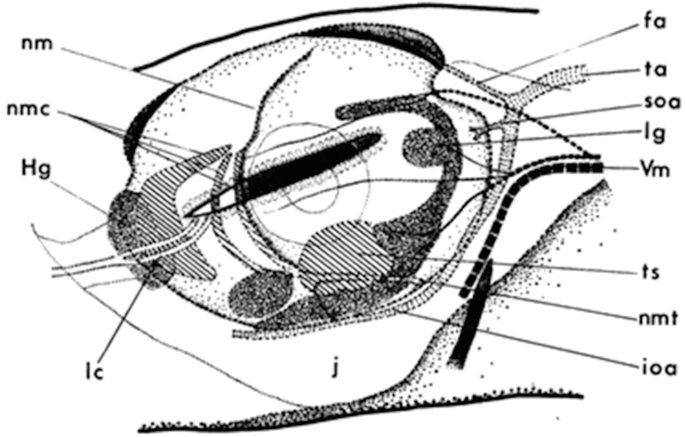
45 label the internal structures of the clam
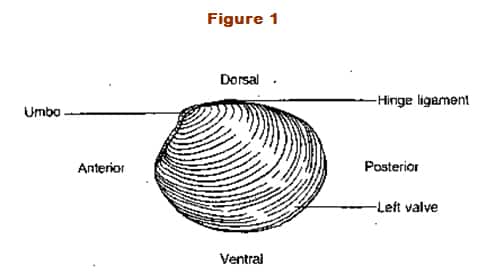
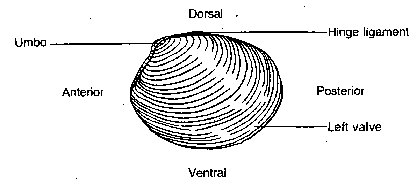
Clam Dissection Lab: Explained | SchoolWorkHelper Place a clam in a dissecting tray and identify the anterior and posterior ends of the clam as well as the dorsal, ventral, & lateral surfaces. Locate the umbo, the bump at the anterior end of the valve. This is the oldest part of the clamshell. Find the hinge ligament which hinges the valves together and observe the growth rings. How can you label the internal structure of a clam? - Answers An Internal Structure is the way an organism looks on the outside and an External Structure is the looks on the outside. When you open the clam will all the internal organs be visible?...
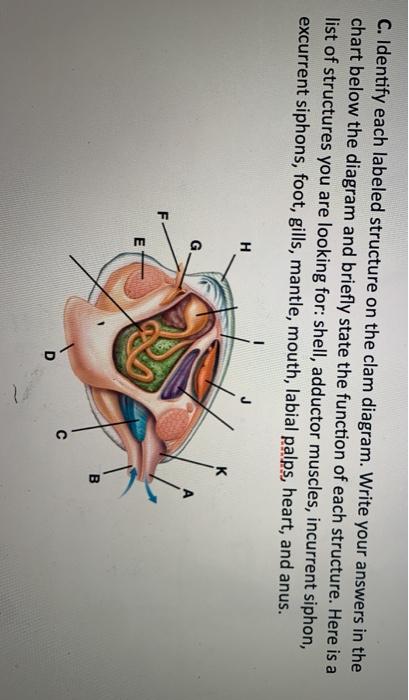
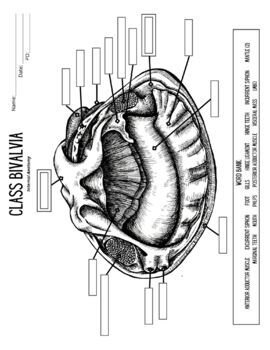
Clam Dissection.docx - Google Docs Label the internal structures of the clam and draw arrows showing the pathway of food as it travels to the clam's stomach: Clam Dissection Introduction The phylum Mollusca includes snails,...

Label the internal structures of the clam
PDF Clam Dissection Guideline - Monadnock Regional High School clam shell is the umbo, and it is from the hinge area that the clam extends as it grows. I. Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to identify the internal and external structures of a mollusk by dissecting a clam. II. Materials: 2 pairs of safety goggles 2 pairs of gloves 1 preserved clam 1 dissecting tray 1 paper towel 1 pair of scissors PDF Anatomy of a Clam 1. Obtain clam specimens (fresh or preserved). 2. Divide the class into small groups (2-4 per group when possible). 3. Prepare one dissection kit, pan, and clean-up materials per group. 4. Copy the dissection guide for each student. 5. Copy the External and Internal Clam Anatomy handouts for each student. 6. Study 25 Terms | clam dissection functions Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying clam dissection functions. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. ... these are the respiratory structures obtaining oxygen and getting food. Foot ... clam dissection: internal anatomy: parts & functions 17 Terms. bolish. functions 76 Terms. kendalltucker1 PLUS. Clam Practical 46 Terms.
Label the internal structures of the clam. Clam structures and functions Flashcards | Quizlet intestine 1. finishes chemical digestion 2. nutrients are absorbed into the visceral mass 3. sends waste to rectum pericardial sac protects heart heart sends blood through branched vessels to open areas within the visceral mass kidney remove waste from "blood" (water) what family are the clams a part of? mollusk Solved Results 1. Draw a diagram and label the internal - Chegg Results 1. Draw a diagram and label the internal anatomy of the clam. Which structures were difficult to locate? 2. In what ways does the clam differ from other mollusks? What modifications are critical for its unique habitat and lifestyle? This problem has been solved! Clam Dissection - js082.k12.sd.us The tube-like structure that runs through the pericardium is the intestine. 25. Answer the questions on your lab report & label the diagrams of the internal structures of the clam. Also, use arrows on the clam diagram to trace the pathway of food as it travels to the clam's stomach. Continue the arrows showing wastes leaving through the anus. PDF Label the Clam Anatomy @Sheri Amsel Label the Clam Anatomy @Sheri Amsel . Created Date: 6/8/2018 3:46:07 PM
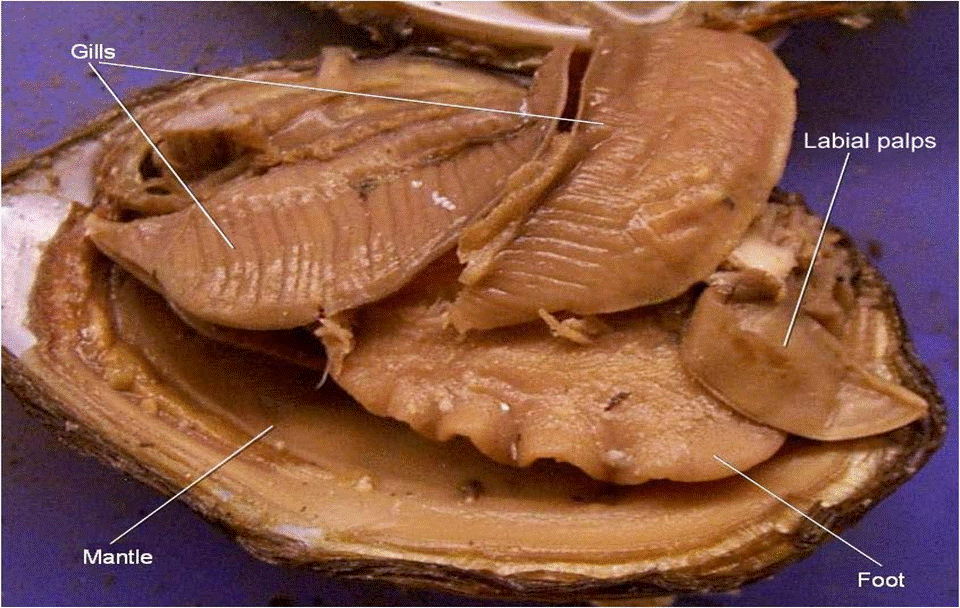
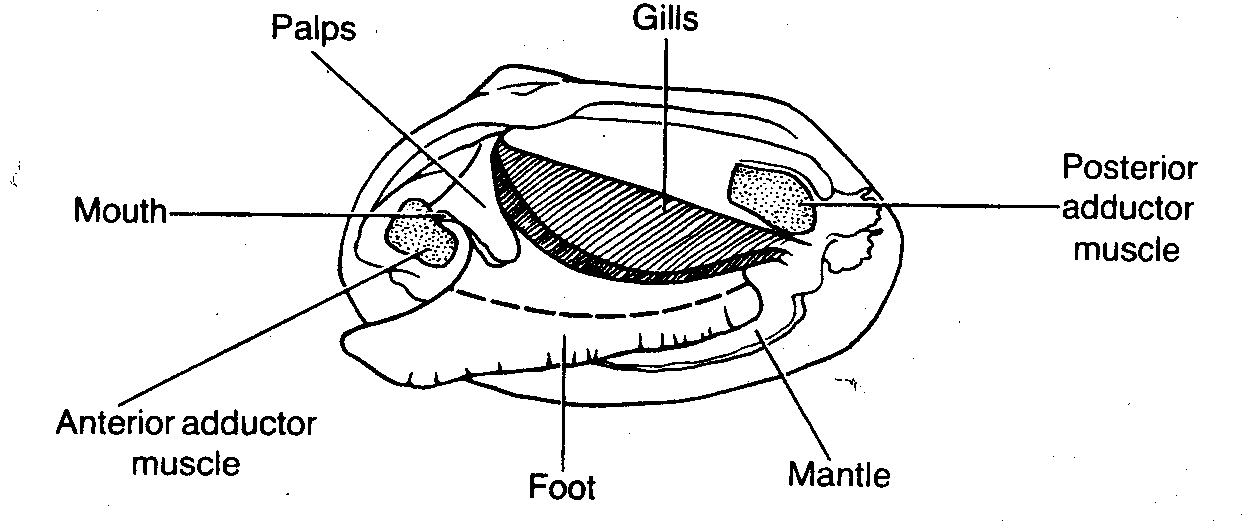
Clam dissection: A first step into dissection and anatomy for young ... This is known as the dorsal body, and it is like a robe that covers the internal organs of the clam. Over time, the mantle secretes what will become the shell, allowing the animal to grow a larger home. Foot In your clam there is a large pouch that might look like a stomach, filled with green and brown mush. Clam Diagram & Parts | What Is a Clam? | Study.com The labeled internal anatomy of a clam. Lesson Summary Clams are invertebrate (lacking a backbone) bivalve (two shells) animals belonging to a taxonomic group of related organisms known as mollusks. Solved in 7 Sketch and label the basic external anatom of a - Chegg in 7 sketch and label the basic external anatom of a tapeworm 8 discuss the diversity of trematodes trematodes the correct answer . are parasitic flukes, and most are circle b. mostly reside in the lung, liver, bile and pancreatic ducts, intestine, and blood c. include taenia sp. and dugesia sp d both a and b e all of the above 9 label the … [Solved] Draw a diagram and label the internal anatomy of the clam ... There is no cephalization of the neurological system. It is made up of three pairs of segmented ganglia that are linked together by nerves. Mollusks abandon a more active life style for a sedentary existence like the clam. Mollusks are mostly marine organisms that dwell in a variety of settings ranging from shallow coastal areas to deep seas.
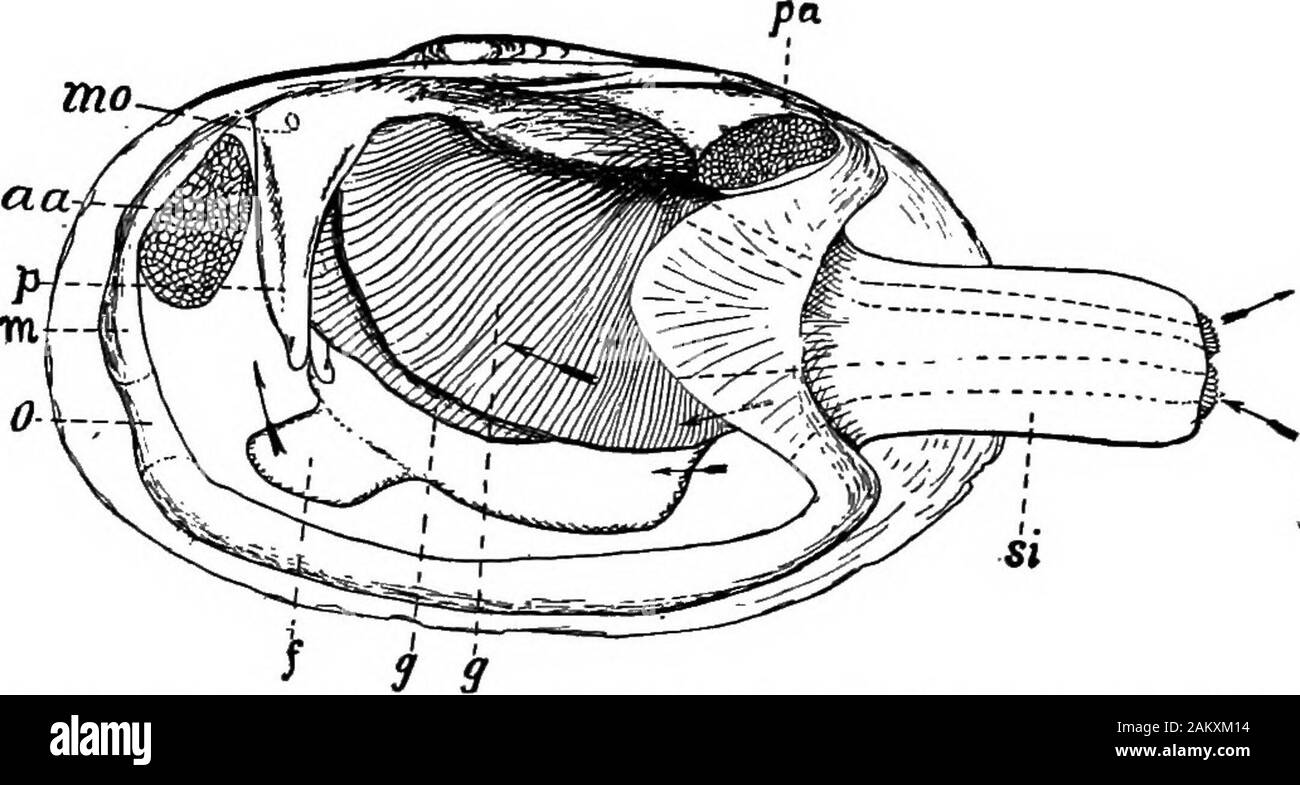
Clam study: the shell, the internal anatomy and how they feed Clam study: the shell, the internal anatomy and how they feed Summary Compare different sizes of shells and learn about how shells grow. Dissect a clam and discover that inside a familiar clam shell, often seen on the beach, there is a living animal. Identify the major body parts of a clam, and compare their function to equivalent organs in people. PDF Lab 5: Phylum Mollusca - Amherst 2. Study the figures of the internal structure of the clam. Locate the adductor and retractor muscles. The adductor muscles (which were cut in two to open the shell) close the valves, whereas the retractor muscles pull in the foot. Notice the large mass of the two adductor muscles, which allow for the prolonged closure of the valves. clam | mollusk | Britannica clam, in general, any member of the invertebrate class Bivalvia—mollusks with a bivalved shell (i.e., one with two separate sections). More than 15,000 living species of bivalves are known, of which about 500 live in fresh water; the others occur in all seas. Bivalves usually live on or in sandy or muddy bottoms. True clams, in the strict sense, are bivalves with equal shells closed by two ... The hatchery culture of bivalves: a practical manual Figure 7: The internal, soft tissue anatomy of a clam of the genus Tapes. In this view, the uppermost gill lamellae have been removed to reveal the foot and other adjacent tissues. Modified from Cesari and Pellizzato, 1990. 2.1.3 Internal anatomy. Careful removal of one of the shell valves reveals the soft parts of the animals.
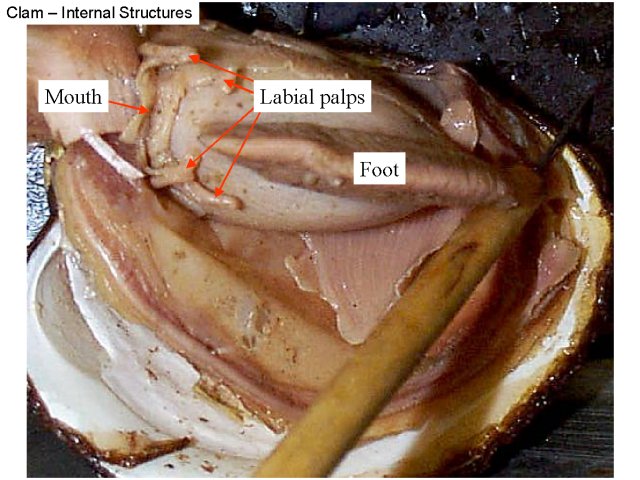
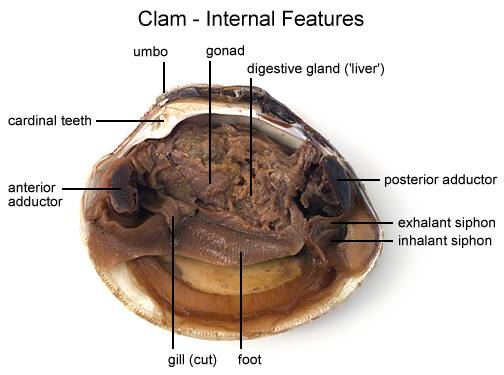
photograph of the external structure of the clam List and label key ... Observe and locate two flap-like palps abovethe foot, the dorsal area of the clam (near umbo),and the ventral to the heart. We then takephotographs of the internal anatomy of the clam and label the umbo, heart, kidney, posterior andanterior muscles, gills, digestive glands, palps, foot, and mantle.
Clams Anatomy - Barnegat Bay Shellfish Clam shells are made up in three layers: Nacreous Layer Prismatic Layer Periostracum Layer Nacreous Layer (nacre) The innermost layer of the shell which touches the clam and connects it to the shell. Also known as "Mother of Pearl", this layer is smooth and made up of soothing material Prismatic Layer
Internal Structure of the Clam 09 2 - YouTube Here is the second part to the Clam dissection for Tim Revell's Bio 2 class Spring 2009.
Basic Clam Anatomy (Internal) Quiz - purposegames.com Basic Clam Anatomy (Internal) by sarah.warren 13,284 plays 9 questions ~ 30 sec More 4 too few (you: not rated) Language English Tries Unlimited [?] Last Played February 22, 2022 - 12:00 am There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. From the quiz author
Clam Dissection Questions - vmsteacher.org 1. What is the oldest part of a clam's shell called and how can it be located? 2. the clam's shell indicate? 3. siphons. 4. shells together? 5. close the clam? 6. located in the clam? What is its function? 7. How do clams breathe? 8. over the gills? 9. found and what is their function? 10. heart located? 11.
Clam Dissection Questions - BIOLOGY JUNCTION 1. Give the kingdom, phylum, and class for the clam. 2. Describe the body of bivalves. 3. How do bivalves move? 4. Why are they called bivalves? 5. Is their digestive tract complete or incomplete? Explain your answer. 6. Do bivalves show cephalization? Explain your answer. 7. What are siphons & what is their purpose? 8.
Bivalve Anatomy - bivalves.teacherfriendlyguide.org The soft body inside of the shell includes a muscular foot, gills (or ctenidia, used for respiration and feeding), muscles, a digestive system, nerves, a three-chambered heart and an open circulatory system (with sinuses). Some species, such as the Hard-Shelled Clam here, have siphons for directing water flow in and out of the body chamber.
Internal Structure of the Clam 09 1 - YouTube Here is the first part of the Clam dissection for Tim Revell's Bio 2 class 2009.
PDF Biology and Anatomy of Hard Clam Biology and Anatomy of Hard Clam
Clam Dissection - JKL Bahweting Middle School Label the internal structures of the clam and draw red arrows showing the pathway of food as it travels to the clam's stomach: Click on image to enlarge Guided Exploration 1. What is the oldest part of a clam's shell called and how can it be located? 2. What do the rings on the clam's shell indicate? 3. Name the clam's siphons. 4.
Clam Dissection - BIOLOGY JUNCTION Place a clam in a dissecting tray and identify the anterior and posterior ends of the clam as well as the dorsal, ventral, & lateral surfaces. Figure 1 Figure 1 Locate the umbo, the bump at the anterior end of the valve. This is the oldest part of the clam shell. Find the hinge ligament which hinges the valves together and observe the growth rings.
Study 25 Terms | clam dissection functions Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying clam dissection functions. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. ... these are the respiratory structures obtaining oxygen and getting food. Foot ... clam dissection: internal anatomy: parts & functions 17 Terms. bolish. functions 76 Terms. kendalltucker1 PLUS. Clam Practical 46 Terms.
PDF Anatomy of a Clam 1. Obtain clam specimens (fresh or preserved). 2. Divide the class into small groups (2-4 per group when possible). 3. Prepare one dissection kit, pan, and clean-up materials per group. 4. Copy the dissection guide for each student. 5. Copy the External and Internal Clam Anatomy handouts for each student. 6.
PDF Clam Dissection Guideline - Monadnock Regional High School clam shell is the umbo, and it is from the hinge area that the clam extends as it grows. I. Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to identify the internal and external structures of a mollusk by dissecting a clam. II. Materials: 2 pairs of safety goggles 2 pairs of gloves 1 preserved clam 1 dissecting tray 1 paper towel 1 pair of scissors
























0 Response to "45 label the internal structures of the clam"
Post a Comment