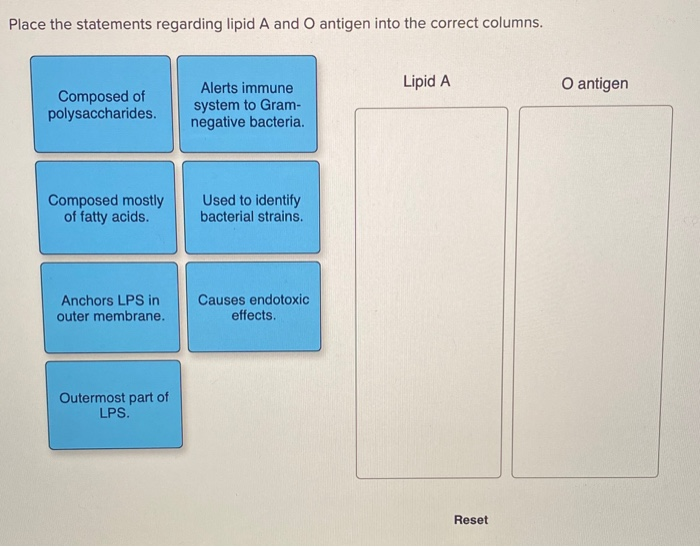
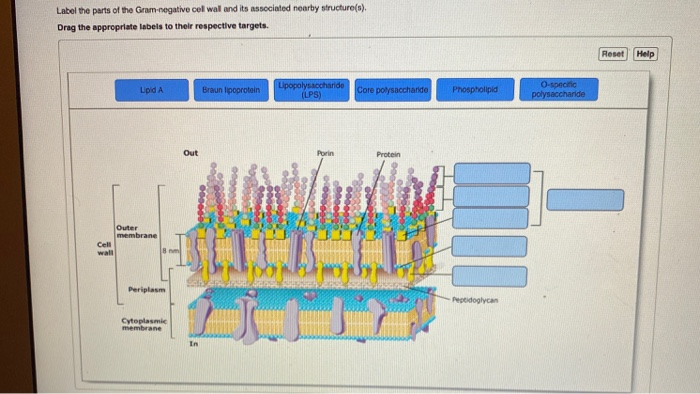
38 examine and correctly label the various portions of bacterial lipopolysaccharide as shown here.
Examine and correctly label the various portions of bacterial ... Examine and correctly label the various portions of bacterial lipopolysaccharide as shown here A. O-antigen polysaccharide B. Core polysaccharide D. Lipid A C. Disaccharide E. Fatty acids Which class of molecules can directly cross the cell membrane without the aid of transport proteins?- Uncharged gassesA B D C E Uncharged gasses Prokaryotic Membranes and Cell Walls Flashcards | Quizlet The figure shows the cell fractionation process. This process can be used to identify proteins produced under different environmental conditions. Examine and correctly label the various portions of bacterial lipopolysaccharide as shown here - O- antigen polysaccharide -Core antigen polysaccharide -disaccharide diphosphate -Lipid _Fatty tails
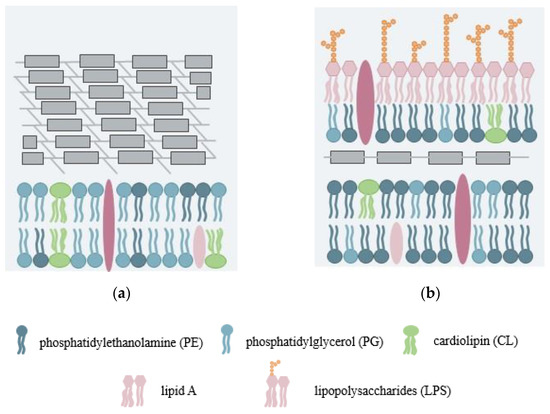
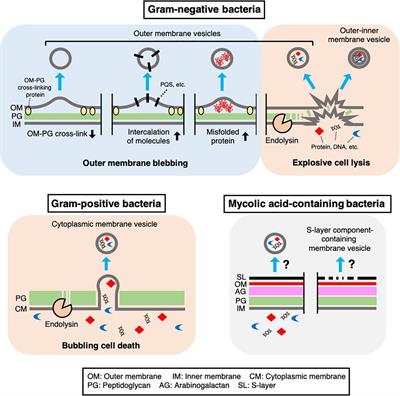
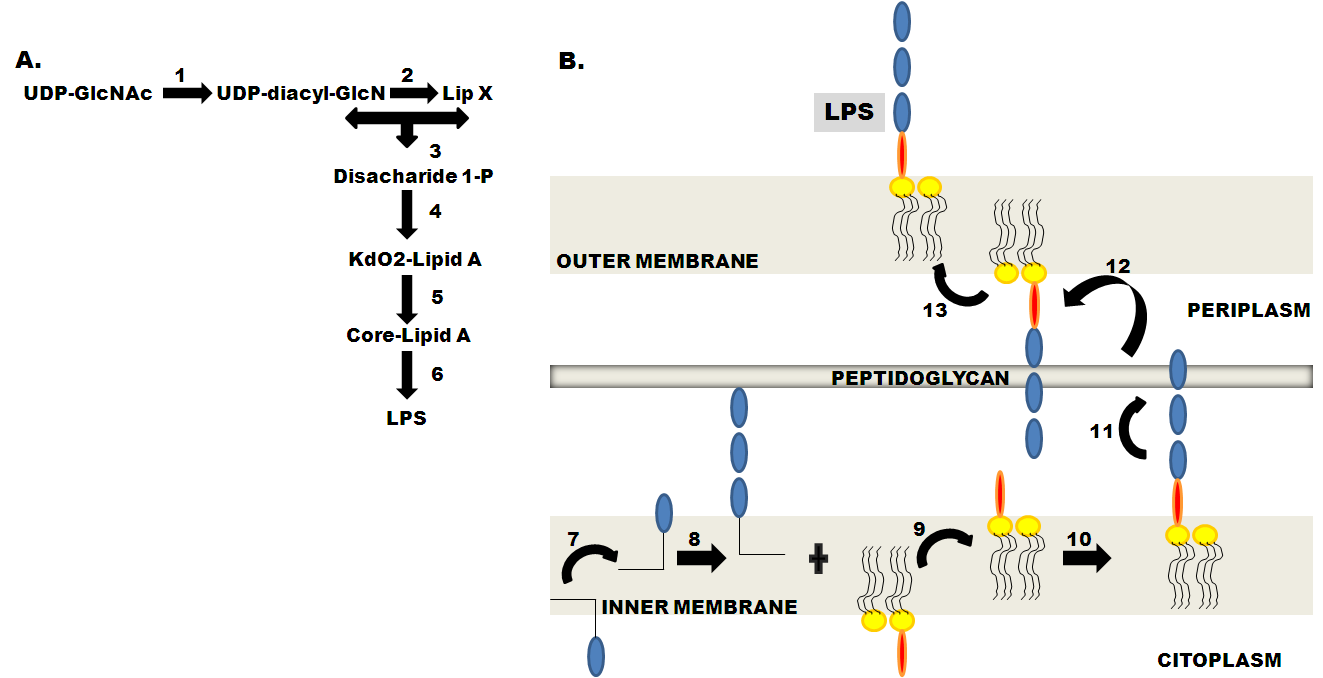
Bacterial lipopolysaccharides: structure, metabolism and mechanisms of ... Endotoxins (lipopolysaccharides, LPS) are biologically active substances present in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. They induce a spectrum of biological effects which may be harmful or beneficiary for the host. Lipid A is the biologically active part of the LPS molecule. This was demonstrated using soluble forms of lipid A and ...
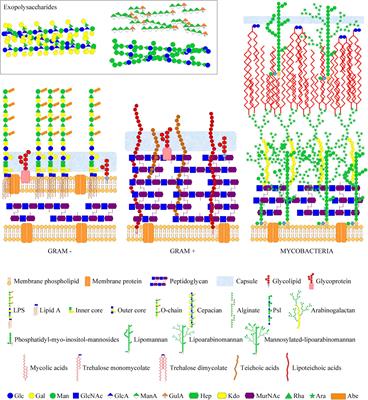
Examine and correctly label the various portions of bacterial lipopolysaccharide as shown here.
Lipopolysaccharides - Sigma-Aldrich Lipopolysaccharides are heat-stable endotoxins and have long been recognized as a key factor in septic shock (septicemia) in humans 1,7 and, more generally, in inducing a strong immune response in normal mammalian cells. The lipid A moiety has been identified as critical to the endotoxin activity of lipopolysaccharide. Lipopolysaccharide and Its Constituents | Encyclopedia.com Lipopolysaccharide is medically important to humans. When free from the bacterium, LPS is toxic. The portion of the LPS that is responsible for the toxicity is the core and lipid A portion (the endotoxin). Endotoxin can produce a fever, decrease in the number of white blood cells, and damage to blood vessels resulting in reduced blood pressure. Bacterium Lipopolysaccharide - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics LPSs are amphiphilic macromolecules generally comprising three defined regions distinguished by their genetics, structures, and function: the lipid A, the core oligosaccharide and a polysaccharide portion, the O-chain. In some Gram-negative bacteria, LPS can terminate with the core portion to form rough-type LPS (R-LPS, LOS).
Examine and correctly label the various portions of bacterial lipopolysaccharide as shown here.. Lipopolysaccharide - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is the major surface membrane component present in almost all Gram-negative bacteria and it is essential to both the form and function of the outer membrane. The distinctive structural properties of LPS are crucial for the protective barrier properties of the outer membrane. Microbiology-Chapter 19 Homework Flashcards | Quizlet Drag the labels to the correct category to demonstrate your understanding of streptococcal infections. Use the hints that pop up when you roll over the empty boxes to help you place the labels correctly. Match the pathogen to the disease it causes to test your understanding of microorganisms that cause upper respiratory tract diseases. Smartwork chapter 3 Flashcards | Quizlet Label the following illustration of a bacterial cell (plasma) membrane by dragging the items to their respective targets. Water molecules are sufficiently small that they do not require specific transporters to cross biological membranes. But because they are polar, diffusion of these molecules across the phospholipid bilayer is slow. Lipopolysaccharides - Sigma-Aldrich Product Information. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are characteristic components of the cell wall of Gram negative bacteria; they are not found in Gram positive bacteria. They are localized in the outer layer of the membrane and are, in noncapsulated strains, exposed on the cell surface. They contribute to the integrity of the outer membrane, and ...
Microbiology Ch . 25 Review Flashcards | Quizlet Examine various aspects of applied microbiology and biotechnology by completing each sentence. Match each description to the correct sewage treatment phase. Select all of the microbial products made through mass production to test your understanding of industrial microbiology applications today. Health care products such as antibiotics [Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide lipid A in bacteria--a ... Abstract Lipid A, the hydrophobic group of lipopolysaccharide, covers the surface of most Gram-negative bacteria. Lipopolysaccharide, known as endotoxin, can cause fatal disease like sepsis syndrome. Recent studies have shown that it is only the lipid A part of lipopolysaccharide that has the function of endotoxin. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides and innate immunity - PubMed Bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are the major outer surface membrane components present in almost all Gram-negative bacteria and act as extremely strong stimulators of innate or natural immunity in diverse eukaryotic species ranging from insects to humans. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharides - ScienceDirect 1. Introduction. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is vital to both the structural and functional integrity of the Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane. Ubiquitously expressed by all Gram-negative bacteria, and containing several well-conserved domains, LPS also serves as one of the primary targets of the innate arm of the mammalian immune system.
Lipopolysaccharide modification in Gram-negative bacteria during ... Abstract. The Gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a major component of the outer membrane that plays a key role in host-pathogen interactions with the innate immune system. During infection, bacteria are exposed to a host environment that is typically dominated by inflammatory cells and soluble factors, including antibiotics ... Chapter 9 Microbiology Flashcards | Quizlet Please examine and correctly label this image illustrating the two basic types of transposition. A. Replicative transposition B. Duplication caused by previous insertion C. Target sequence D. Nonreplicative transposition E. Transposable element F. Recipient DNA Students also viewed Chapter 10 45 terms kamryndennise Chapter 9 54 terms maggiecrowe2 Characterization of the aggregates formed by various bacterial ... - PubMed Characterization of the aggregates formed by various bacterial lipopolysaccharides in solution and upon interaction with antimicrobial peptides Langmuir. 2015 Jan 20;31(2) :741-51. doi ... (cryoTEM) were used to examine the structures formed by both smooth and rough LPS chemotypes and the effect of the peptides, by visualization of the ... Bacterium Lipopolysaccharide - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics LPSs are amphiphilic macromolecules generally comprising three defined regions distinguished by their genetics, structures, and function: the lipid A, the core oligosaccharide and a polysaccharide portion, the O-chain. In some Gram-negative bacteria, LPS can terminate with the core portion to form rough-type LPS (R-LPS, LOS).
Lipopolysaccharide and Its Constituents | Encyclopedia.com Lipopolysaccharide is medically important to humans. When free from the bacterium, LPS is toxic. The portion of the LPS that is responsible for the toxicity is the core and lipid A portion (the endotoxin). Endotoxin can produce a fever, decrease in the number of white blood cells, and damage to blood vessels resulting in reduced blood pressure.
Lipopolysaccharides - Sigma-Aldrich Lipopolysaccharides are heat-stable endotoxins and have long been recognized as a key factor in septic shock (septicemia) in humans 1,7 and, more generally, in inducing a strong immune response in normal mammalian cells. The lipid A moiety has been identified as critical to the endotoxin activity of lipopolysaccharide.

















0 Response to "38 examine and correctly label the various portions of bacterial lipopolysaccharide as shown here."
Post a Comment