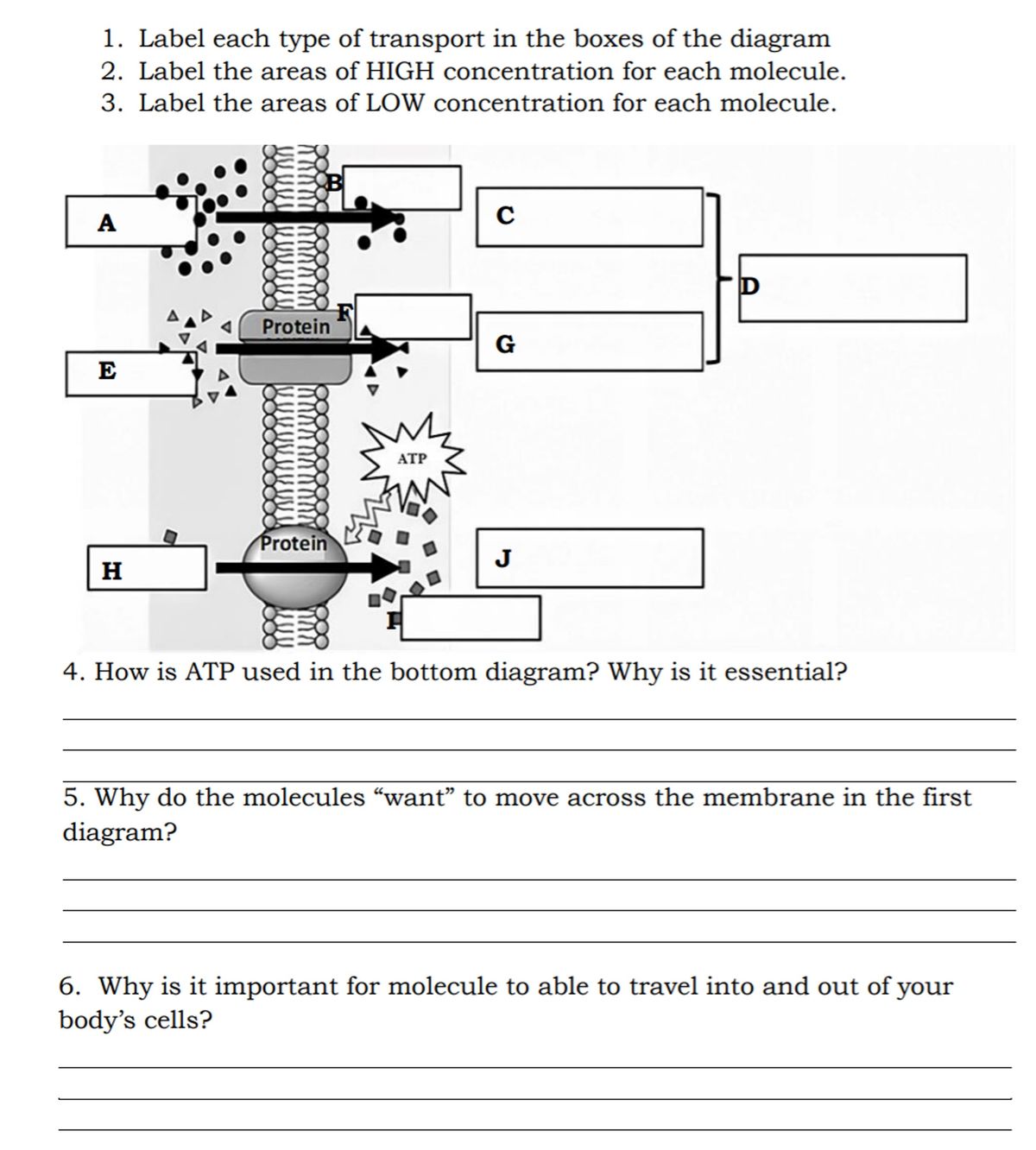
Biology- Chapter 5 Structure and Function of Plasma Membrane A and B are solutions of salt dissolved in water that are separated from each other by a semipermeable membrane in each scenario. Water can pass through this membrane, but the salt cannot. Match each pair of solutions to the net direction the water will flow between the two solutions.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function This is a structural diagram of ATP. It is made up of the molecule adenosine (which itself is made up of adenine and a ribose sugar) and three phosphate groups. It is soluble in water and has a high energy content due to having two phosphoanhydride bonds connecting the three phosphate groups. Functions of ATP Energy Source
DOCX www3.nd.edu _____ is a 5-carbon sugar molecule that is part of an ATP molecule. The _____ of ATP are the key to its ability to store and supply energy. ATP releases energy when it _____ bonds between its phosphate groups. Most cells only store enough ATP for _____ of activity. THINK VISUALLY. 7. Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below.
adenosine triphosphate | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Cells require chemical energy for three general types of tasks: to drive metabolic reactions that would not occur automatically; to transport needed substances across ...















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)

0 Response to "39 label each part of the diagram of an atp molecule"
Post a Comment