40 can you label the way nucleotides pair up in replicating dna?
Why Life Does Not Really Exist - Scientific American Blog Network 02.12.2013 · Similarly, software platforms like Avida create "digital organisms" that "are made up of digital bits that can mutate in much the same way DNA mutates." In other words they, too, evolve. Helicase - Wikipedia One label is a fluorescent lanthanide chelate, which serves as the label that is monitored through an adequate 96/384 well plate reader. The other label is an organic quencher molecule. The basis of this assay is the "quenching" or repressing of the lanthanide chelate signal by the organic quencher molecule when the two are in close proximity – as they would be when the DNA …
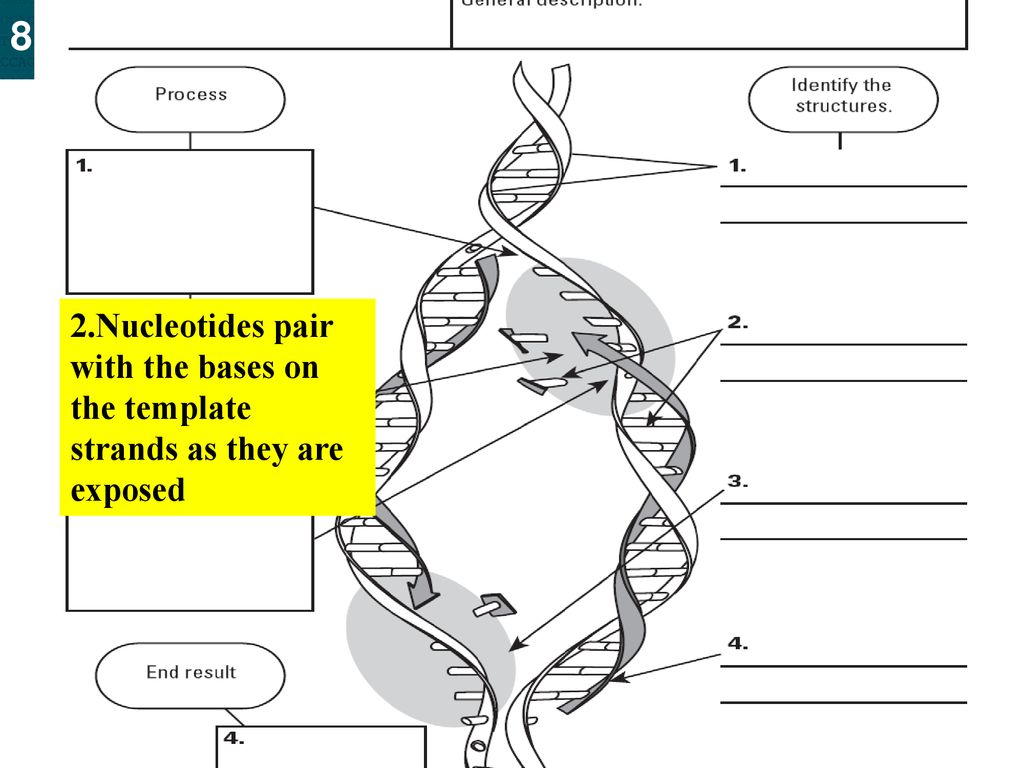
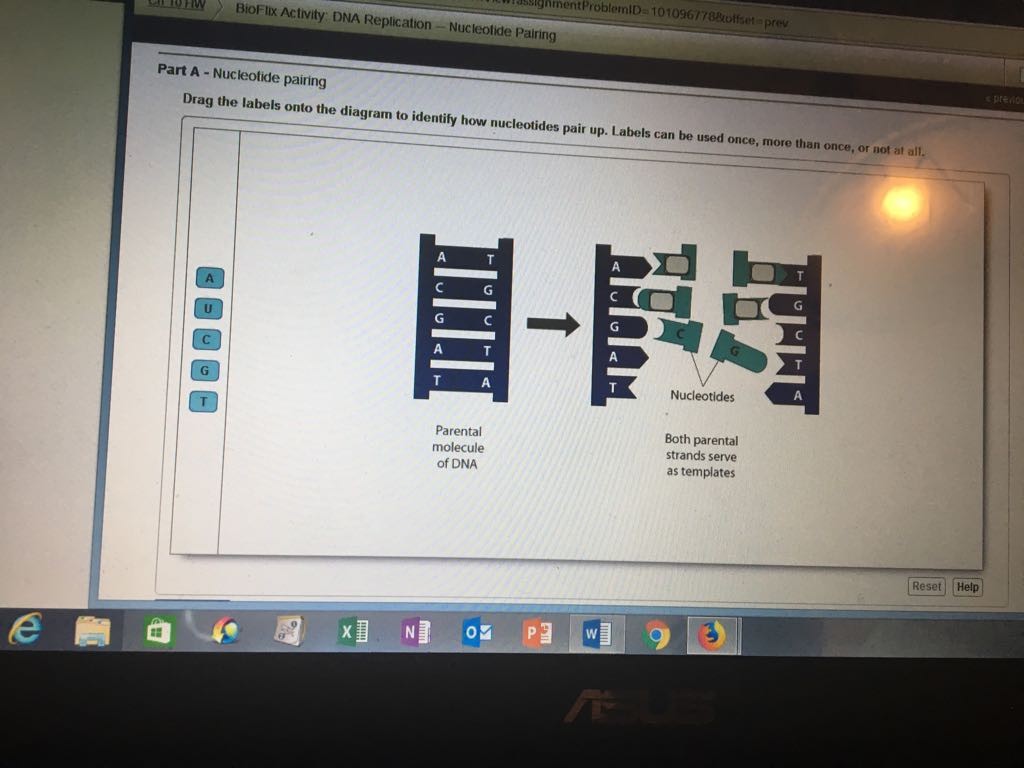
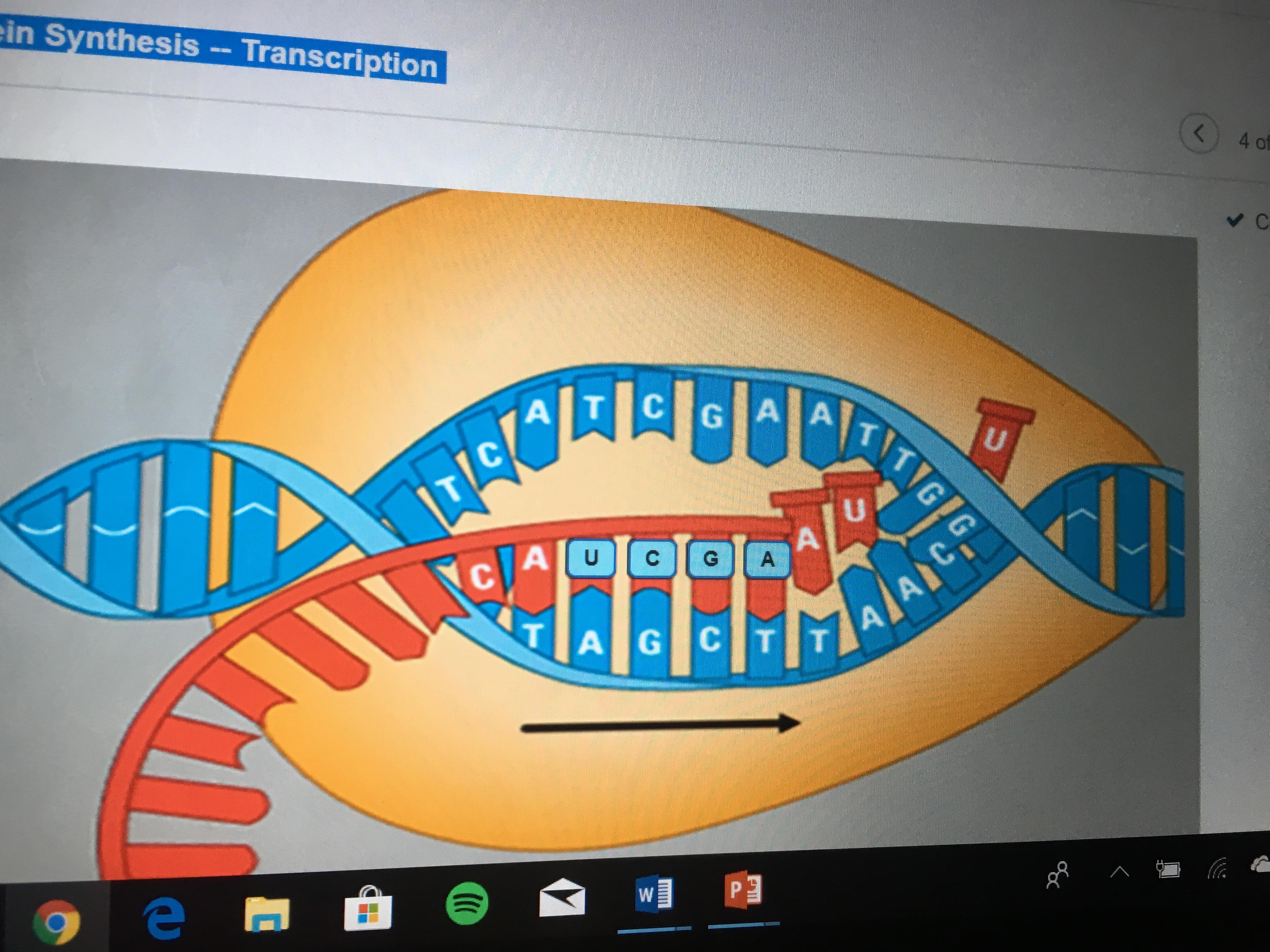
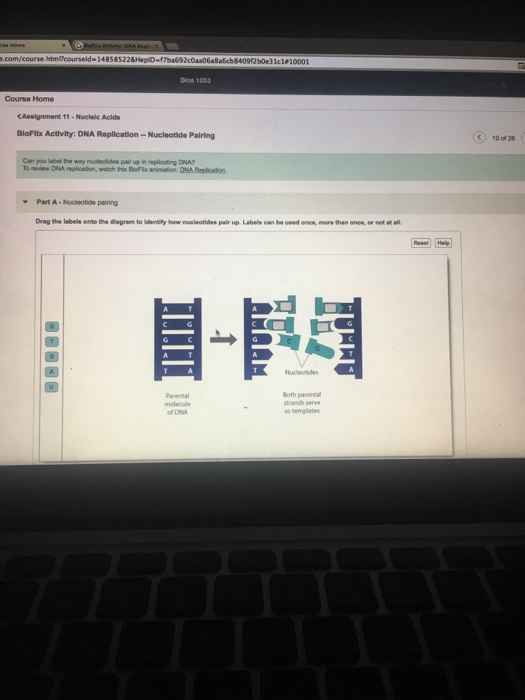
Chapter 10 Core Content Flashcards | Quizlet Can you label the way nucleotides pair up in replicating DNA? To review DNA replication, watch this BioFlix animation: DNA Replication. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify how nucleotides pair up. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. A pairs with T G pairs with C Which of the following build (s) new strands of DNA?
Can you label the way nucleotides pair up in replicating dna?
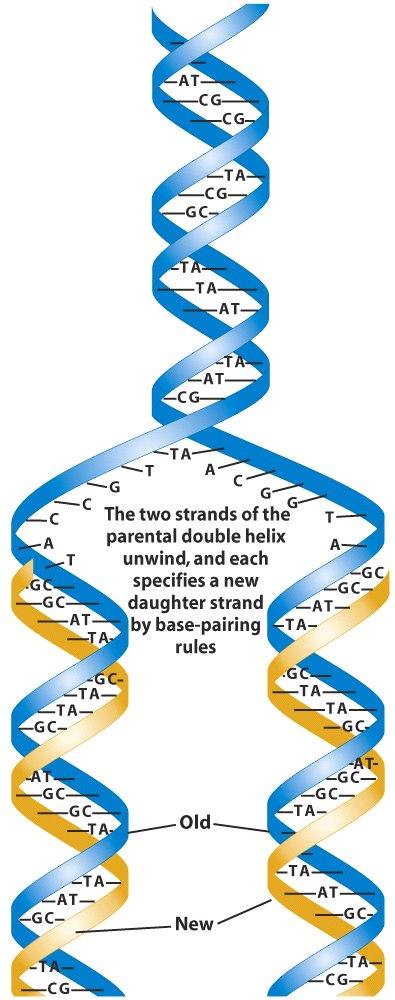
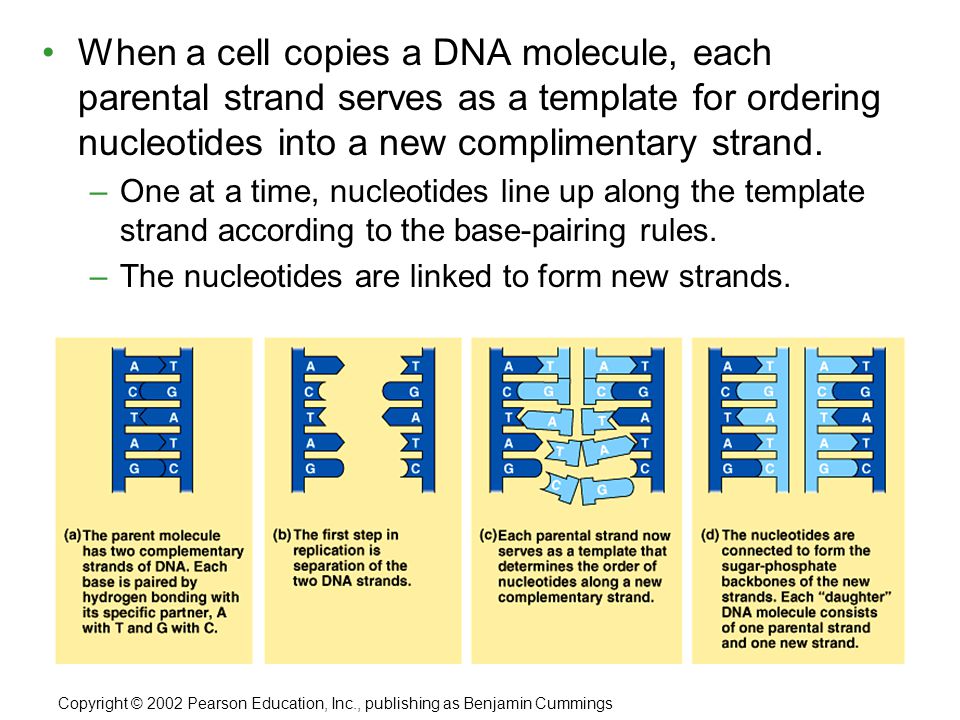
Mastering Bio Chapter 10 Flashcards | Quizlet Which of the following statements regarding DNA is false? DNA contains the nitrogenous base uracil. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify how nucleotides pair up. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. T A G C Short segments of newly synthesized DNA are joined into a continuous strand by _____. ligase DNA Replication Steps and Process - ThoughtCo Enzymes that participate in the eukaryotic DNA replication process include: DNA helicase - unwinds and separates double stranded DNA as it moves along the DNA. It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in DNA. DNA primase - a type of RNA polymerase that generates RNA primers. DNA Base Pairs and Replication | Biology for Majors I - Lumen Learning During DNA replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or "old" strand. When two daughter DNA copies are formed, they have the same sequence and are divided equally into the two daughter cells.
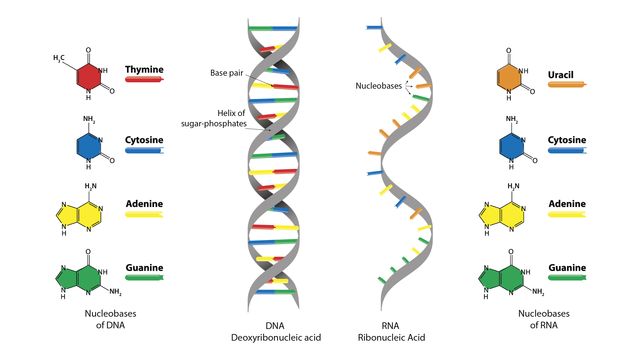
Can you label the way nucleotides pair up in replicating dna?. How do the different DNA nucleotides pair during DNA replication ... What are the nucleotides in DNA and how do they pair? Nucleotides form a pair in a molecule of DNA where two adjacent bases form hydrogen bonds. The nitrogenous bases of the DNA always pair up in specific way, purine with pyrimidine (A with T, G with C), held together by weak hydrogen bonds. How do DNA nucleotides pair? How do the nucleotides in DNA pair? - Answers See answer (1) Best Answer. Copy. The four nucleic acids that make up the linking structures of the nucleotides in DNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). They form base ... Basic Genetics - University of Utah If Learn.Genetics is useful to you, please take a moment to donate – even a few dollars from each of our visitors would add up to a significant amount! Your support will help us keep Learn.Genetics free and available to everyone. It will also help us develop new content for you. Please help us keep Learn.Genetics going! Thank you, How do the nucleotides in DNA pair up? - eNotes.com Expert Answers. DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a double helical molecule, with its two strands connected to each other through nucleotide pairing. There are 4 different nucleotides in a DNA ...
Solved Drag the labels onto the diagram to identity how - Chegg Expert Answer. 100% (13 ratings) ANSWER: *A- T A-T *C- G C- G *G- …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identity how nucleotides pair up. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. View Available Hints) Reset Help T C G A G с u А a A Nucleotides Parental molecule of DNA Both ... Glossary of genetics - Wikipedia Also three-prime untranslated region and trailer sequence. 3'-end Also three-prime end. One of two ends of a single linear strand of DNA or RNA, specifically the end at which the chain of nucleotides terminates at the third carbon atom in the furanose ring of deoxyribose or ribose (i.e. the terminus at which the 3' carbon is not attached to another nucleotide via a phosphodiester … Solved T-Mobile LTE 1:01 PM @ 39%. | Chegg.com To review DNA replication, watch this BioFlix animation: DNAReplication. Part A- Nucleotide pairing Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify how nucleotides pair up. Labels can be used o more than once, or not at all Both parental DNA as This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (42 ratings) Plasmid - Wikipedia In order for plasmids to replicate independently within a cell, they must possess a stretch of DNA that can act as an origin of replication.The self-replicating unit, in this case, the plasmid, is called a replicon.A typical bacterial replicon may consist of a number of elements, such as the gene for plasmid-specific replication initiation protein (Rep), repeating units called iterons, …
DNA Replication - Genome.gov DNA replication is the process by which the genome's DNA is copied in cells. Before a cell divides, it must first copy (or replicate) its entire genome so that each resulting daughter cell ends up with its own complete genome. Narration 00:00 01:17 DNA replication is probably one of the most amazing tricks that DNA does. G-quadruplex - Wikipedia G-quadruplex structures can be computationally predicted from DNA or RNA sequence motifs, but their actual structures can be quite varied within and between the motifs, which can number over 100,000 per genome. Their activities in basic genetic processes are an active area of research in telomere, gene regulation, and functional genomics research. Molecular Biology, Robert Weaver, 5th Edition - Academia.edu Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. ... The Flow of Genetic Information from DNA to RNA to Protein. samwel hashondali. Advances in COVID-19 mRNA vaccine development 23.03.2022 · To date, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has determined 399,600,607 cases and 5,757,562 deaths worldwide. COVID-19 is ...
5.2: Structure and Replication of DNA - Biology LibreTexts DNA is replicated when a cell makes a duplicate copy of its DNA, then the cell divides, resulting in the correct distribution of one DNA copy to each resulting cell. DNA can also be enzymatically degraded and used as a source of nucleotides for the cell. Unlike other macromolecules, DNA does not serve a structural role in cells.
BioFlix Activity DNA Replication Nucleotide Pairing Can you label the ... Part A - Nucleotide pairing Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify how nucleotides pair up. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. ANSWER: Correct Activity: Covalent Bonds HelpReset A G T C U T A G C Adenine would pair with thymine or vice versa. Guanine would pair with cytosine or vice versa.
DNA Replication - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf In some cases, complete circular molecules in the process of replicating could be observed. These DNA molecules contained two replication forks, representing the regions of active DNA synthesis. At each fork the parental strands of DNA separated and two new daughter strands were synthesized. Figure 5.3 Replication of E. coli DNA.
Replication: DNA copied into DNA - Genomics As the new nucleotides line up opposite each parent strand by hydrogen bonding, enzymes called DNA polymerases join the nucleotides by way of phosphodiester bonds. Actually, the nucleotides lining up by complementary base pairing are deoxynucleoside triphosphates, composed of a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose, and three phosphates.
(PDF) Raven Biology of Plants | Michael Branks - Academia.edu Raven Biology of Plants
Bacterial growth: a statistical physicist's guide - IOPscience Nov 14, 2018 · From a statistical physicist's point of view, a bacterium can be viewed as a microscopic particle, or cell, which is bounded by a pair of membranes with a stiff wall in between them (specifically, this is the case for a large class of bacteria that are known as Gram negatives; Gram positive bacteria have a thicker wall and lack the outer membrane).
Paired DNA Strands - HHMI BioInteractive Description. This animation describes the general structure of DNA: two strands of nucleotides that pair in a predictable way. DNA is well-known for its double helix structure. The animation untwists the double helix to show DNA as two parallel strands. Each strand is made up of a sequence of four nucleotides, A, C, G, and T.
Biotechnology Inspection Guide (11/91) | FDA DNA Hybridization (Dot Blot) Analysis - Detection of DNA to the nanogram level using hybridization of cellular DNA with specific DNA probes. Manifestation can be by 32P- labeling ...
Genome - Wikipedia In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses).The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident ...
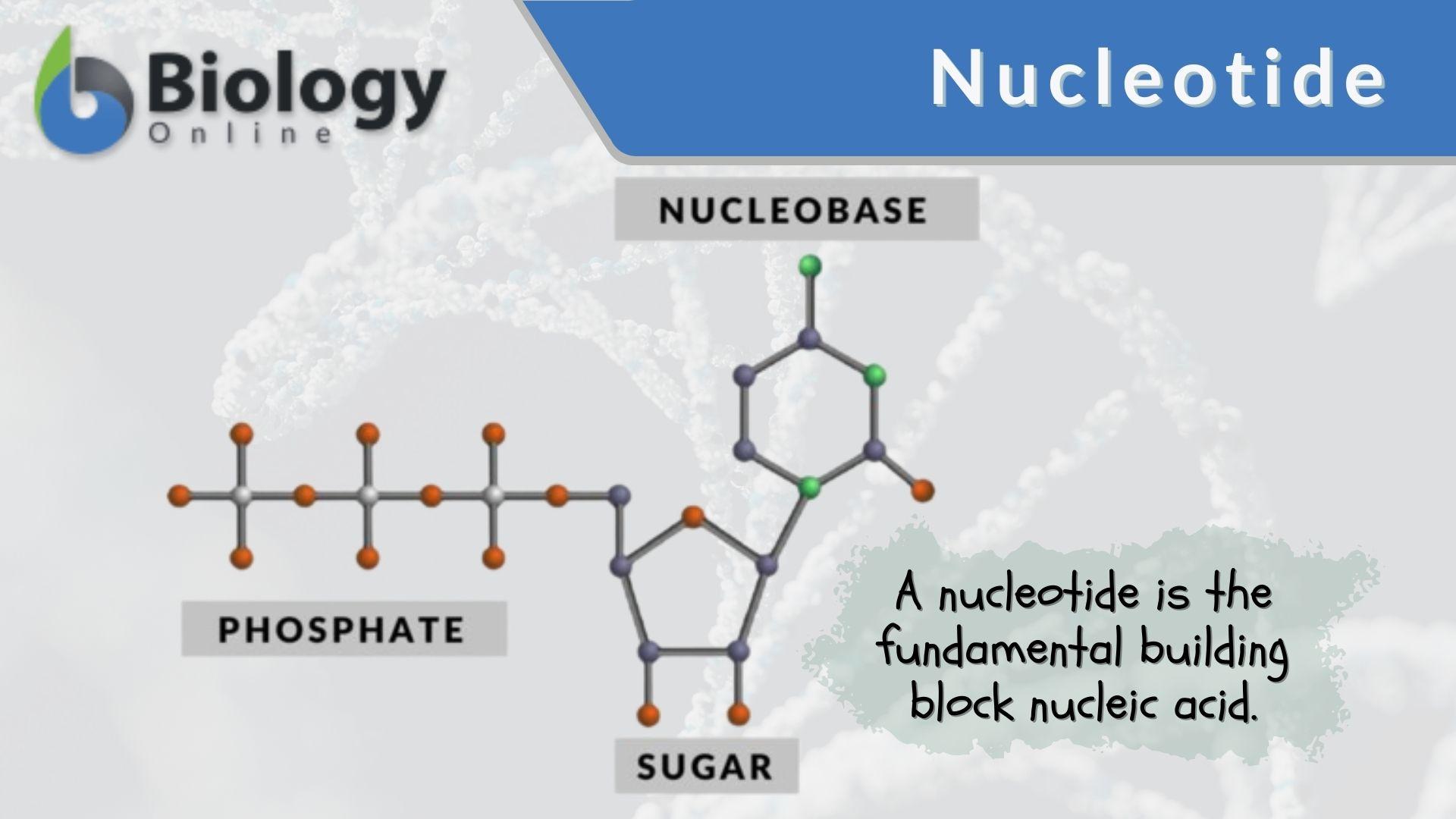
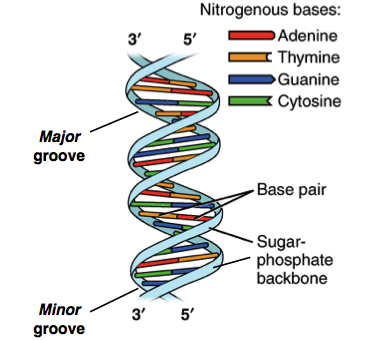
Base Pair - Genome.gov A base pair consists of two complementary DNA nucleotide bases that pair together to form a "rung of the DNA ladder." DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups.
Amino acid - Wikipedia Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code.. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional …
DNA Replication Lab - BIOLOGY JUNCTION During DNA replication, special enzymes move up along the DNA ladder, unzipping the molecule as it moves along. New nucleotides move in to each side of the unzipped ladder. The bases on these nucleotides are very particular about what they connect to. When the enzyme has passed the end of the DNA, two identical molecules of DNA are left behind.
DNA Base Pairs and Replication | Biology for Majors I - Lumen Learning During DNA replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or "old" strand. When two daughter DNA copies are formed, they have the same sequence and are divided equally into the two daughter cells.
DNA Replication Steps and Process - ThoughtCo Enzymes that participate in the eukaryotic DNA replication process include: DNA helicase - unwinds and separates double stranded DNA as it moves along the DNA. It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in DNA. DNA primase - a type of RNA polymerase that generates RNA primers.
Mastering Bio Chapter 10 Flashcards | Quizlet Which of the following statements regarding DNA is false? DNA contains the nitrogenous base uracil. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify how nucleotides pair up. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. T A G C Short segments of newly synthesized DNA are joined into a continuous strand by _____. ligase






![Chapter 8: Genetics [compatibility mode]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter8-geneticscompatibilitymode-141214140247-conversion-gate02/85/chapter-8-genetics-compatibility-mode-57-320.jpg?cb=1668050999)










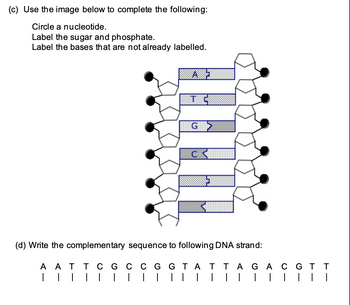


0 Response to "40 can you label the way nucleotides pair up in replicating dna?"
Post a Comment