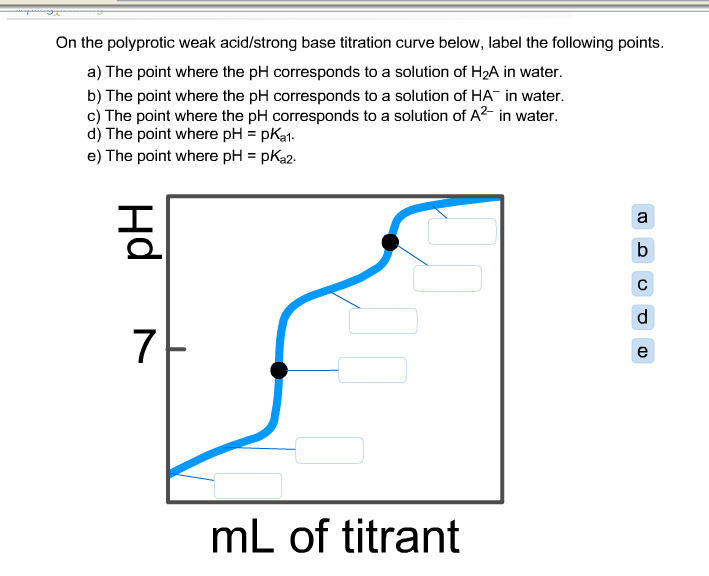
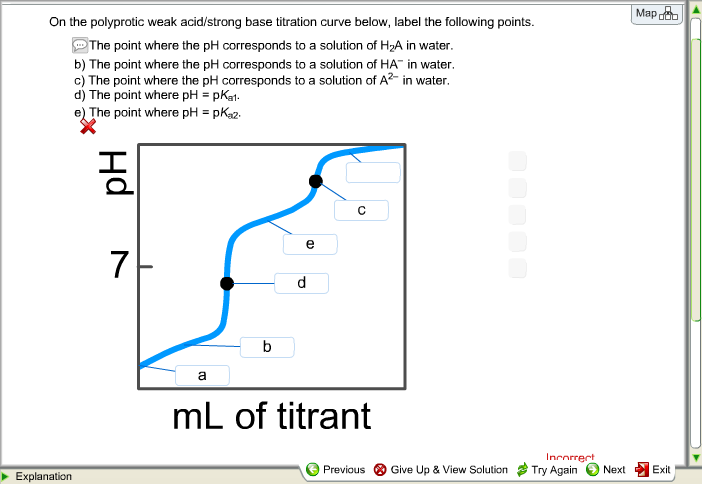
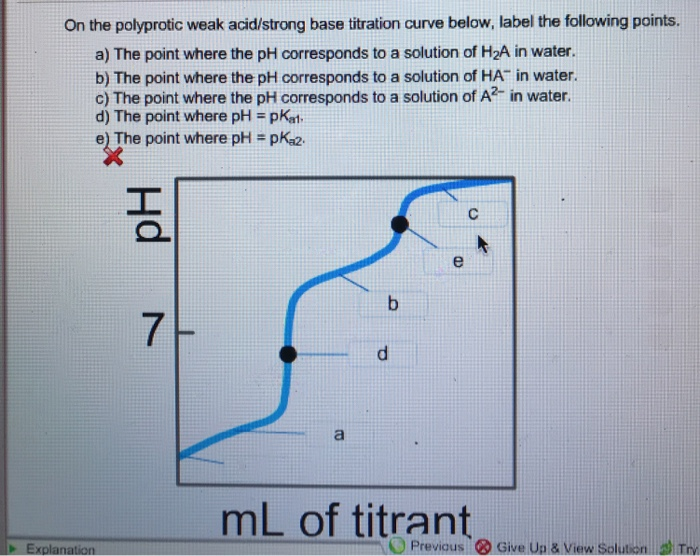
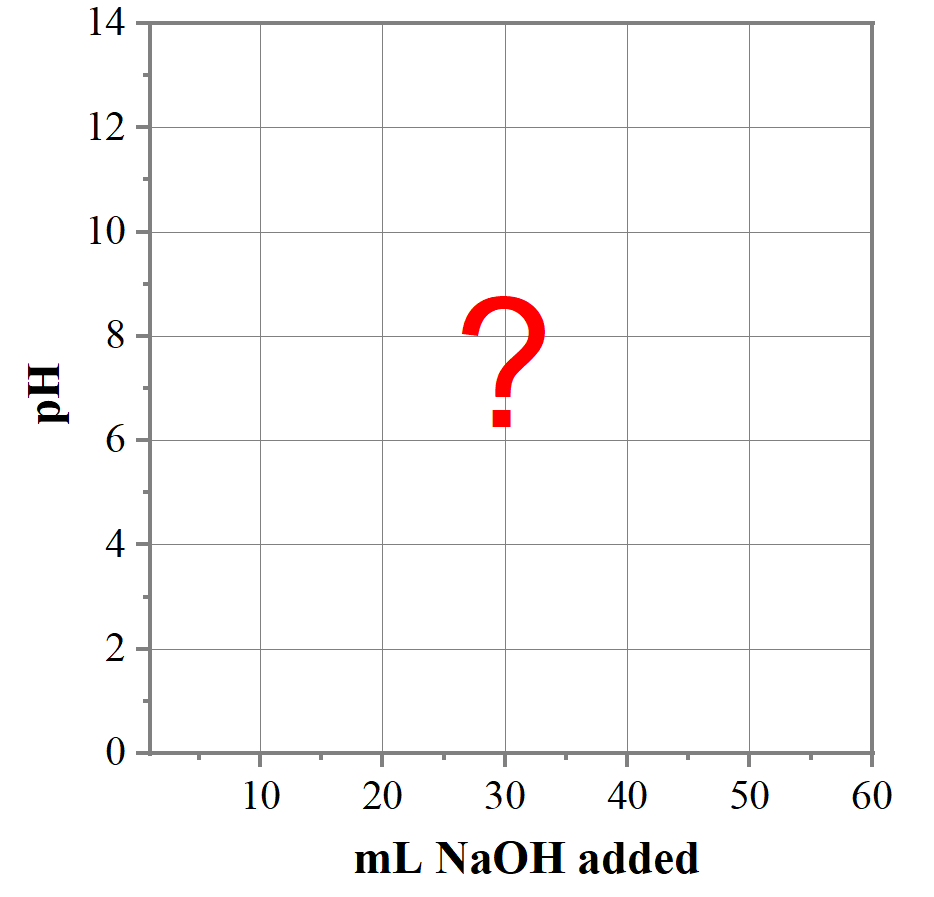
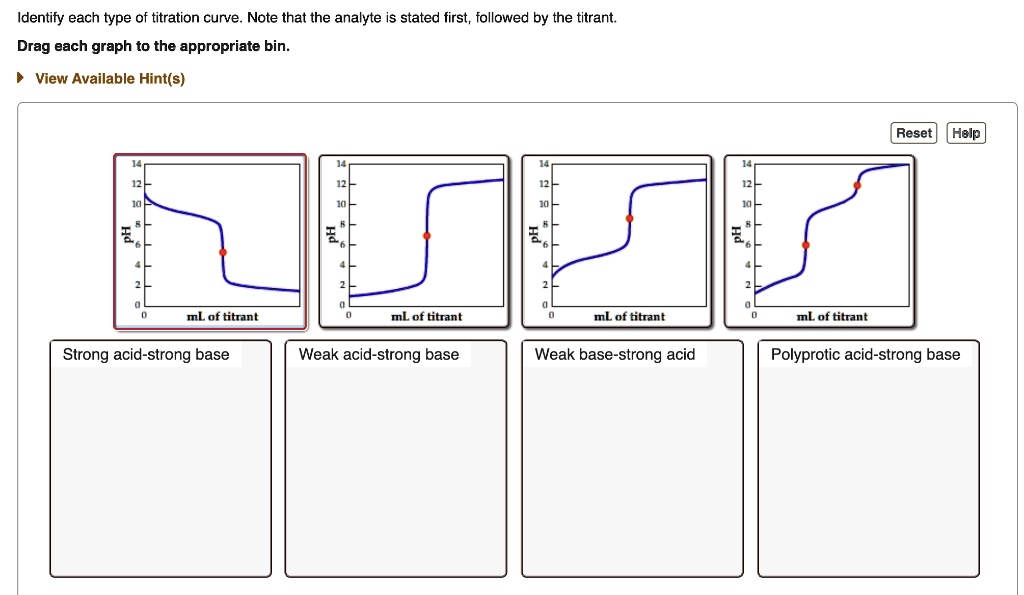
39 on the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points.
Solved On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration | Chegg.com On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points. The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of H_2A in water. The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of HA^-in water. The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of A^2- in water. The point where pH = pK_a1. The point where pH = pK_a2. Solved On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration - Chegg On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points. The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of H_2 A in water. The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of H_2 A in water. The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of A^2- in water. The point where pH = pK_a1. The point where pH = pK_a2.
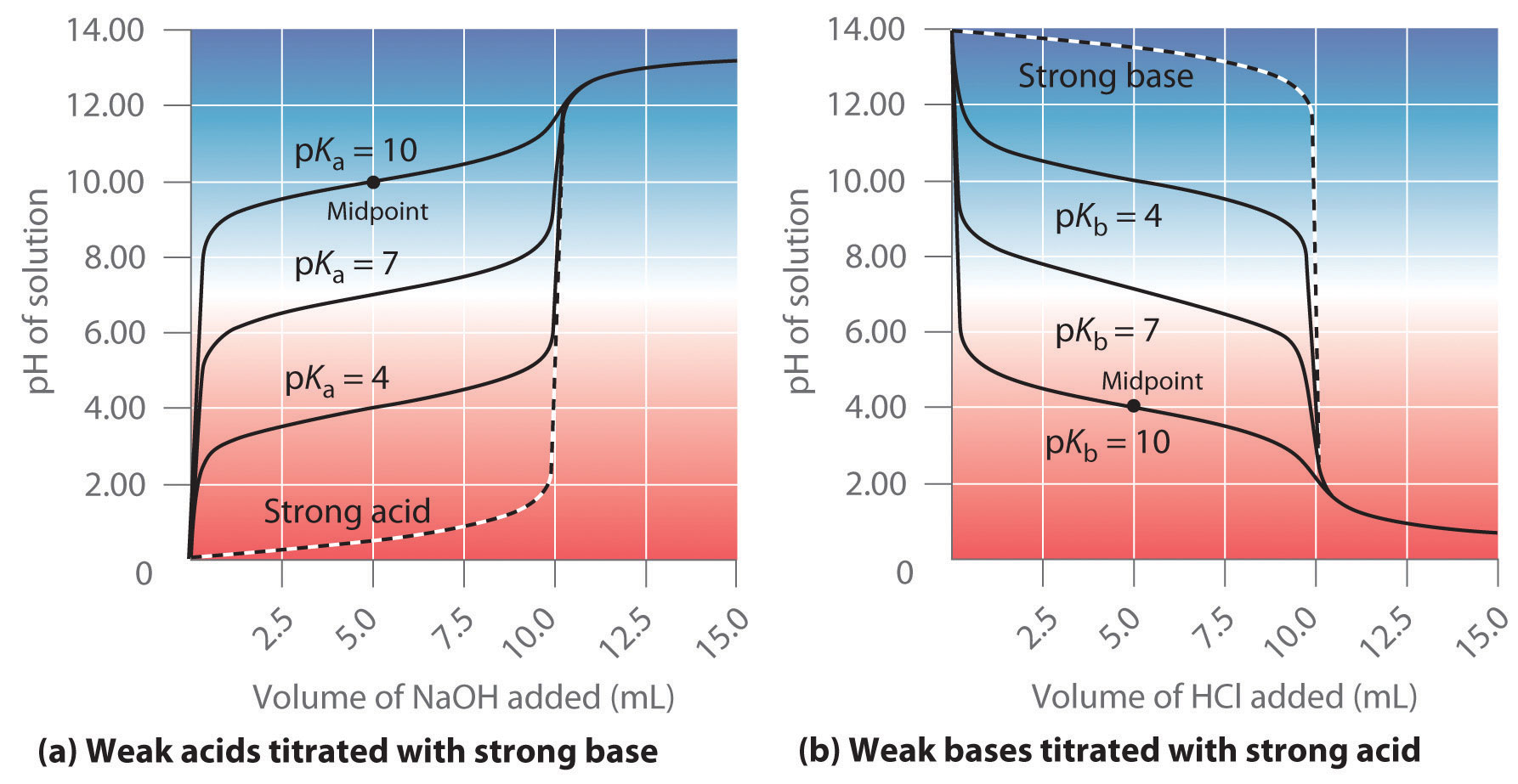
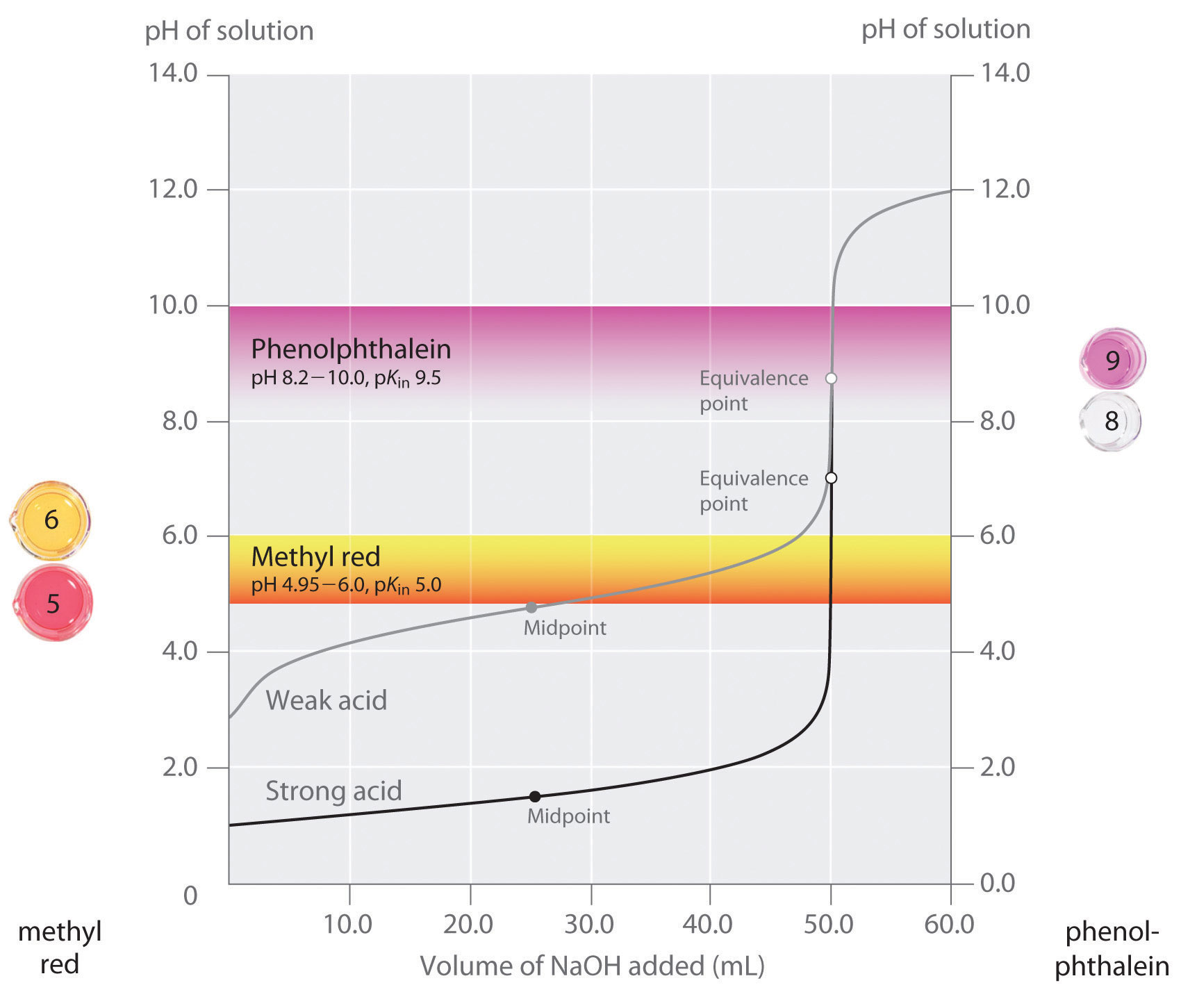
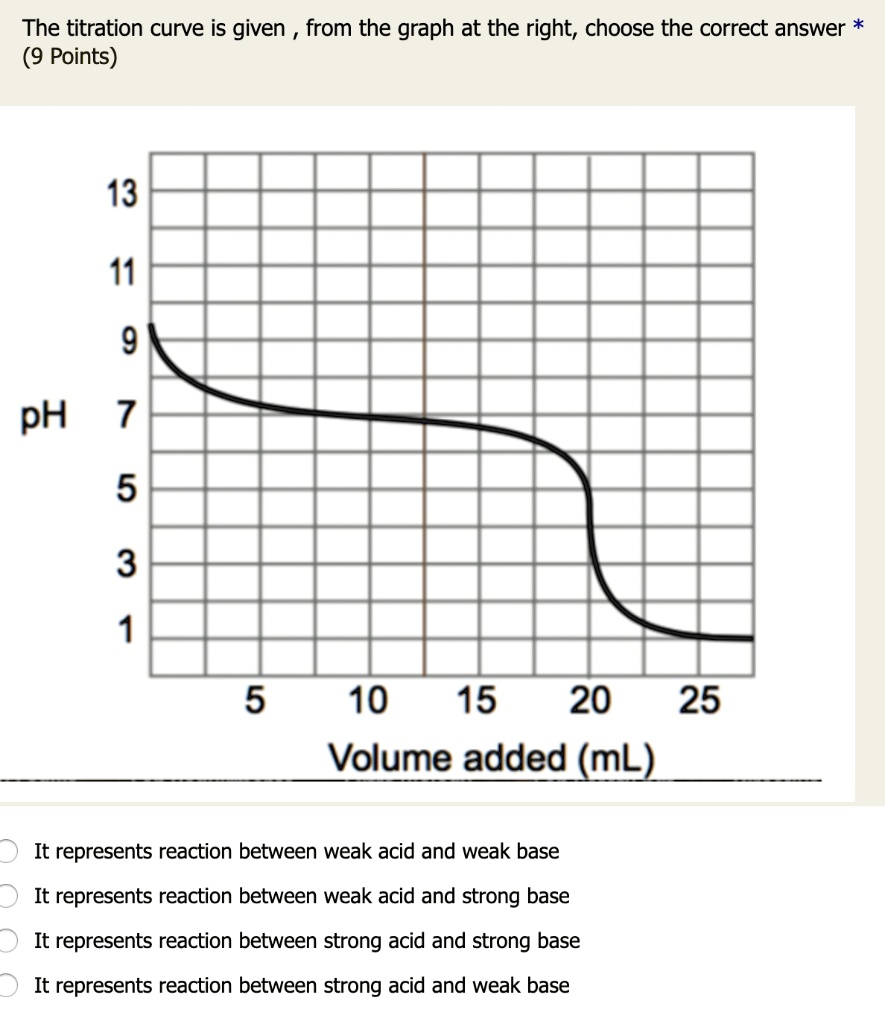
Titration of a Weak Acid with a Strong Base - Chemistry LibreTexts There are several characteristics that are seen in all titration curves of a weak acid with a strong base. These characteristics are stated below. The initial pH (before the addition of any strong base) is higher or less acidic than the titration of a strong acid There is a sharp increase in pH at the beginning of the titration.
On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points.
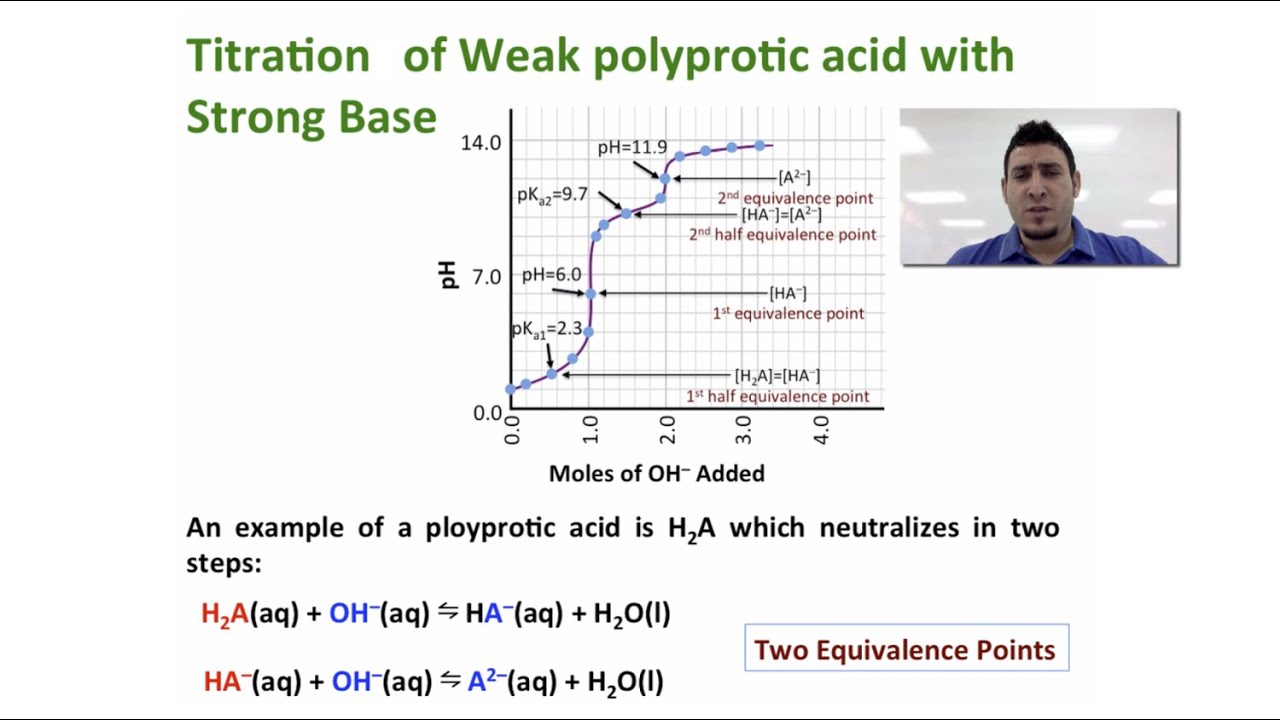
Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry- 9th Edition - Academia.edu Calculations of pH and of titration curves are also described. I n this chapter, we describe methods for treating complex acid/base systems, including the calculation of titration curves. We define complex systems as solutions made up of (1) two acids or two bases of different strengths, (2) an acid or a base that has two or more acidic or basic functional groups, or (3) an … Titration of polyprotic acids/bases and mixtures Titration curves of polyprotic acids, presented below, show these problems. 0.1M solution of sulfuric acid titrated with 0.1M solution of strong base. pK a1 =-3, pK a2 =2. Sulfuric acid - while its second proton is much less acidic than the first one - is strong enough so that both protons get titrated together. Titrations of polyprotic acids (video) | Khan Academy Titrating a polyprotic acid with a strong base produces a pH curve with as many equivalence points as there are acidic protons on the acid. The pKₐ values for these protons can be estimated from the corresponding half-equivalence points on the curve, where pH = pKₐ.
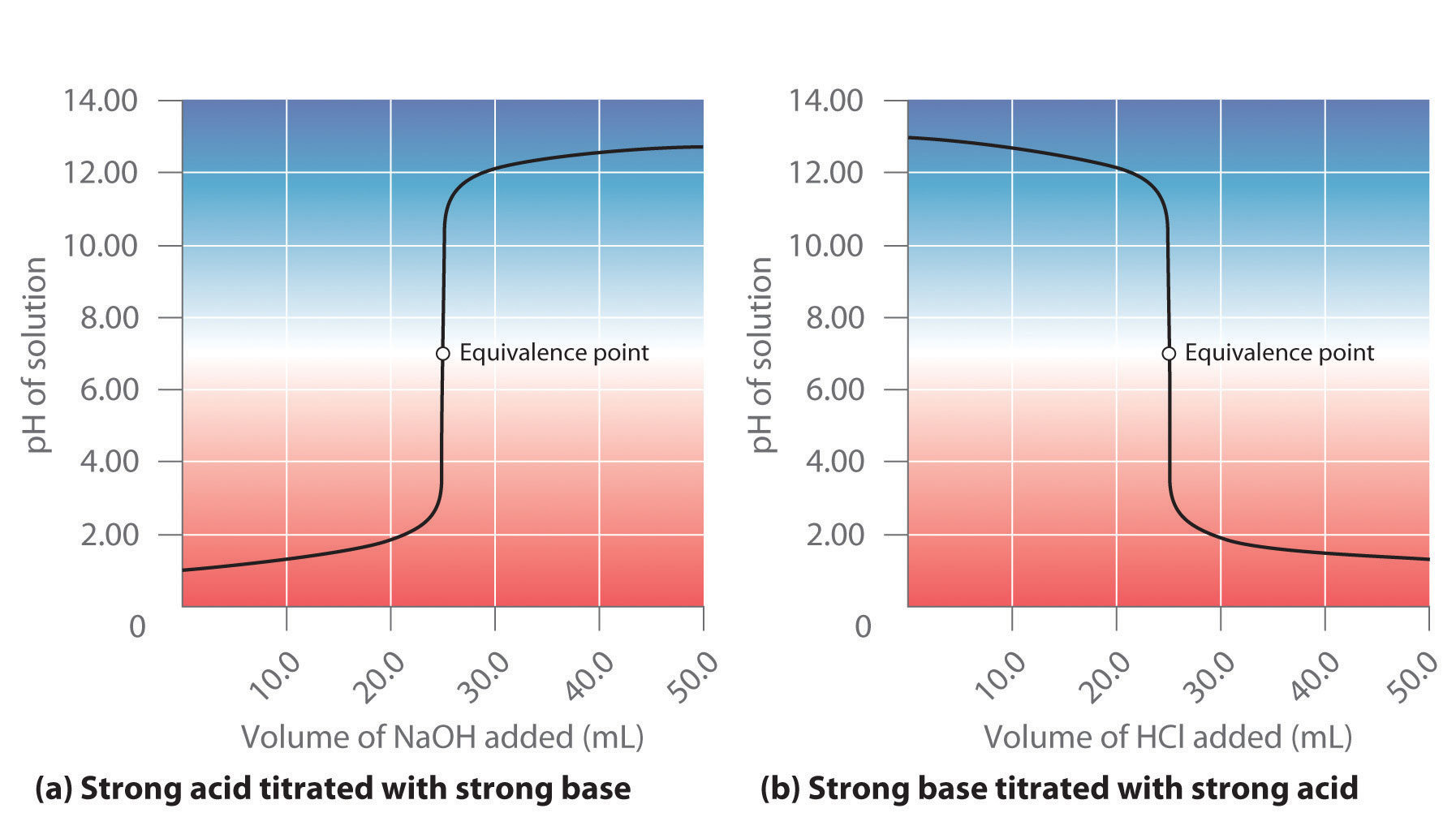
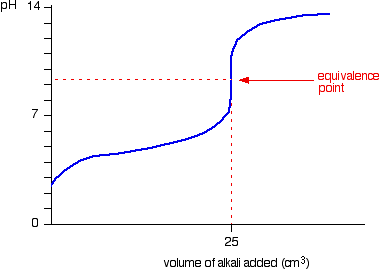
On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points.. JoVE | Peer Reviewed Scientific Video Journal - Methods and Protocols A polyprotic acid contains more than one ionizable hydrogen and undergoes a stepwise ionization process. If the acid dissociation constants of the ionizable protons differ sufficiently from each other, then the titration curve for such polyprotic acid generates a distinct equivalence point for each of its ionizable hydrogens. On the weak base/strong acid titration curve, label A. the point where ... On the weak base/strong acid titration curve, label A. the point where the pH corresponds to a solution of the weak base (B) in water; B. the point where the pH corresponds to a solution of the conjugate acid (BH ) in water; C. the point where pH 2 See answers Advertisement Busiyijide Answer: 15.6: Acid-Base Titration Curves - Chemistry LibreTexts The titration curves of strong acid titrated with strong base and strong base titrated with strong acid are inverses of each other. At the equivalence point (when 25.0 mL of NaOH solution has been added), the neutralization is complete: only a salt remains in solution (NaCl), and the pH of the solution is 7.00. Titration of a Weak Base with a Strong Acid - Chemistry LibreTexts Titration of a Weak Acid with a Strong Base Titration of a Weak Polyprotic Acid Table of contents Titrant added before the equivalence point At the equivalence point Data obtained through the process of titration can be used to compute the molarity and the correlated acidity of a solution at various times of the titration.
Diprotic and Triprotic Acids and Bases - Purdue University Triprotic Acids. Our techniques for working diprotic acid or diprotic base equilibrium problems can be applied to triprotic acids and bases as well. To illustrate this, let's calculate the H 3 O + , H 3 PO 4, H 2 PO 4-, HPO 42- , and PO 43- concentrations at equilibrium in a 0.10 M H 3 PO 4 solution, for which Ka1 = 7.1 x 10 -3, Ka2 = 6.3 x 10 ... Solved On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration - Chegg On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points a) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of H2A in water. b) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of HA in water. c) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of A2 in water. d) The point where pH = pK,1. On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label ... On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points. Subject: Chemistry Price: 2.85 Bought 3. Share With. On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points. The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of H2A in water. Titration Curves of Acids and Bases - ThoughtCo The first curve shows a strong acid being titrated by a strong base. There is the initial slow rise in pH until the reaction nears the point where just enough base is added to neutralize all the initial acid. This point is called the equivalence point. For a strong acid/base reaction, this occurs at pH = 7.
Solved On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration - Chegg Question: On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points. a) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of H2A in water. b) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of HA" in water. c) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of A2 in water. General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (10th … Following ten years of teaching, research, consulting, and directing the NSF Institutes for Secondary School Science Teachers at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, Dr. Petrucci joined the planning staff of the new California State University campus at San Bernardino in 1964. There, in addition to his faculty appointment, he served as Chairman of the Natural … Please help and explain, thank you. - OneClass On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points. a) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of H2A in water. b) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of HA in water c) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of A n water. d) The point where pH EpKa1. Vogel's TEXTBOOK OF QUANTITATIVE CHEMICAL ANALYSIS 5th ed … Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
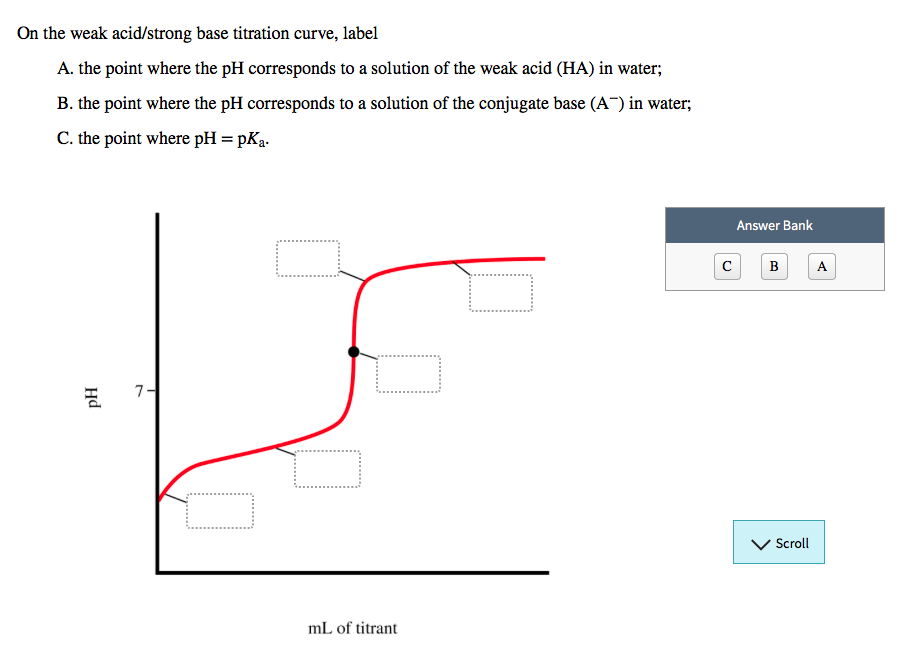
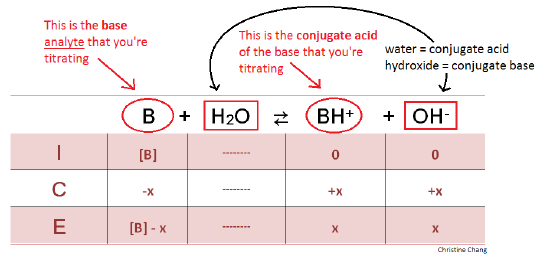
CHP 11 Flashcards | Quizlet The weaker the acid, the higher the pH at the equivalence point. On the weak acid/strong base titration curve, label. A. the point where the pH corresponds to a solution of the weak acid (HA) in water; B. the point where the pH corresponds to a solution of the conjugate base (A−) in water; C. the point where pH=p𝐾a.
Titration curve of a diprotic acid with a strong base titrant This would be a strong acid too and the inflection point would be that for water at pH 7. Note that the pKa 1.69 is assuming H X + X X − and is taken at 1/2 of the N a X + O H X − used. Knowing that H X 2 S O X 4 has two protons, the second pKa should be taken at 150% on the plot which would give the correct pKa value of 1.99.
On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label ... On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points. a) The point where the pH corresponds to a Solution of H2A in water. b) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of HA^- in water. C) The point where...
M16Q6: Titration of a Weak Acid with a Strong Base; Titration ... - Unizin Example 1. Titration of a Weak Acid with a Strong Base The titration curve shown in Figure 1 is for the titration of 25.00 mL of 0.100 M CH 3 COOH with 0.100 M NaOH. The reaction can be represented as: CH 3 COOH(aq) + OH - (aq) → CH 3 COO - (aq) + H 2 O(ℓ). What is the initial pH before any amount of the NaOH solution has been added?
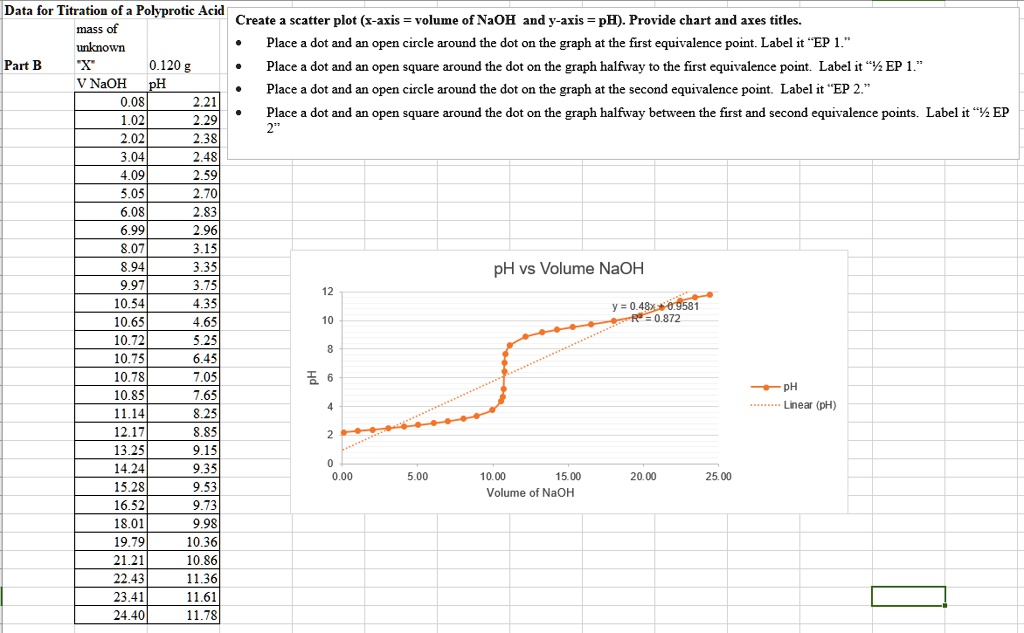
D30.2 Titration of Polyprotic Acids and Bases - Unizin The curve for the titration of 25.0 mL of 0.100-M H 3 PO 4 solution with 0.100-M NaOH. Species in solution at each midpoint are shown. Note the two distinct equivalence points corresponding to deprotonation of H 3 PO 4 at pH ≈ 4.6 and H 2 PO 4- at pH ≈ 9.8.
17.4: Titrations and pH Curves - Chemistry LibreTexts 14.08.2020 · The titration curve for the reaction of a polyprotic base with a strong acid is the mirror image of the curve shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\). The initial pH is high, but as acid is added, the pH decreases in steps if the successive \(pK_b\) values are well separated. Table E1 lists the ionization constants and \(pK_a\) values for some common ...
Assignment Essays - Best Custom Writing Services Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply.
polyprotic weak acid with strong base titration curve I have to label the points on a titration curve for a polyproctic weak acid/strong base titration. I have to label the points where; a) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of H2A in water. b) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of HA- in water. c) The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of A2- in water.
On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label ... Get the detailed answer: On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, ... On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points. 🏷️ LIMITED TIME OFFER: GET 20% OFF GRADE+ YEARLY SUBSCRIPTION → ...
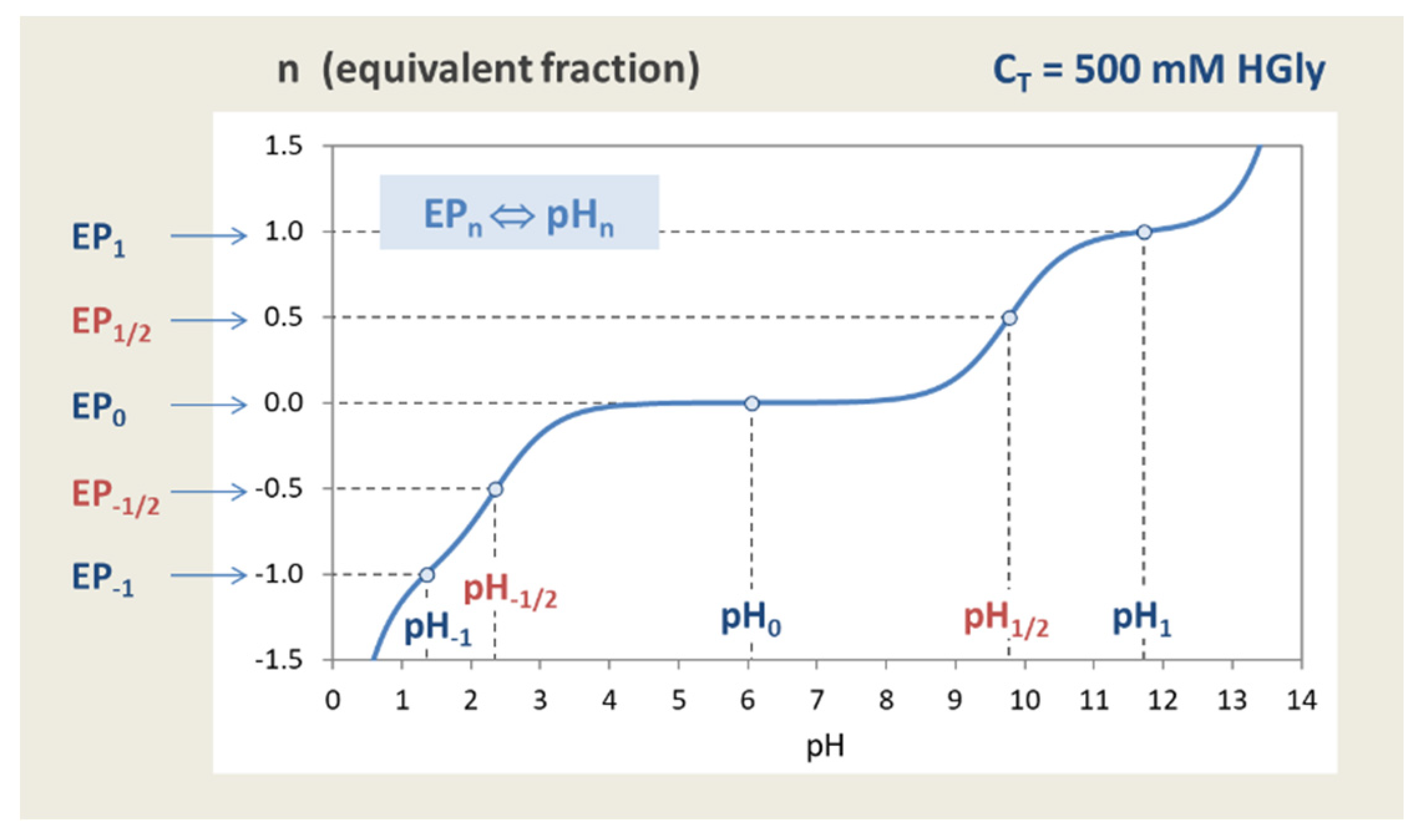
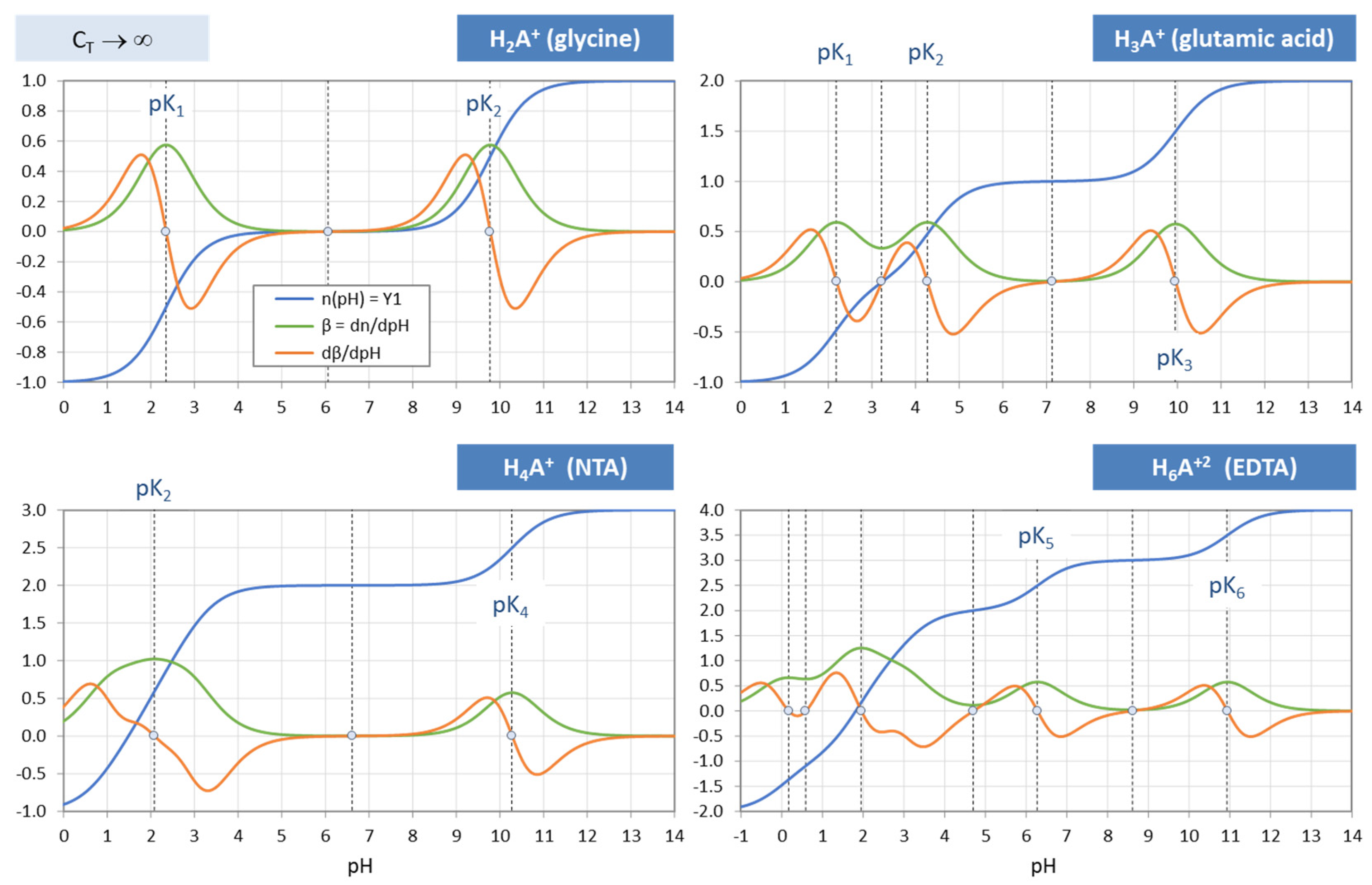
Titration Curves of Aminoacids - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham This curve empirically defines several characteristics. The precise number of each characteristic depends on the nature of the acid being titrated: 1) the number of ionizing groups, 2) the pKa of the ionizing group (s), 3) the buffer region (s). Fig: 1: Titration curve Amino Acids are weak Polyprotic Acids.
Solved On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration | Chegg.com On the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points. The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of H2A in water. The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of HA- in water. The point where the pH corresponds to a solution of A2- in water. The point where pH = pKa1. The point where pH = pKa2.
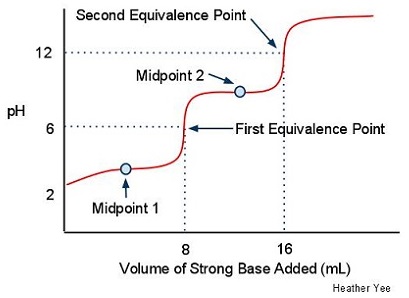
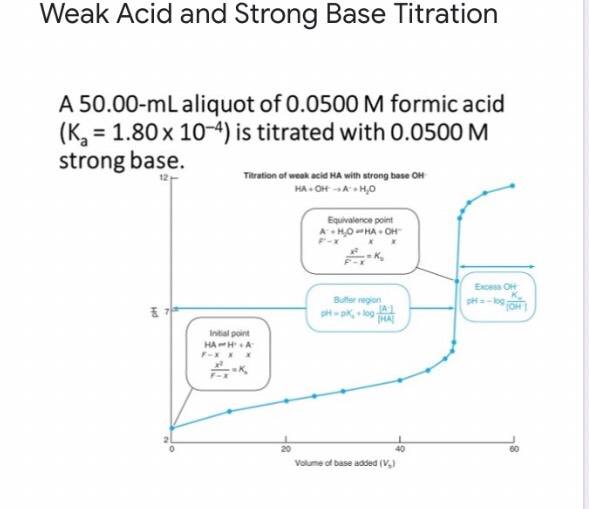
Titration of a Weak Polyprotic Acid - Chemistry LibreTexts The weak polyprotic acid (analyte) is in green and is titrated with teh strong base (the titrant) in red. (CC BY; Heather Yee via LibreTexts) When an acid is titrated, there is an equivalence, or stoichiometric, point, which is when the moles of the strong base added equal of the moles of weak acid present.
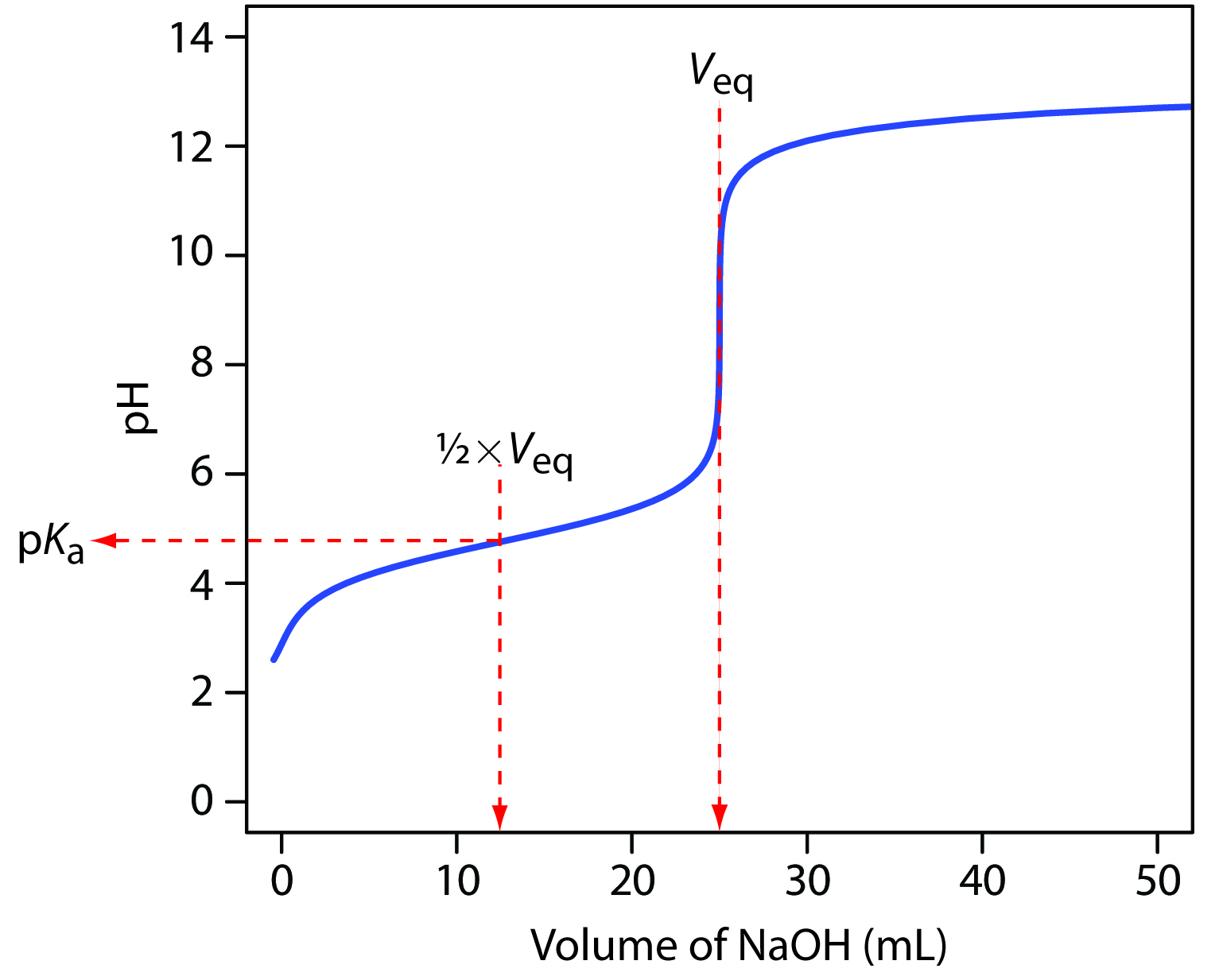
M16Q5: Interpretation of Titration Curves - Chem 103/104 ... - Unizin After the equivalence point, all of the acid has been used up and the pH is reflective of the excess base present. Figure 1: Titration curve of a strong acid with a strong base. Point 1 marks the pH at the beginning of the titration before any strong base has been added. Point 2 marks the pH at 10 mL, the half-equivalence point.
Weak Acid-Strong Base Titrations | Introduction to Chemistry - Course Hero Titrations are reactions between specifically selected reactants—in this case, a strong base and a weak acid. A titration curve reflects the strength of the corresponding acid and base, showing the pH change during titration. The titration curve demonstrating the pH change during the titration of the strong base with a weak acid shows that at ...
Titration Curves | Dornshuld The following titration curve is characteristic of a weak acid (p Ka = 5.0) and strong base titration. HA ( a q) + OH − ( a q) ⇌ H 2 O ( l) + A − ( a q) Titration Details 50.00 mL of a 0.1 M weak, monoprotic acid (p Ka = 5) 0.1 M strong base 25 °C The initial pH of the solution indicates a weakly acidic solution.
Titrations of polyprotic acids (video) | Khan Academy Titrating a polyprotic acid with a strong base produces a pH curve with as many equivalence points as there are acidic protons on the acid. The pKₐ values for these protons can be estimated from the corresponding half-equivalence points on the curve, where pH = pKₐ.
Titration of polyprotic acids/bases and mixtures Titration curves of polyprotic acids, presented below, show these problems. 0.1M solution of sulfuric acid titrated with 0.1M solution of strong base. pK a1 =-3, pK a2 =2. Sulfuric acid - while its second proton is much less acidic than the first one - is strong enough so that both protons get titrated together.
Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry- 9th Edition - Academia.edu Calculations of pH and of titration curves are also described. I n this chapter, we describe methods for treating complex acid/base systems, including the calculation of titration curves. We define complex systems as solutions made up of (1) two acids or two bases of different strengths, (2) an acid or a base that has two or more acidic or basic functional groups, or (3) an …











![Acid-Base Titrations | Chemistry [Master] | | Course Hero](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wp-content/uploads/sites/1941/2017/05/30163125/tit3.png)

0 Response to "39 on the polyprotic weak acid/strong base titration curve below, label the following points."
Post a Comment