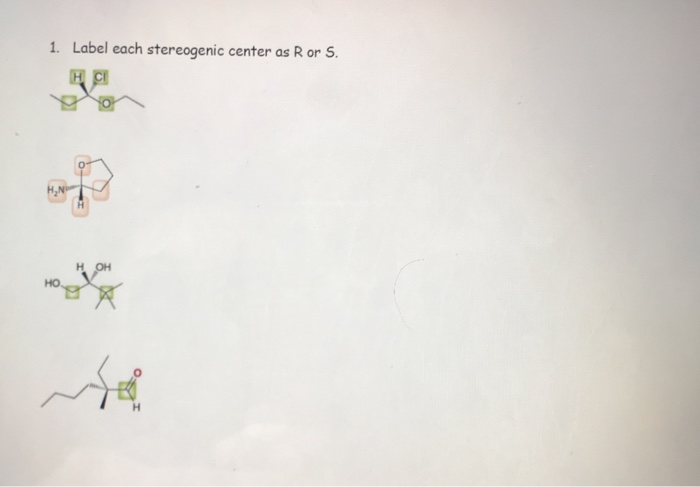
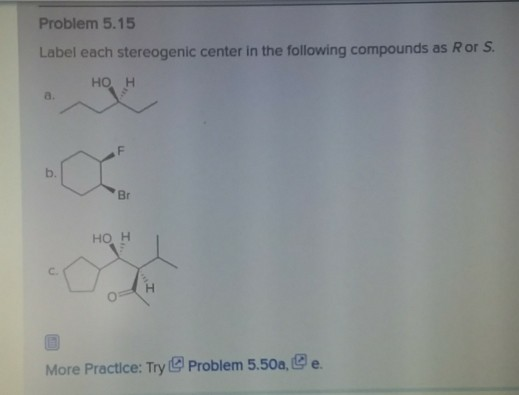
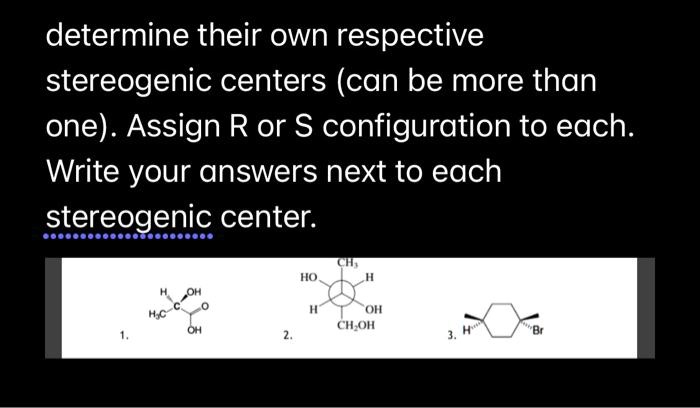
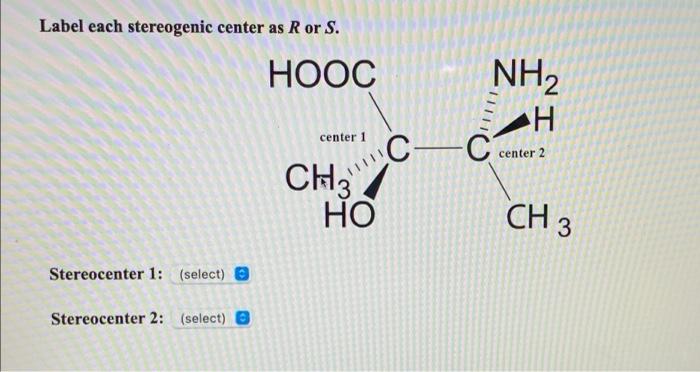
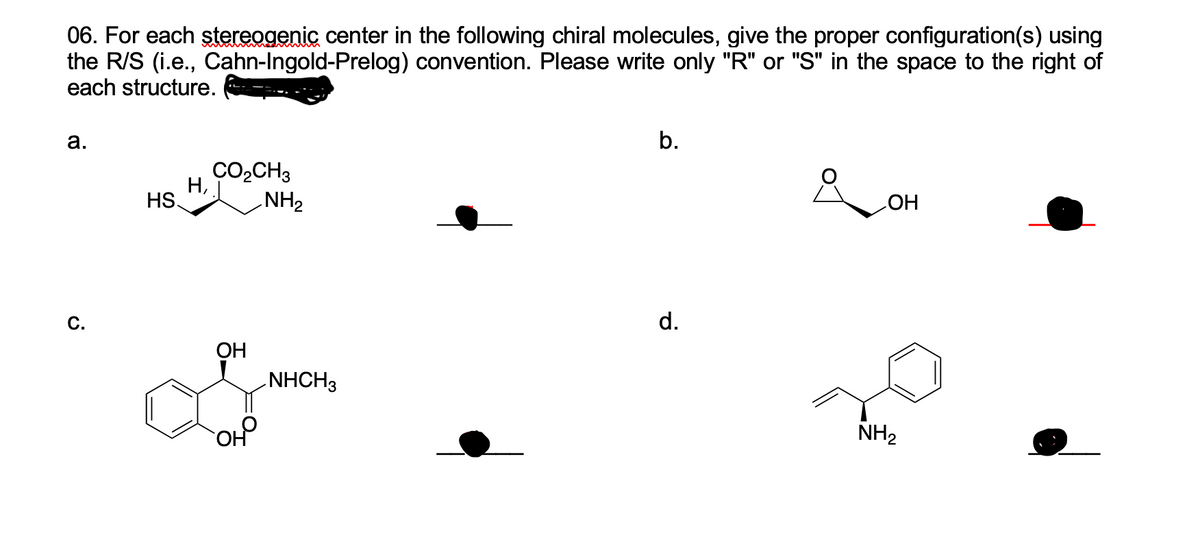
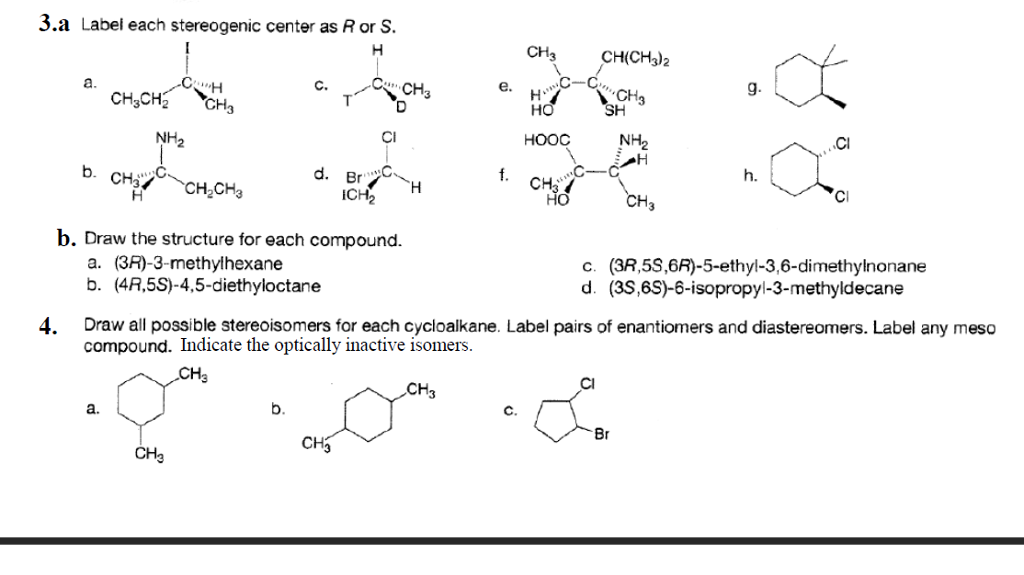
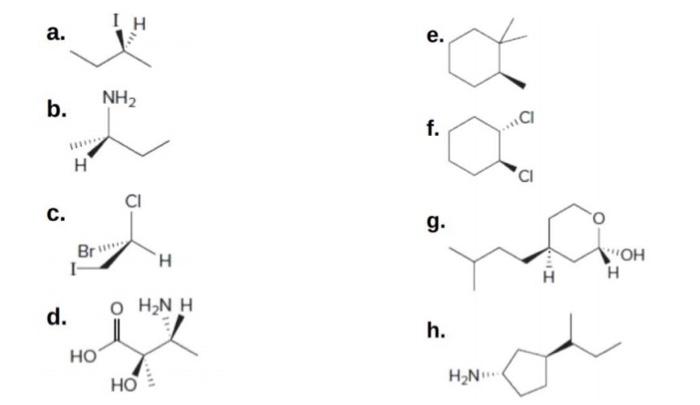
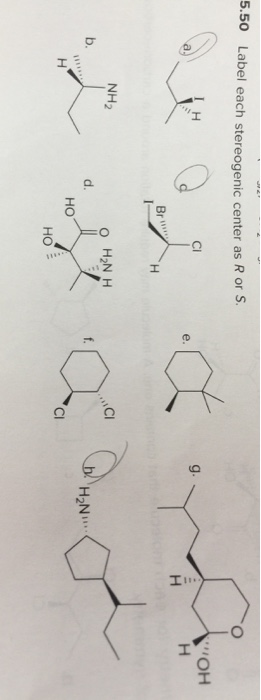
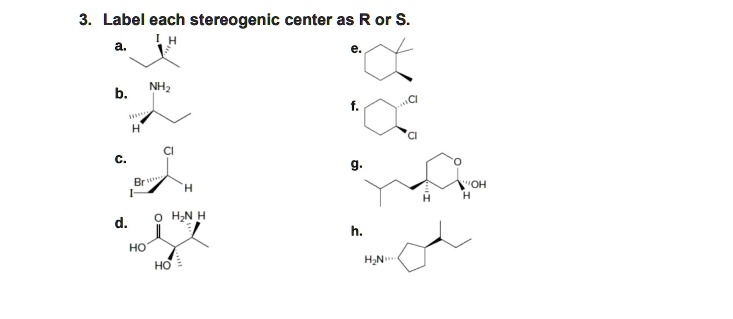
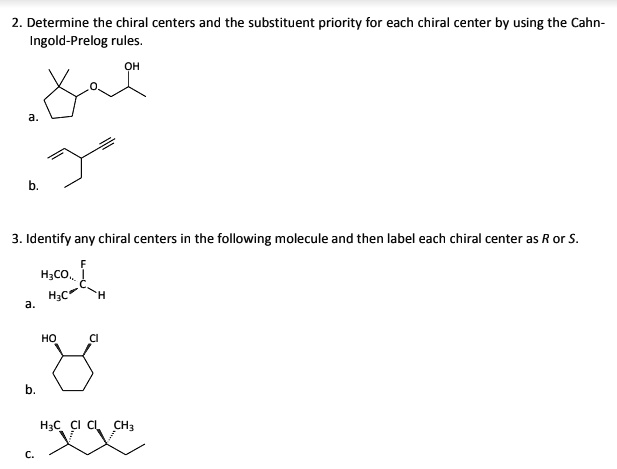
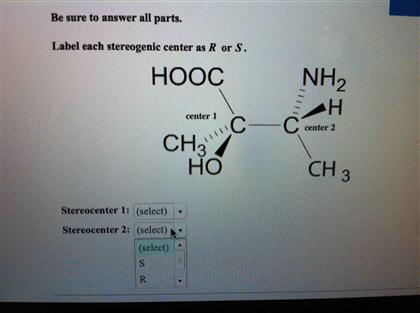
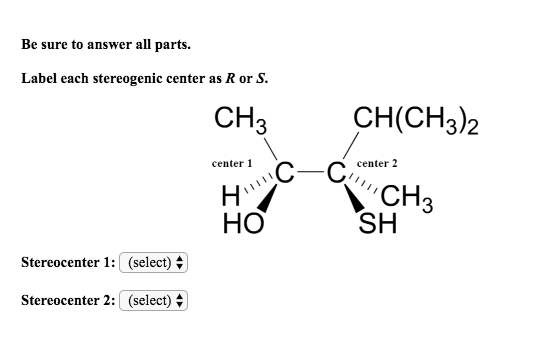
45 label each stereogenic center as r or s
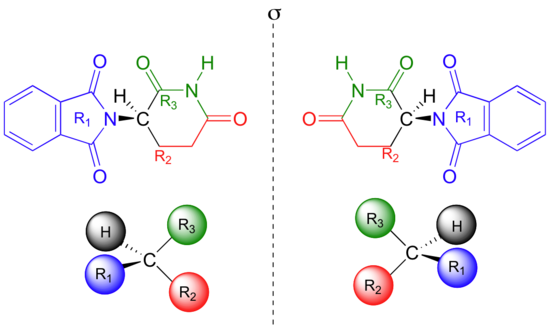
Rearrangement - Michigan State University In each case a green capitol letter (C, H, L or S) designates the type of reaction. The first three reactions illustrate the Hofmann rearrangement, which is a particularly useful method for preparing amines. The last example shows a Curtius reaction applied to a diester by way of an intermediate bis-acylhydrazide. An alternative Curtius approach to the amine product of example # 2 is also ... Lone pair - Wikipedia The repulsive force of the oxygen atom's lone pairs pushes the hydrogens further apart, until the forces of all electrons on the hydrogen atom are in equilibrium. This is an illustration of the VSEPR theory. Dipole moments. Lone pairs can contribute to a molecule's dipole moment. NH 3 has a dipole moment of 1.42 D.
The RDKit Book — The RDKit 2022.09.1 documentation The algorithm identifies features in the molecule by doing substructure searches using a small number (12 in the 2019.03 release of the RDKit) of very generic SMARTS patterns - like [*]~[*]~[*](~[*])~[*] or [R]~1[R]~[R]~[R]~1, and then hashing each occurrence of a pattern based on the atom and bond types involved. The fact that particular pattern matched the molecule at all …
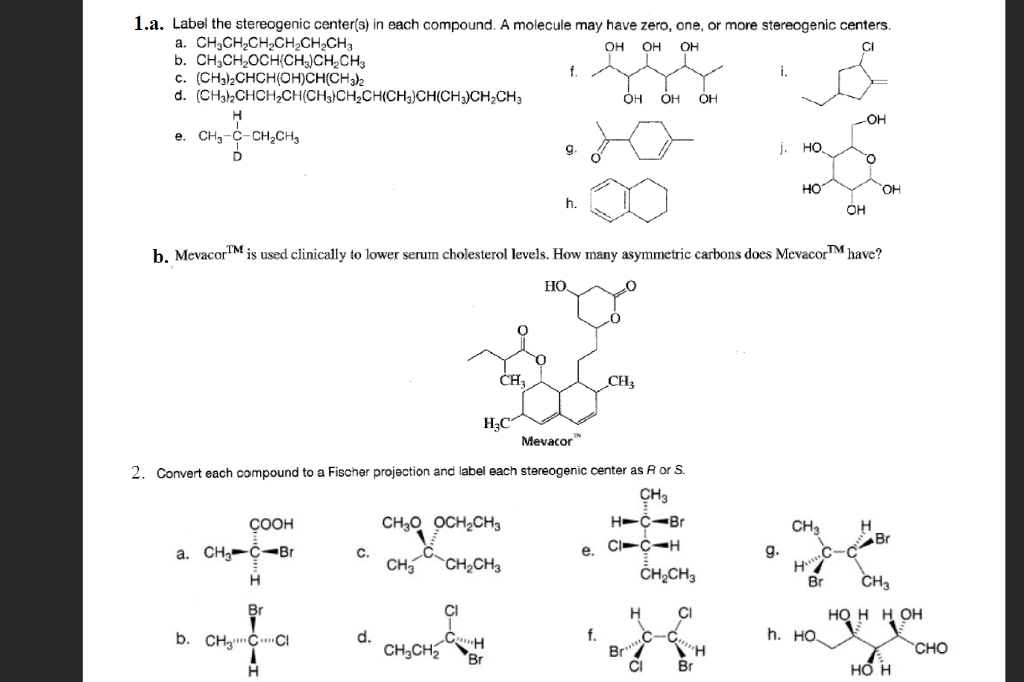
Label each stereogenic center as r or s
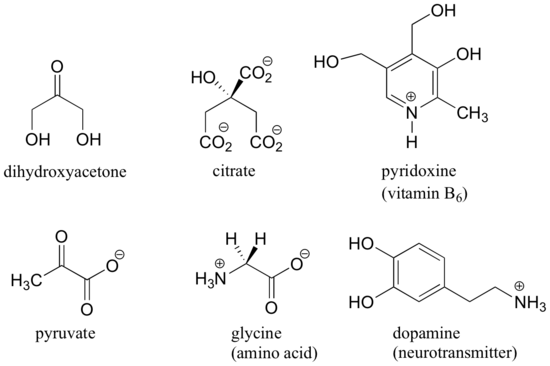
Biochemistry PDF | PDF | Cell (Biology) | Biochemistry - Scribd The fourth is commonly denoted "R" and is different for each amino acid. There are twenty standard amino acids. Some of these have functions by themselves or in a modified form; for instance, glutamate functions as an important neurotransmitter. Amino acids can be joined together via a peptide bond. In this dehydration synthesis, a water molecule is removed and … Answered: Identify the stereogenic carbon in (S)-… | bartleby Identify the stereogenic carbon in (S)- and (R)-limonene, rank the substituents around it and rationalize the assignment of their stereochemical configurations. Hint: When ranking carbons that have multiple bonds, consider the bolded carbon of C=C being connected to 2 carbons and the bolded carbon of C≡C being connected to 3 carbons. 5.4: Stereogenic Centers - Chemistry LibreTexts A stereogenic element is a center, axis or plane that is a focus of stereoisomerism, such that an interchange of two groups attached to this feature leads to a stereoisomer. Stereogenic elements may be chiral or achiral. An asymmetric carbon is often a chiral stereogenic center, since interchanging any two substituent groups converts one enantiomer to the other. Alkenes …
Label each stereogenic center as r or s. General Principles- Introduction objectives Chiral refers to molecule with a center of three-dimensional asymmetry. Definiton: Chirality- "handedness"; (Greek cheir - the hand); molecules which are not superimposable on (cannot be made to coincide with) their mirror image. achiral molecules can be superimposed on its mirror image. CH103 – Chapter 8: The Major Macromolecules – Chemistry Proteins are very large molecules containing many amino acid residues linked together in very specific order. Proteins range in size from 50 amino acids in length to the largest known protein containing 33,423 amino acids. Macromolecules with fewer than 50 amino acids are known as peptides.. Figure 11.4 Peptides and Proteins are macromolecules built from long chains of … Chiral drugs - Wikipedia Each twin is called an enantiomer. ... identify the chiral center, label the four atoms directly attached to the stereogenic center in question, assign priorities according to the sequence rule ( from 1 to 4), rotate the molecule until the lowest priority (number 4) substituent is away from the observer/viewer, draw a curve from number 1 to number 2 to number 3 substituent. If the curve … What are Enantiomers- Properties, Structure, Chemical Nature Enantiomers are a pair of molecules that exist in two forms that can not be superimposed on each other but are mirror images of each other. Enantiomers have a Chiral Carbon. A Chiral Carbon is a center of Carbon that is bound to four distinct atoms or groups. The existence of Chiral Carbon is referred to as Chirality (in a molecule). Two ...
solomons, graham - fundamentals of organic chemistry.pdf Help Center; less; Download Free PDF. Download Free PDF. solomons, graham - fundamentals of organic chemistry.pdf. solomons, graham - fundamentals of organic chemistry.pdf. guven kizilkaya . Abstract. chemistry. Continue Reading. Download Free PDF. Download. Related Papers. WIM DEHAEN ADVANCED ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Cường … Molecules: Identifying Chiral Centers, Meso Compounds, and ... 17.12.2021 · For example, cis-1,2-dibromocyclopentane (shown in the first figure) is meso because a plane cuts the molecule into two halves that are reflections of each other.Trans-1,2-dibromocyclopentane, however, is chiral because no plane splits the molecule into two mirror-image halves.. Now look at the mirror images of these two molecules in the second figure to … Caffeine - Wikipedia Caffeine does not contain any stereogenic centers and hence is classified as an ... Berzelius stated that the French chemists had made their discoveries independently of any knowledge of Runge's or each other's work . However, Berzelius later acknowledged Runge's priority in the extraction of caffeine, stating: "However, at this point, it should not remain unmentioned that … 5.4: Stereogenic Centers - Chemistry LibreTexts A stereogenic element is a center, axis or plane that is a focus of stereoisomerism, such that an interchange of two groups attached to this feature leads to a stereoisomer. Stereogenic elements may be chiral or achiral. An asymmetric carbon is often a chiral stereogenic center, since interchanging any two substituent groups converts one enantiomer to the other. Alkenes …
Answered: Identify the stereogenic carbon in (S)-… | bartleby Identify the stereogenic carbon in (S)- and (R)-limonene, rank the substituents around it and rationalize the assignment of their stereochemical configurations. Hint: When ranking carbons that have multiple bonds, consider the bolded carbon of C=C being connected to 2 carbons and the bolded carbon of C≡C being connected to 3 carbons. Biochemistry PDF | PDF | Cell (Biology) | Biochemistry - Scribd The fourth is commonly denoted "R" and is different for each amino acid. There are twenty standard amino acids. Some of these have functions by themselves or in a modified form; for instance, glutamate functions as an important neurotransmitter. Amino acids can be joined together via a peptide bond. In this dehydration synthesis, a water molecule is removed and …




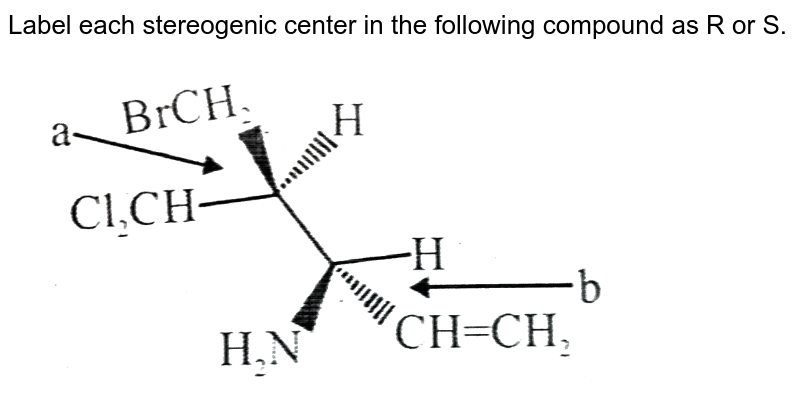

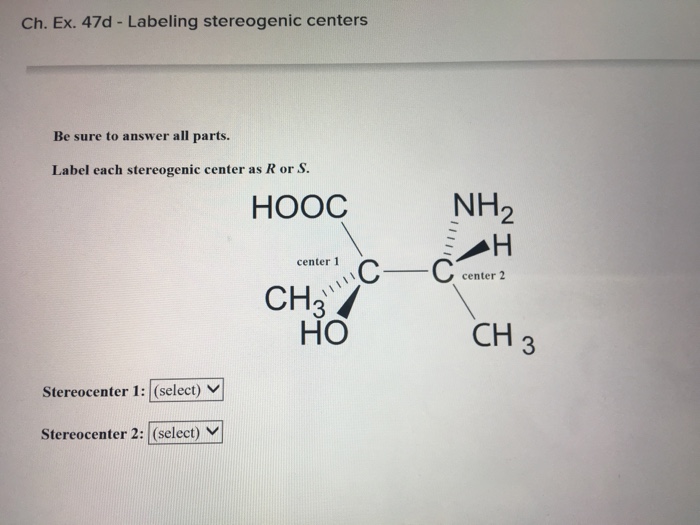
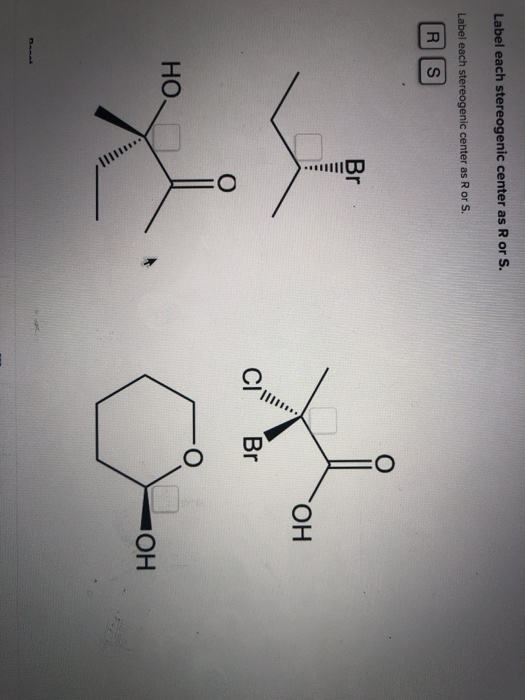



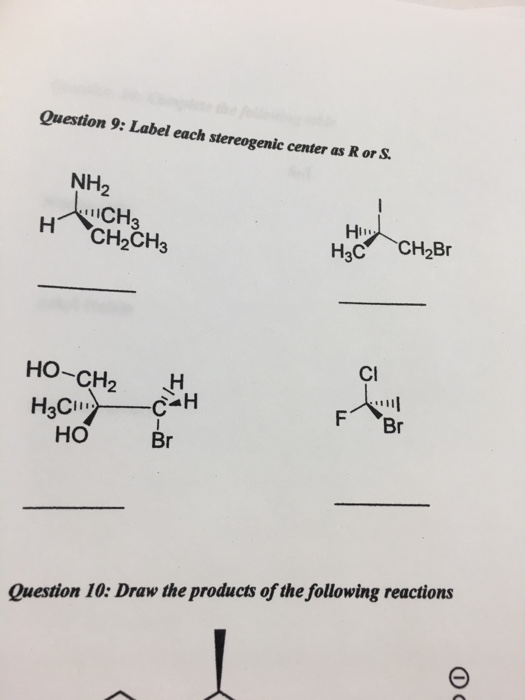
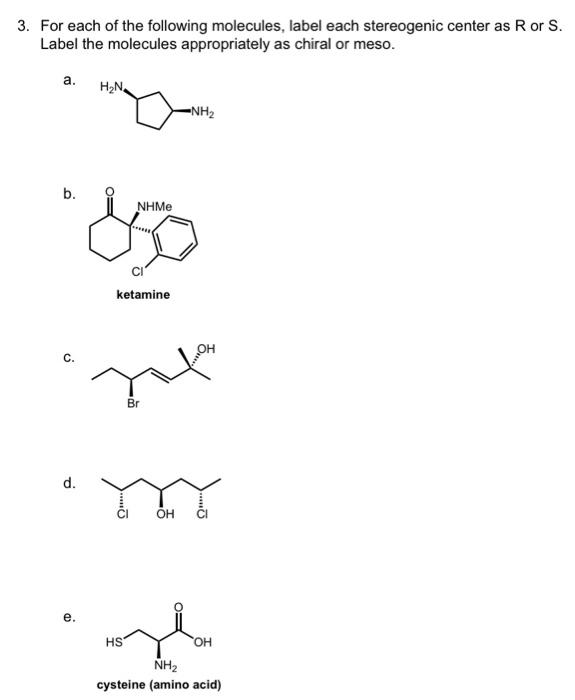
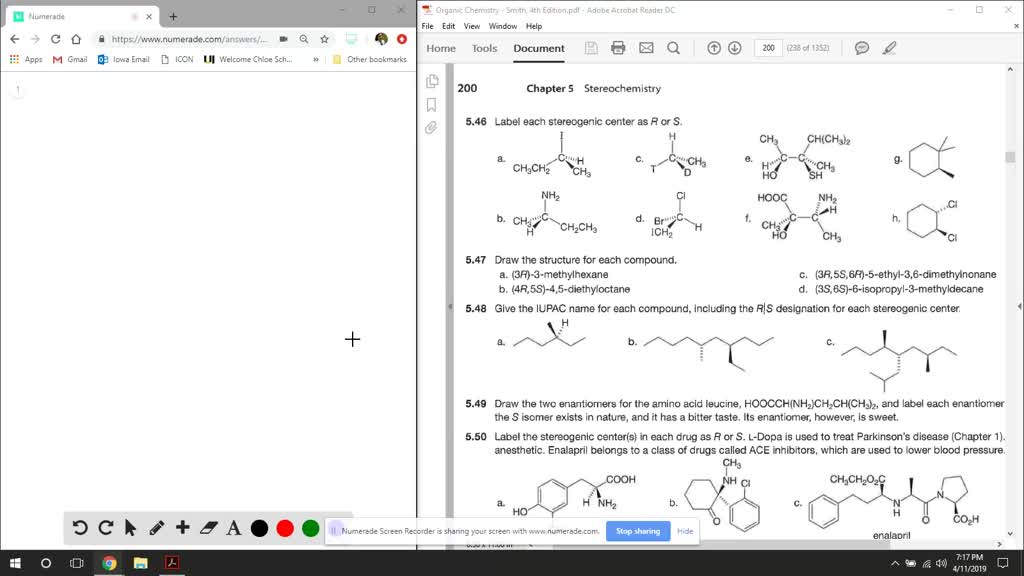
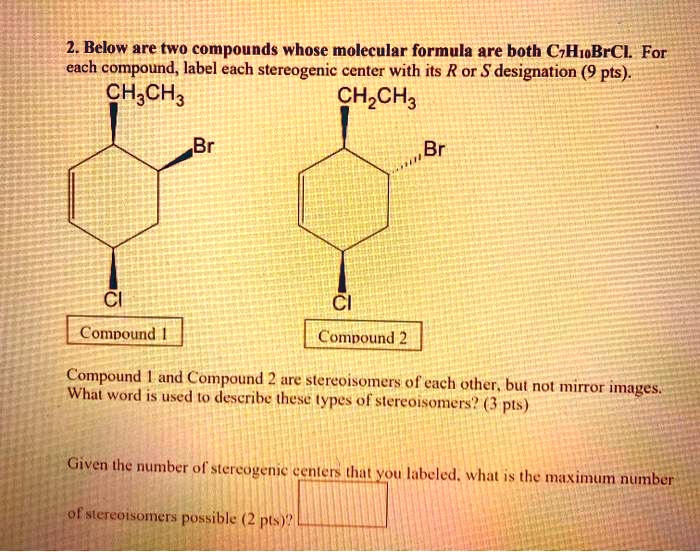




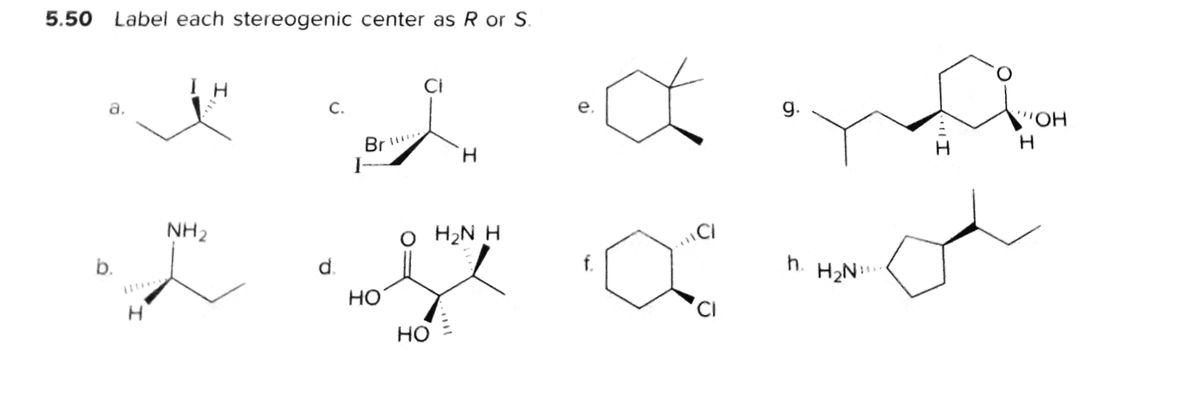
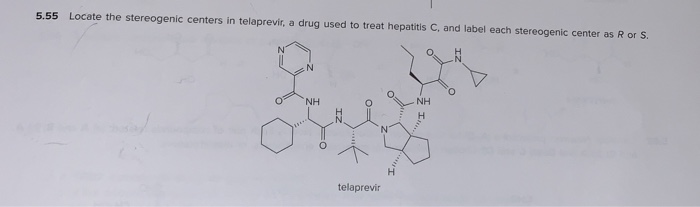
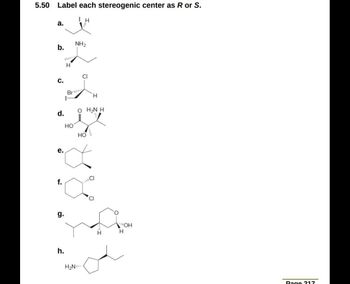

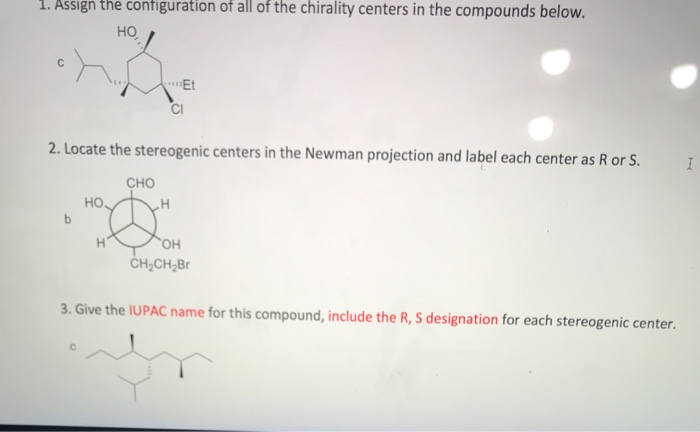




0 Response to "45 label each stereogenic center as r or s"
Post a Comment